* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Murmurs - stjpap 2011
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
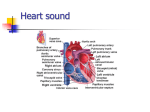
Murmurs Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Mitral Valve Prolapse Aortic Stenosis Localized, mid-dilated, low pitch “Opening snap w/ apical diastolic rumble” IR Atrial fibrillation, decrescendo Dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea Clubbing, Rales, Elevated JVD “Holostolic” soft S1 LV hypertrophy IR Atrial fibrillation “Floppy” (free flap) Mid-systolic click Asymptomatic (mild) Dyspnea, orthopnea, PND Pulmonary edema & rales Asymptomatic OR nonspecific dyspnea or fatigue * lean individuals Valvular narrowing w/ resistant LV outflow Diminished carotid pulses; soft split S2 Mid-systolic ejection R2ICS w/ radiation to the neck Crescendo-decrescendo; “systolic thrill” MCC: calcification of valves Aortic Regurgitation Hyperactive, enlarged LV “Blowing”; decrescendo L2ICS; diastolic infective endocarditis/ aortic dissection- surgery Triad: angina pectoris, syncope, heart failure marfan’s syndrome; HTN Pulmonic Stenosis Lesion assoc. w/ obstruction to RV outflow Audible in LU sternal border to the back/ post. lung fields Systolic ejection: crescendo-decrescendo; “systolic thrill” Hx of murmur since birth Acyanosis, Dyspnea, Dizziness [10% - CHF] High pressure pulmn loud, diastolic Low pressure pulmn soft or none Graham-Steel: high pitched decrescendo, diastolic at 2ICS & mid-sternal border Pulmonary HTN Tolerated well Pulmonic Regurgitation Tricuspid Regurgitation Holostolic, blowing, high pitched Inc. w/ inspiration Seen w/ RV failure & pulmn HTN Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis LV outflow narrowed during systole; loud S4; triple apical impulse; worsened via cardiac contractility or LV filling (Valsalva manuever) Syncope, Arrhythmias Chest Pain, Dyspnea incidence of sudden death Blood Flow Laminar flow is the normal blood flow turbulent flow occurs when laminar flow is disrupted Atria Systole- atria contract Ventricle Systole- ventricles contract Diastole- heart fills with blood after systole Heart Valves Thin leaflets composed of tough, flexible endothelium-covered fibrous tissue, attached to fibrous valve rings Murmur Description Location; intensity; duration; pitch; quality; timing S1 closure of mitral valve [lub] S2 closure of aortic valve [dub] S3 ventricular diastolic gallop [CHF] S4 decreased ventricular compliance [MI] Grading of MURMURS: 1. very faint, “tuned in” 2. quiet but heard after placing stethoscope of chest 3. moderately loud 4. loud w/ palpable thrill 5. very loud, sthethoscope partially off the chest 6. very loud, sthethoscope completely off the chest R. Sided murmurs: intensity w/ inspiration L. Sided murmurs: intensity w/ inspiration Diagnostics Chest X-Ray Electrocardiogram (EKG) Heart size, primary pulmonary disease, aortic abnormalities Hypertrophy of chambers, aortic stenosis (LV), tricuspid stenosis (RA), aortic regurgitation Echocardiogram Valve morphology, LV mass/ function, atrial/ ventricular chamber size, BEST for stenotic Transesophageal Echocardiography Valvular vegetations, thrombi Doppler Ultrasound Pulsed, color flow, tissue Stress Echocardiography Evaluate gradient changes durin and after exercise, NOT for aortic stenosis Cardiac Catheterization R.heart: elevated pressure due to pulm and cardiac disease; CX: pneumothorax, PE infxn L.heart: evaluate pressure and severity of CAD; helpful for regurgitant valves Treatment Drugs- Diuretics (relieve fluid build up in lungs), ACE-I (reduce workload for the heart), Digoxin (stabilize rhythm/ pumping), B-Blockers (dec. palpitations), Anticoagulants (prolong clotting). Vasodilators (lessen work load) Surgery- when drugs cannot control obstruction; valvuloplasty, percutaneous ballon valvotomy, repair/ replacement Antibiotic Prophylaxis- *pts w/ prolapse AND regurgitant valves [clicks and murmurs] NOT for mitral valve prolapse