* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Management
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
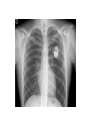
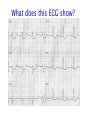
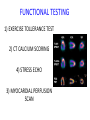
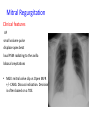
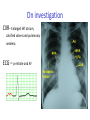
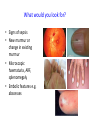
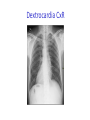
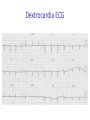
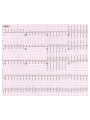
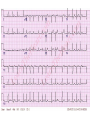
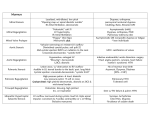
Cardiology for Finals FY1s Poornima Mohan & Ghazal Saadat Overview • • • • • • Scars Acute coronary syndromes Valvular heart disease Infective Endocarditis Dextrocardia Arrhythmias Midline sternotomy scar What is this scar? Which 3 procedures would cause this scar? What else would you look for? Grafts What could this be? What are the indications? Where else should you look? “We have this patient with chest pain” 66 year old with a background of DM type 2, hypertension and a 40 pack yr smoking hx. Day 1 post inguinal hernia repair. Has been having central crushing chest pain for last 15 minutes. No relief from GTN. Hot & sweaty, vomited twice. Obs: BP- 120/60 P-75 RR- 24 Sats 98% on RA What ECG features suggest an STEMI?? ST elevation in 2mm in 2 or more contigous limb leads ST elevation in 2 or more contigous chest leads New onset LBBB Posterior MI . What features suggest an to NSTEMI ??? ST depression and /or T wave inversion in 2 or more leads. Risk is assessed using the TIMI score. What does this ECG show? Management What would you do as an F1? 1) Assess haemodynamic stability 2) oxygen(?) 3) Initiate ACS protocol 4) Nitrates 5) Analgesia STEMI - Primary PCI NSTEMI – Risk assessment and PCI Unstable angina – Functional Testing +/- Angiogram Universal Secondary Prevention and Cardiac Rehabilitation FUNCTIONAL TESTING 1) EXERCISE TOLLERANCE TEST 2) CT CALCIUM SCORING 4) STRESS ECHO 3) MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION SCAN Valvular heart disease • Common exam question • Can find lots of patients with valve replacement • Things to know are - Which valve - What the cause could have been - Clinical signs - Basic principles of management • Questions about complications of surgery Scenario 1 “ A 72 year gentleman man presents with a history of collapse as he was rushing up a hill to catch a bus. There was no LOC. He reports no associated weakness/numbness/tingling in the limbs, visual disturbance, slurred speech, headache, chest pain, or palpitaions. This had never occurred before. He has noticed that he is increasingly SOB of late whilst gardening/ doing house-work etc. He has no previous cardiac history. He suffers from hypertension and gout.” Aortic Stenosis Causes 1) Senile calcification 2) Biscuspid Aortic valve 3) strep associated – Rheumatic fever Symptoms Exertional : Dysponea, syncope angina Features of AS on examination ???? Features on Examination narrow pulse pressure slow rising pulse LV heave Forcefull apex beat ESM radiating to the carotid- heard all over the precordium Features of left ventricular dysfunction Severe Stenosis → 1) Narrow PP 2) Quite or loss of S2 DDX for an ESM → 1) HOCM 2) VSD 3) Aortic sclerosis. Management : TAVI vs Open AVR +/- CABG? Exam tip : Which heart sound is metallic in an AVR?? Mitral Regurgitation “ A 72 year old lady presents with a history of increasing SOB, orthoponea and palpitations over a few months. She has a history of Angina, Hypertension. She is found to be in Atrial fibrillation” Causes Valve Annulus ACUTE CHRONIC Leaflets Papillary Muscle Infective Endocarditis MyocardiaI schemia Function – Chronic ischemia (post MI) Prolapse CCF (LV dilatation) Connective tissue disorders Amyloidinfiltration of the chords. Mitral Regurgitation Clinical features AF small volume pulse displace apex beat loud PSM radiating to the axilla bibasal crepitations • MGX: mitral valve clip vs Open MVR +/- CABG. Discuss indication. Decision is often based on a TOE. Mitral Regurgitation Management Consider patients pre-morbid state Medical : Diuresis Rate control Anti coagulation ACE inhibitors and B-blockers. Surgical : Assessment with an TTE / TOE and angiogram. Mitral clip or an open Valve Replacement Mitral Stenosis Cause: Congenital Rheumatic Heart disease Senile Degeneration Clinical Signs Malar flush Irregular pulse Tapping apex beat – palpable 1st HS Left parasternal heave / Enlarged LA Loud 1st heart sound Opening snap Mid-diastolic murmur. On investigation CXR- Enlarged left atrium, calcified valves and pulmonary oedema. ECG – p-mitrale and AF Management Medical : Rate control (digoxin) Anti-coagulate Valvuloplasty Surgical : Valve replacement Valveotomy (open / closed) Aortic Regurgitation Causes : Acute (inf. Endocarditis) Chronic: Connective tissue disorders (RA), Rheumatic heart disease, syphilitic heart disease . Aortitis: Marfans / Anklysing spondylitis Clinical features: Wide PP collapsing pulse – hyperdynmaic apex beat Eponymous signs Early diastolic murmur Aortic Regurgitation Other causes of a collapsing pulse? Anything that causes a high circulating volume: Pregnancy Anaemia PDA Thyrotoxicosis Management Valve replacement vs conservative management Murmurs Summary Aortic Stenosis Aortic regurgitation Mitral Stenosis Mitral regurgitation Pulse Slow-rising Collapsing Often AF Apex beat Forceful, not displaced Displaced Tapping, not displaced Murmur Ejection systolic Early diastolic Rumbling mid- Pansystolic diastolic Best heard Aortic area Tricuspid area Mitral area Radiation Carotids Thrusting, +/displaced Mitral area Axilla Complications of Valve replacements • INFECTION : early vs late. • FAILURE OF VALVE: early vs late • DISLODGEMENT • THROMBUS FORMATION vs HAEMMOHRAGE Management • • • • • • What would you do as an F1? ECG CxR Inform seniors Echo Conservative: if AF, rate control. Diuretics improve symptoms • Surgical: Valve repair/ replacement “ A 54 year old lady initially presents with an abscess. She vascular infarcts on CT and is admitted to the acute stroke unit. She has no major risk factors for a CVA. On doing base line bloods she has CRP 300 Urine dip show blood +++ She’s on the stroke ward, she has some left sided weakness. Obs stable, and apyrexial so far “ What is the diagnosis??? Infective endocarditis What would you look for ??? What would you look for? • Signs of sepsis • New murmur or change in existing murmur • Microscopic haematuria, ARF, splenomegaly • Embolic features e.g. abscesses What would you do as an FY1? • • • • • • • • Bloods Blood cultures ABG Urine dip & MCS CxR ECG Echo (TOE) Inform seniors Common questions 1. Risk factors? Lifestyle factors (IVDU), cardiac lesions, aortic or mitral valve disease, PDA, VSD, coarctation, prosthetic valve 2. Organisms? • Strep viridans (35-50%), HACEK (Haemophilus, actinobacillus, cardiobacterium, Eikenella) • Fungi • SLE – Libman-Sachs endocarditis 3. Criteria for Diagnosis? Duke criteria for diagnosis 2 major OR 1 major and 3 minor OR all 5 minor criteria Major • +ve blood culture typical organism in 2 separate cultures or persistently +ve blood cultures • Endocardium involved • Positive echo or new valvular regurgitation Minor • Predisposition • Fever >38C • Vascular/immunological signs • +ve blood cultures that do not meet major criteria • +ve echo that does not meet major criteria Management • MDT decision • Conservative management: Long-term antibiotics and serial echos • Surgical management: Valve replacement Dextrocardia A congenital defect where the heart is situated on the right side of the body 2 types: Isolated dextrocardia – heart placed further to the right in thorax, associated with other cardiac abnormalities Dextrocardia situs inversus – heart placed to the right side as a mirror image Dextrocardia CxR Dextrocardia ECG THANK YOU