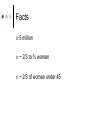* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Valvular Heart Disease
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Marfan syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
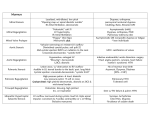
Valvular Heart Disease Valvular Disorders Mitral stenosis Mitral regurgitation Mitral valve prolapse Aortic stenosis Aortic regurgitation Definition STENOSIS - Occurs when valve leaflets close together and cannot fully open or close REGURGITATION or (Insufficiency) Heart valves cannot close completely Acquired Defects Decreasing order of occurrence Mitral stenosis (most common) Mitral regurgitation Mitral valve prolapse Aortic stenosis Aortic regurgitation Facts 5 million ~ 2/3 to ¾ women ~ 2/3 of women under 45 Mitral Stenosis Most common cause: rheumatic fever Results from rheumatic carditis Causing valve thickening by fibrosis and calcification Non-rheumatic causes Atrial tumor Calcium accumulation Thrombus formation What Happens Valve leaflets fuse and become stiff Chordae tendineae contract and shorten Valvular orifice narrows Diagnostics Echocardiogram Chest Xray EKG Cardiac cath *( also TEE) Clinical Manifestations Mild stenosis Asymptomatic Beginning Dyspnea on exertion (DOE) Orthopnea Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) Dry cough Clinical Manifestations Later Hemoptysis Pulmonary edema Right-sided heart failure (DD:Cor Pulmonale) • • • • Hepatomegaly Neck vein distention (JVD) Pitting edema ? One more ? Apical diastolic murmur Mitral Regurgitation Mitral Regurgitation (Insufficiency) Fibrotic and calcific changes prevent the mitral valve from closing completely during systole. End result left atrial and ventricular dilation and hypertrophy. Causes Rheumatic heart disease Degenerative calcification Left ventricular hypertrophy MI Congenital defects Clinical Manifestations Progresses slowly Asymptomatic for decades Chief complaints Fatigue Chronic weakness DOE Orthopnea . Clinical Manifestations …Continued… Normal blood pressure Atrial fibrillation (75% of all clients). Changes in respiratory patterns High pitched systolic murmur at apex Third heart sound (S3 or S4) Mitral Valve Prolapse Mitral Valve Prolapse Valvular leaflets enlarge and prolapse into left atrium during systole Usually benign, but may progress to mitral regurgitation Affects 5%-10% of the population (most common in women 14-30). Clinical Manifestations Chief complaint Atypical chest pain (sharp localized L chest pain) Dizziness Syncope Tachydysrhythmias causing palpitations Systolic murmur at apex Aortic Stenosis Aortic Stenosis Aortic valve orifice narrows and obstructs left ventricular outflow during systole Results in left ventricular hypertrophy Cardiac output becomes fixed and symptoms develop Eventually, can lead to right heart failure as well. Causes Congenital Rheumatic heart disease Atherosclerosis Degenerative calcifications Clinical Manifestations May be asymptomatic for years Classic manifestations: DOE, angina, syncope Other: narrow pulse pressure systolic murmur Aortic Regurgitation Aortic Regurgitation (Insufficiency) Aortic leaflets do not close properly during diastole with possible annulus dilation, loosening, or deformity. Allows blood to flow back into left ventricle from aorta during diastole. End result: left ventricular hypertrophy Clinical Manifestations Asymptomatic (early) Left ventricle has good compensatory mechanisms Progression Chief complaints • • • • • DOE Orthopnea PND Palpitations Nocturnal angina with diaphoresis Clinical Manifestations • • • • High pitched diastolic murmur Diminished diastolic pressure Elevate Systolic blood pressure Wide pulse pressure Causes Mostly results from rheumatic heart disease Non-rheumatic conditions Infective endocarditis Congenital aortic valve problems Hypertension Marfan’s syndrome Assessment Insidious or acute onset History Rheumatic fever? Recent infections? IV drug usage? Fatigue and activity tolerance? Family Hx? Care for All Valvular Disorders Diagnostics Echocardiogram *( also TEE) Chest Xray EKG (atrial fib most common) Cardiac cath Interventions Non-surgical management Drug therapy • • • • • • • Diuretics Digoxin Oxygen Ace Inhibitors Vasodilators (stenosis) Prophylactic antibiotic therapy Anti coagulants for A-Fib Rest Interventions Treating atrial fibrillation Rate control: digitalis, diltiazem, sotalol, amiodaron etc. Rhythm control: • Cardioversion: • Pharmacology • Electrical Anti thrombo-embolic: • Anticoagulant: Coumadin • Antiplatelet: Asetosal Interventions Surgical management Aortic stenosis requires surgical therapy as it is the only definitive treatment Valve replacements • Prosthetic • Biologic Surgical repairs • Balloon valvuloplasty –cath lab • Reconstructive or “Valvuloplasty”: • a. Open commisurotomy • b. Annuloplasty repairs Pre-Operative Care Similar to CABG surgery Pain Incisional care Prevent pulmonary complications STOP oral anticoagulants 72 hours before procedure Post-Operative Care Respiratory care Monitor for hemorrhage Cardiac output reduction Discharge teaching Complications Fluid & Electrolyte imbalances Hypotension Bleeding Cardiac tamponade Complications Altered cerebral perfusion Hypothermia Hypertension Infection Client Education Disease process Medications Anticoagulants Prophylactic antibiotics Rest and activity plan