* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Testcross - dihybrid x recessive homozygous
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
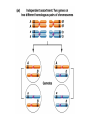
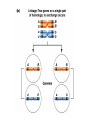
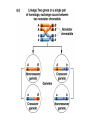
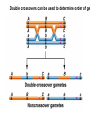
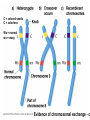
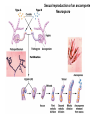
Testcross - dihybrid x recessive homozygo Independent assortment AaBb X aabb Progeny ¼ AaBb ¼ Aabb ¼ aaBb ¼ aabb Perfect linkage AaBb X aabb Progeny ½ AaBb cis ½ aabb or ½ aaBb trans ½ Aabb Deviations from independent assortment P F1 pr/pr vg/vg X pr+/pr+ vg+/vg+ pr+/pr vg+/vg dihybrid Testcross pr+/pr vg+/vg X pr/pr vg/vg F1 dihybrid Tester male female Progeny pr+ vg+ 1339 pr vg 1195 pr+ vg 151 pr vg+ 154 Total 2839 Distance separating two genes is directly proportional to % of total recombinants Total recombinants pr+ vg 151 pr vg+ 154 305 flies Total progeny 2839 flies Total recombinants/total progeny X 100 = % recombination 305/2839 X 100 = 10.7% 1% recombination = 1 map unit (mu, cm) pr 10.7mu vg Linkage and recombination in the X chromosome Test cross b+/b vg+/vg X b/b vg/vg Progeny 283 grey, normal 1,294 grey, vestigial 1,418 black, normal 241 black, vestigial __________________ 3,236 flies Total Adding genes to your map From 1st testcross From 2nd testcross AaBb X aabb a 5mu b AaCc X aacc a 3mu c Two possible arrangements c 3mu a b a 3mu c Which one? 5mu 2mu b Do the following cross: CcBb X ccbb OR Make a three point cross Three point cross Double crossovers can be used to determine order of ge Double crossover Relative gene position Coincidence and Interference Calculate expected frequency of DCOs Multiply the frequency of recombination in region I by the frequen recombination in region II Calculate observed frequency of DCOs from your experimental results Coefficient of coincidence = observed DCOs/expected DC Interference = 1- Coefficient of Coincidence Coefficient of Coincidence = Observed frequency of DCO Expected frequency of DCOs Observed frequency of DCOs = 6/500 0.012 Expected frequency of DCOs = Frequency COs region I x COs region Frequency CO region I = 0.208 Frequency CO region II = 0.10 Expected frequency of DCOs = 0.208 x 0.10 = 0.0208 (0.02) Coefficient of Coincidence = 0.012/0.02 = 0.6 Interference = 1 – Coefficient of Coincidence Interference = 1 – 0.6 = 0.4 A female fruit fly heterozygous for the genes y (yellow body), w (white eyes), and ec (echinus eyes) located on the X chrom is mated to a yellow, white, echinus male. The phenotypes of progeny are: Phenotype y w ec y+ w+ ec+ y w+ ec+ y+ w ec y w ec+ y+ w+ ec y w+ ec y+ w ec+ Number of flies 4685 4759 80 70 193 207 3 3 Total 10,000 flies Determine: order of the genes, distance between genes, coin and interference Evidence of chromosomal exchange - corn C = colored seeds C = colorless Wx = normal wx = waxy Evidence of chromosomal exchange - c Evidence for chromosome exchange – Drosophila Evidence for sister chromatid exchange in mitotic chromosomes Sexual reproduction of an ascomycete Neurospora Three different patterns of ascospores and how they are generated