* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection Lab 2
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
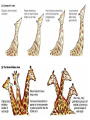
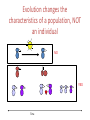
Natural Selection Lab 2 [email protected] The Remind App • Take out your phones please – Enter this number: 81010 – Text this message: @antht The Process of Evolution • Evolution is a change in gene frequency in a population from generation to generation • It is not the changing from an ape into a human…that never happened NO!!! The Real Shape of Evolution • Instead, think of evolution as a branching tree, with everything connected The Process of Evolution • For a trait, count the number of organisms with each form (different forms are called alleles) and you get the frequency • You have certain traits because of your genes, made up of your DNA, which is the blueprint for your body • The number of genes in a population that exists for each form of a trait (like blood type or eye color) is the gene frequency • This is the basis for scientifically testing evolution How Evolution Occurs • How do frequencies change? • Evolutionary forces: • Migration is the flow of genes from one population to the next • Genetic drift is a skewed sample size from one generation to the next • Mutation: any change in the genes from one population to the next • Natural selection: individuals best suited to their environment will survive and reproduce Steps of Natural Selection • More individuals are produced that can survive • Variation means some are better adapted to their environment • Individuals compete for limited resources • Those with better adapted traits will survive and reproduce • They thus pass down the better adapted genes to future generations • This is selective advantage Evolutionary Theory as a Science • Darwin knew evolution was a fact and set out to create a theory explaining how it worked • There are no alternatives to evolution that are testable • So, opponents who say that “evolution is just a theory” are misusing the word theory. Evolution is a fact…it has been tested • However, all the mechanisms of how it works are still being understood https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VwP_a4Ywz_8 CRASH COURSE DUDE Evolution changes the characteristics of a population, NOT an individual NO x YES Time The Vocabulary of Evolution by Natural Selection • Evolution: Change over time • Natural Selection: Process by which species evolve • Reproductive Success: The number of offspring an individual produces and rears to reproductive age • Fitness: A measure of relative reproductive success • Adaptation: An anatomical, physiological, or behavioral trait which improves an organism’s fitness in a given environment • Selective Pressures: Forces in the environment that influence reproductive success in individuals Birds of the Galapagos show us how natural selection works Medium Ground Finch Daphne Major Postulate 1: Environment constrains population growth • Severe drought occurred 1976-78 • Drought affected seed availability and quality • Many birds died of starvation Postulate 2: Individuals vary in ability to survive and reproduce • Beak size varies • Small beaked birds have trouble with large seeds • During drought, larger beaked birds were at advantage Postulate 3: Variation is transmitted from parents to offspring • Beak size is inherited Characteristics of population changed over time • Large beaked adults survived better • Large beaked birds had large beaked offspring • Mean beak size increased in population TODAYS LAB • EXERCISE 2: NATURAL SELECTION – Read through Lab as a group – Complete Lab by the end of today