* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phonocardiogram
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
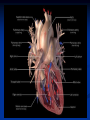
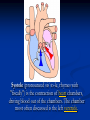
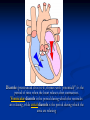
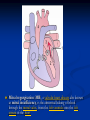
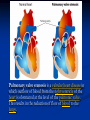
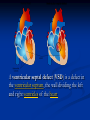
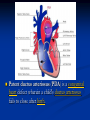
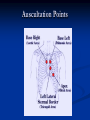
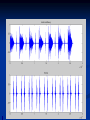
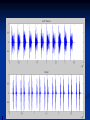
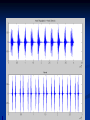
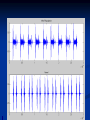
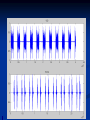
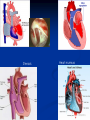
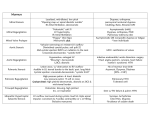
Phono Cardiogram The Human Circulatory System Systole (pronounced sis´to-le, rhymes with "fiscally") is the contraction of heart chambers, driving blood out of the chambers. The chamber most often discussed is the left ventricle. Diastole (pronounced di-as´to-le, rhymes with "potentially") is the period of time when the heart relaxes after contraction. Ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing Heart Sounds Need makes Persuasion Persuasion forces Idea Idea drives Invention S1 Sound The S1 sound is normally the first heart sound heard. See the diagram below for the location of S1 during the cardiac cycle. The S1 is best heard in the mitral area, and corresponds to closure of the mitral and tricuspid (AV) valves. A normal S1 is low-pitched and of longer duration than S2. S2 Sound The S2 sound is normally the second sound heard. The S2 is best heard over the aortic area, and corresponds to closure of the pulmonic and aortic valves. A normal S2 is higher-pitched and of shorter duration than S1. The flow from the ventricles is more forceful than the flow from the atria. Therefore, S2 will normally be the louder sound. Abnormal Heart Sounds S3 Sound The S3 sound is heard immediately following S2, and is normal in children and adolescents, but usually disappears after age 30. When heard in adults, an S3 is called a “gallop” and indicates left ventricular failure. S4 Sound The S4 sound is heard immediately before the S1, and may be present in infants and children. The S4 is produced with decreased compliance of the ventricle and may indicate myocardial infarction or shock. Regurgitation and Stenosis Regurgitation is blood flow in the opposite direction from normal, as the backward flowing of blood into the heart or between heart chambers. stenosis(narrowing) is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel. Anomalies Mitral regurgitation (MR), a valvular heart disease also known as mitral insufficiency, is the abnormal leaking of blood through the mitral valve, from the left ventricle into the left atrium of the heart Aortic insufficiency (AI), also known as aortic regurgitation (AR), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle Aortic valve stenosis (AS) is a valvular heart disease caused by the incomplete opening of the aortic valve Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the orifice of the mitral valve of the heart Pulmonary valve stenosis is a valvular heart disease in which outflow of blood from the right ventricle of the heart is obstructed at the level of the pulmonic valve. This results in the reduction of flow of blood to the lungs. Tricuspid insufficiency, a valvular heart disease also called Tricuspid regurgitation, refers to the failure of the heart's tricuspid valve to close properly during systole. As a result, with each heart beat, blood is pumped out from the right side of the heart in the opposite direction to normal A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect wherein a child's ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth. Auscultation Auscultation Points Area Abnormality Location Aortic 2nd ICS R sternal border Aortic Stenosis S2 is loudest here Pulmonic 2nd ICS L sternal border Pulmonary stenosis or regurgitation Tricuspid L lower sternal border Tricuspid stenosis Mitral 5th ICS Mitral stenosis or regurgitation S1 is loudest here Stethoscope is an acoustic device for auscultation or listening to the Heart, lung and stomach sounds of an animal or human. Also used to listen to intestines and blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a sphygmomanometer used to measure blood pressure. Ancient Stethoscopes The first stethoscope was invented in France in 1846 It looked nothing like the stethoscope of today – far from being soft and flexible. It was made from wood and resembled a bathroom plunger. Regular Stethoscopes The stereo stethoscope was developed by Rappaport & Sprague in the 1940s. Great strides made during the 1960s and 1970s in improving the materials used in acoustic stethoscopes. It lead to more precise diagnoses, lower prices and better comfort. Bell mode - High Frequency neonate, paediatric Diaphragm mode - low frequency adults Dr. William Proctor Harvey is a “virtuoso” who could diagnose complex heart conditions just by listening heartbeat of patient through stethoscope. Top Manufacturers: WelchAllyn, Littman, Thinklab, etc Modern Stethoscopes 1.Digital Stethoscopes 2.Vi scopes Allows the Doctor not only to hear, but also to see graphical waveform evaluate heart sounds for effective Cardiac Treatment Detect heart anomalies like Septal defects Regurgitation Stenosis Murmurs Allows the Doctor not only to hear, but also to see and evaluate heart sounds for effective Cardiac Treatment Early Detection of Chronic Cardiac Conditions Adjustable Volume levels to auscultate in noisy environments Triage Quality Improved at the point of Care Stenosis Heart murmurs