* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investigating Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
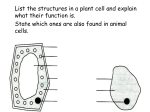
Investigating Cells Standard Grade Biology Living Cells • • • • • Cells are the basic units of life Cells cannot be seen by the naked eye They can be seen using a microscope Total mag. = Eyepiece mag. X objective mag Cells must be stained e.g. using iodine to allow their structure to be clearly seen • Cells are measured in micrometres (µm) 1mm = 1000µm Typical Plant and Animal Cells Parts of the Cell Part Function Found in Nucleus Controls the cell’s functions Both Cytoplasm Site of all the chemical reactions Both Cell Membrane Controls entry and exit of substances Both Vacuole Contains cell sap, gives support to the cell Chloroplasts Site of photosynthesis contain chlorophyll Cell wall Gives shape to the cell, prevents lysis Plant cells only Green plant cells only Plant cells only Cell Division • All cells have thread-like structures called chromosomes in the nucleus • Chromosomes carry information necessary for the development of the cell • The number of chromosomes in a cell is specific to a species • This is the chromosome complement of that species • Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged as 23 pairs Cell Division • Increases the number of cells • Is controlled by the nucleus • Is how a unicellular organism e.g. amoeba reproduces • Is how a multi-cellular organism grows • Is how damaged tissues are repaired • Starts with the division of the nucleus • Ensures that daughter cells have an exact copy of the genetic information in the parent cell and that no information is lost. Mitosis (Division of the Nucleus) Mitosis in a Root • Mitosis takes place in the area just behind the root cap • The root tip might be damaged as it pushes through the soil Enzymes • • • • • • • • • Are biological catalysts Are found in all living cells Are proteins Work best at their optimum temperature (37ºC for mammalian enzymes, 20ºC for plant enzymes) Work best at their optimum pH (pH3 for pepsin) Are specific i.e. they only work on one substrate Are inactive at low temp. but recover their activity if temp. increases Are denatured at high temp. and do not recover their activity if the temp. falls Catalyse synthesis and breakdown reactions Optimum Conditions (pH) Optimum Conditions (temp) The Working Range of an Enzyme Substrates and Products Substrate Enzyme Product Hydrogen peroxide Catalase Oxygen + water starch Amylase (a carbohydrase) Maltose Fats Lipase Fatty acids + glycerol Protein Pepsin (a protease) Polypeptides (amino acids) Glucose-1-phosphate phosphorylase starch How an Enzyme Works Uses of Energy • Energy for these processes comes from respiration • Food contains chemical energy • Fats and oils contain more energy per gram than carbohydrates or proteins • The sum of all the chemical processes in an organism or cell is called its metabolism • Respiration is the release of energy from food using oxygen Glucose+ oxygen → CO2 + H2O + Energy Respiration Equation Apparatus to Find out if Respiration Produces CO2 To Prove that Respiration Produces Heat A Simple Respirometer Respirometer • Small animal – respires Remember – germinating peas respire , they do not photosynthesise • Soda lime or sodium hydroxide absorbs CO2 • Movement of the level of coloured water shows the change in gas volume as oxygen is used up • Water bath keeps the temp. constant. Changes in temp. would affect the result. • A control expt would keep everything the same except it would have glass beads in place of the animal or boiled peas in place of germinating peas • A control makes the expt. fair • Repeating the expt. makes it reliable Diffusion • Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area where they are in high concentration to an area where they are in low concentration along a concentration gradient until they are evenly spread. • Diffusion is faster in gases than liquids • Diffusion is faster in liquids than solids Selectively Permeable Membranes • The cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane • It allows small , soluble molecules through • It does not allow large , insoluble molecules through • Visking tubing acts like a cell membrane Model of Diffusion Diffusion in a Multi-cellular Animal Osmosis • Osmosis is the special case of the diffusion of water molecules from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration until they are evenly spread. Osmosis in Animal Cells Osmosis in Plant Cells