* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download variable expression of neural adhesion molecule (cd56)
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
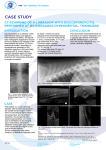
VARIABLE EXPRESSION OF NEURAL ADHESION MOLECULE (CD56) IN INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS OF CHONDRODYSTROPHOID CANINES: ASSOCIATION WITH CLUSTER FORMING NP CELLS *Tamura,F; +* Sakai, D; * Serigano,K; *Mochida, J *Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgical Science and Center for Regenerative Medicine, Tokai University School of Medicine, Bohseidai, Kanagwa, Japan, 259-1193, Tel 81463931121, Fax 81463964404, [email protected] INTRODUCTION: Despite the significant impairment associated with degenerative disc disease, a clear understanding of its pathogenesis is still lacking. The Figure 1 nucleus pulposus (NP) of the intervertebral discs (IVDs) contain a mixed (a) Caudal NP (b) Lumbar NP population of cell types at various stages of differentiation. The NP is formed either by or with the help of cells from the embryonic notochord, which appear to be replaced during development by a population of chondrocyte-like cells. Studies that explore this cellular heterogeneity are important in determining treatment options and cell types for disc repair. Recently, neural adhesion molecule (CD56) gene, a marker for neuron has been reported as one candidate for NP cell marker [1]. CD56 has also been reported as a marker for superior selectivity of mesenchymal stem cells [2]. In order to understand the relevance of CD56 in the IVDs, the present study explores the variability of CD56 (c) Caudal (Safranin-O) (d) Lumbar (Safranin-O) expression in the IVDs of chondrodystrophoid canines. METHODS: Lumbar and caudal IVDs were collected from six mature beagles (age about 1.5 year). Histological analysis was performed using Hematoxylin-Eosin(H-E), and Safranin-O stain. Immunohistochemistry was performed for expression of filamentous actin (F-actin) by fluorescently tagged phalloidin, for gap junction by connexin-43 and CD56. In order to assess the difference in matrix production ability between lumbar and caudal NP cells, NP cells were isolated by enzymatic digestion and expanded in monolayer culture in standard (e)Lumbar (f)Caudal (g) Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/F-12 supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. At passage 1, IVD cells were seeded into alginate beads at a cell density of 106 cells per milliliter. Proteoglycan (PG) and DNA content were assessed using DMMB assay and DAPI after 14 days. Influence on cell cycle was 25μm 25μm 50μm assessed in CD56 (+) NP cells by flow-cytometric BrdU/7AAD assay. Statistical differences were analyzed by ANOVA using the Fisher’s PLSD as a post hoc test. Figure 2 Caudal (CD56) Figure 3 RESULTS: Histological sections indicated clusters of large cells in caudal NP, containing from 3 to over 30 cells. Some of these caudal NP cells contained vacuole-like inclusions and these clusters stained intensely with Safranin-O. In contrast, lumbar NP contained relatively few cells, usually alone or in small clusters (3-8 cells in two-dimensional section). These cells generally resembled chondrocytes, with smaller diameters (~15μm) and no inclusions (Fig.1 a-d). F-actin was largely absent in lumbar IVD but was more prevalent in NP cell clusters of caudal IVD (Fig.1 e-f). Connexin-43 was scattered over the part of caudal NP cell Figure 4 (CD56 positivity) clusters, with a concentration in the vicinity of cell-cell junction (Fig.1 g). CD56 (+) cell was scarce in chondrocyte-like cells but was more prevalent in caudal NP cell clusters (Fig. 2). In vitro cell culture study showed significant increase of PG production in caudal NP cells containing CD 56 (+) cells (lumbar; 0.668±0.212, caudal; 1.30±0.769) (Fig. 3). Percentage of CD 56(+) NP cells was significantly higher in cells in S phase compared to other phases in cell cycle analysis (Fig. 4). DISCUSSION: Chondrodystrophoid canines are among the few species that possess chondrocyte-like cells in the lumbar IVDs. Hunter et al. has reported that NP cell clusters interconnected with F-actin and expressing connexin-43 REFERENCES: may be a feature of notochordal cell population [3]. We identified these [1] Sakai D, et al. Differential phenotype of intervertebral disc cells: NP cell clusters in caudal IVDs of chondrodystrophoid canines but microarray and immunohistochemical analysis of canine nucleus significantly less in lumbar IVDs. CD56 a marker identified as highly pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Spine 2009;34:1448-56. expressed in caudal IVDs in chondrodystrophoid canines in microarray [2] Battula VL, et al. Isolation of functionally distinct mesenchymal analysis was also located to be positive in caudal NP cell clusters. The stem cell subsets using antibodies against CD56, CD271, and caudal disc cells which contain more CD56(+) cells and NP cell clusters mesenchymal stem cell antigen-1. Haematologica 2009;94:173–184. showed higher PG production ability with high proliferative activity [3] Hunter CJ, et al. Cytomorphology of notochordal and chondrocytic shown by the cell cycle analysis. Regarding the fact that there have been cells from the nucleus pulposus: a species comparison. J Anat. reports suggesting that notochordal cell population activates other NP 2004;205:357-62. cells [4], our findings support the fact that presence of NP cell clusters [4] Erwin MW et al. Erwin, et al: Notochord cells regulate intervertebral may be important for biological properties of NP cells. Furthermore, disc chondrocyte proteoglycan production and cell proliferation. Spine with regard to CD56, a marker for cells with high potential [2], CD56 2006;31:1094-9. may serve as a useful marker for determining active NP cells that is associated with proliferating cell clusters. Poster No. 1434 • 56th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society