* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquake Locations/Terminology Elastic Rebound Theory Seismic
Seismic anisotropy wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
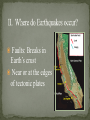
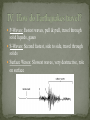
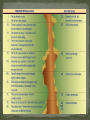
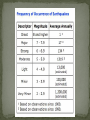
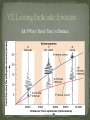
Earthquake Locations/Terminology Elastic Rebound Theory Seismic Waves Measuring Earthquakes I. Seismology: Study of Earthquakes Faults: Breaks in Earth’s crust Near or at the edges of tectonic plates Deformation: A change in the shape of rock due to stress. Elastic Rebound: Return of deformed rock to its original shape. Seismic Waves P-Waves: Fastest waves, pull & pull, travel through solid liquids, gases S-Waves: Second fastest, side to side, travel through solids Surface Waves: Slowest waves, very destructive, role on surface Richter Scale: Shows magnitude (energy). A calculation based on amount of movement recorded on seismograph. Modified Mercalli Scale: Quantifies intensity or damage of Earthquakes. S waves show mantle core boundary. Why? Shadow zone shows thickness of outer mantle. VI. Seismometer: Instrument that records seismographs (All three seismic waves) S& P Wave Travel Time vs Distance Record S and P waves at 3 cities Subtract P time from S time for each city. Use S & P Travel Time vs Distance Graph to find Distance to Epicenter for each earthquake