* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Radioactive Elements (pages 139–146)
Nuclear fission product wikipedia , lookup
Fallout shelter wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive waste wikipedia , lookup
Isotope analysis wikipedia , lookup
Ionizing radiation wikipedia , lookup
Technetium-99m wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Radioactive decay wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
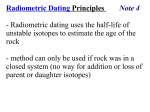
SX05_BkK_AdRdStdyWkBk.fm Page 58 Monday, April 18, 2005 8:09 AM Name Date Exploring Materials ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study Radioactive Elements Radioactivity (pages 139–146) (pages 140–141) Key Concept: In 1896, the French scientist Henri Becquerel discovered radioactive decay quite by accident while studying a mineral containing uranium. • A nuclear reaction is a reaction that involves the nucleus of an atom. A nuclear reaction can change an element into a different element. • Some isotopes of elements break apart naturally. Radioactive decay is a process in which the nuclei of unstable isotopes give off atomic particles and energy. • Radioactive decay was first discovered by Henri Becquerel. He observed that uranium gives off energy all by itself all the time. • Radioactivity is the energy and atomic particles given off by an unstable nucleus. Nuclear reactions cause radioactivity. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 1. Draw a line from each term to its meaning. Term Meaning nuclear reaction a. the energy and atomic particles given off by an unstable nucleus radioactive decay radioactivity b. a reaction that involves the nucleus of an atom c. the process in which nuclei give off atomic particles and energy © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 58 SX05_BkK_AdRdStdyWkBk.fm Page 59 Monday, April 18, 2005 8:09 AM Name Date Exploring Materials ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study 2. Is the following sentence true or false? A nuclear reaction can change an element to another element. Types of Radioactive Decay (pages 141–142) Key Concept: Natural radioactive decay can produce alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. • Radiation is the particles and energy given off during radioactive decay. The three forms of radiation are alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma radiation. • An alpha particle is made up of two protons and two neutrons. When an atom releases an alpha particle, the atom’s atomic number decreases by 2. The atom has become a different element. • A beta particle is a fast-moving electron given off by a nucleus. A beta particle forms when an unstable neutron changes into a proton and an electron. The proton stays in the nucleus, and the electron is the beta particle. The atomic number of the atom increases by 1. The atom is a different element. • Gamma radiation is the energy that is released in a nuclear reaction. Whenever an alpha particle or a beta particle is released, gamma radiation is also released. The release of gamma radiation does not change the atomic number of an atom. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 3. Circle the letter of the form of radiation that does NOT change the atomic number of an atom. a. alpha particle b. beta particle c. gamma radiation © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 59 SX05_BkK_AdRdStdyWkBk.fm Page 60 Monday, April 18, 2005 8:09 AM Name Date Exploring Materials ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study 4. The picture shows radioactive decay in which an alpha particle is produced. a. Circle the alpha particle. b. After releasing the alpha particle, how has the atom changed? a. The atom has not changed. b. The atomic number of the atom has decreased by 2. c. The atomic number of the atom has increased by 2. © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 60 SX05_BkK_AdRdStdyWkBk.fm Page 61 Monday, April 18, 2005 8:09 AM Name Date Exploring Materials ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study Using Radioactive Isotopes (pages 142–146) Key Concept: Uses of radioactive isotopes include determining the ages of natural materials on Earth, tracing the steps of chemical reactions and industrial processes, diagnosing and treating disease, and providing sources of energy. • Radioactive isotopes are useful for two reasons. First, radioactive isotopes change into different elements. Second, radioactive isotopes give off radiation that can be observed. • When radioactive isotopes break down, not all of the atoms in a sample break down at the same time. Halflife is the length of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample to break down. Every isotope has a different half-life. • Half-life is useful in finding out the age of rocks and fossils. This process is called radioactive dating. • Because radiation can be observed, a radioactive isotope can be used to follow the steps of a chemical reaction. Tracers are radioactive isotopes used to trace the steps of a reaction. Doctors use tracers to find medical problems and kill unhealthy cells. • Some power plants use the energy given off by the decay of radioactive isotopes to make electricity. • Radioactive materials are dangerous. Radiation can kill healthy body cells and upset the chemical reactions in the body. © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 61 SX05_BkK_AdRdStdyWkBk.fm Page 62 Monday, April 18, 2005 8:09 AM Name Date Exploring Materials ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas on page 61. 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about why radioactive isotopes are useful. a. Radioactive isotopes change into different elements. b. Radioactive isotopes can upset chemical reactions in the body. c. Radioactive isotopes give off radiation that can be observed. 6. Draw a line from each term to its meaning. Term Meaning half-life a. radioactive isotopes used to trace the steps of a reaction radioactive dating b. using radioactive isotopes to find out the age of rocks and fossils tracers c. the length of time it takes for half of the atoms in a radioactive sample to break down 7. How do doctors use radioactive isotopes? a. to find the age of a person b. to kill unhealthy cells in the body c. to make electricity © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 62