* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jewish History Presentation
History of the Jews in Gdańsk wikipedia , lookup
Homosexuality and Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Haredim and Zionism wikipedia , lookup
The Invention of the Jewish People wikipedia , lookup
Conservative Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Orthodox Judaism wikipedia , lookup
The Reform Jewish cantorate during the 19th century wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Hamburg Temple disputes wikipedia , lookup
Jewish military history wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish holidays wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
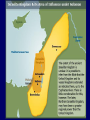
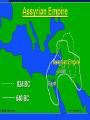
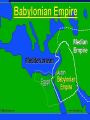
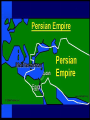
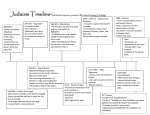
Focus: Judaism Hear, Oh Israel, the LORD our God, the Lord is One. Major Ideas -ethical monotheism *the Ten Commandments Major Ideas -ethical monotheism -covenant Major Ideas -ethical monotheism -covenant -The Land Major Persons -Abraham Major Persons -Abraham -The Patriarchs Major Persons -Abraham -The Patriarchs -Moses Major Persons -Abraham -The Patriarchs -Moses -The Prophets Major Persons -Abraham -The Patriarchs -Moses -The Prophets -The Kings David Major Events: 2100 BC (BCE) The Call of Abram (Abraham) The Exodus Circa1200 BCE The United Kingdom 1000 BC David rules from Jerusalem 960-925 Solomon rules Israel; builds the Temple The Divided Kingdom Judah vs. Israel Assyrian Empire destroys the Israel 800-701 Jerusalem Destroyed 586-581 Nebuchadnezzer destroys Jerusalem; destroys the temple; Babylonian Captivity The Diaspora Begins The Return 500-401 BC Jews return rebuild Jerusalem and the temple 400-4 BC During the four hundred years before Jesus, the Jews enjoyed little political independence as a series of Empires dominated the Middle East Persians Greeks Romans all dominated Palestine (Judea, Samaria, and Galilee) Two More Events of Note Greek Translation of the Jewish Bible (200 BC) The Septuagint Maccabean Revolt against Antiochus IV 167 BC-Hanukkah Major Holidays Observing the Holidays: Almost all Jewish people, regardless of the branch to which they belong observe at least some of the Jewish holidays. Rosh Hashanah Jewish New Year Sept/Oct Joyful atmosphere, marks the first part of a ten day period known as the High Holy Days. Yom Kippur Day of Atonement Sept/Oct Most solemn day. Day of fasting and prayer; seeking God’s forgiveness Sukkot Feast of Tabernacles or Booths Sept/Oct Festive holiday, temporary booth set up in yard for meals. Hanukkah Festival of Lights Nov/Dec Festive holiday celebrating the Jewish victory over the Syrian armies of Antiochus Epiphanes. Marked by the lighting of the Menorah over a period eight days. Purim Story of Queen Esther Feb/March Festive holiday recounting the story Esther and the victory of the Jews over their persecutors. Passover Deliverance from Egyptian bondage March/April Most popular holiday. Story of the Exodus is recounted by reading thru the Haggadah which is done at the seder. (Feast of Unleavened Bread) Purim Story of Queen Esther Feb/March Festive holiday recounting the story Esther and the victory of the Jews over their persecutors. Passover Deliverance from Egyptian bondage March/April Most popular holiday. Story of the Exodus is recounted by reading thru the Haggadah which is done at the seder. (Feast of Unleavened Bread) JudaismMajor Branches Orthodox Reform Conservative Orthodox Judaism -The only form of Judaism until the 18’th Century -Later called Orthodox to separate it from other branches -Characterized by tradition and strict observance of the Law as interpreted by the rabbis -Orthodoxy claims 6% of all American Jews -In Israel, the distinctions are between the observant and the nonobservant (Believers verses Unbelievers) -Dominant expression of Judaism in Israel today -Exercises considerable influence in national and civil affairs -Ultra-orthodox is the Hasidim REFORM JUDAISM -Began in Germany at the time of the Enlightenment -Sought to modernize outmoded ways of thinking -Attempt to prevent increasing assimilation of German Jews -Reform Judaism emphasizes ethics and the precepts of the prophets -Very small minority in Israel (perhaps only one synagogue) -Approximately 40% of American Jews CONSERVATIVE JUDAISM -Developed in the 19’th century as a middle ground branch of Judaism -Very small minority in Israel -Approximately 35% of all American Jews are affiliated with a Conservative Synagogue