* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
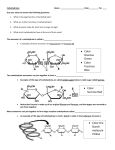
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 1 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Subscribe to our interactive unit study classroom and make science fun and exciting! 2 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates In nutrition you learned that carbohydrates are a source of energy and they are commonly called sugars. In biochemistry, sugars play another role besides being the main energy source for metabolism via the process of glycolysis – they can also combine with proteins to create glycoprotein hormones that are essential for all mammal reproduction or combine with lipids to create glycolipids which make up parts of the phospholipid bilayer on the plasma membrane. If proteins are the molecular machinery of the cell, then carbohydrates are the fuel that powers it. Carbohydrates and sugars are the same thing and the words can be used interchangeably when describing these molecules. Sugars are what we use to create almost all of the ATP that powers our bodies. In fact, the brain runs almost entirely on sugars! When you compare an amino acid and a nucleic acid to a carbohydrate you will see some differences and some similarities. The amino acid is not like a carbohydrate at all because if you remember, the amino acid is made up of a carbon backbone with a nitrogen at one end and oxygen at the other. Nucleic acids don't have anything in common with carbohydrates either, but the backbone of DNA is made up of a sugarphosphate molecule. ATP is also created using sugars as connectors. 3 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Basic lipid structures do not have much in common with carbohydrates but carbohydrates can combine with all the main metabolic macromolecules to create new entities that have a completely different function. The basic sugar structure comes in two forms; an open chain and a ring. The open chain looks like this: And the ring structure looks like this: 4 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Glucose is the most common carbohydrate in the body and although it is easier to draw a glucose molecule in the open chain configuration, this is really not the most accurate representation as it is always in a ring configuration when in an aqueous environment. This is true for most other sugars as well. Sugars can be divided into three main categories: MONOSACCHARIDES: The word monosaccharide comes from the Greek monos meaning, one, and sacchar, meaning sugar. That is in fact what they are – one sugar. This is the simplest form of carbohydrate. DISACCHARIDES: are made up of two monosaccharide molecules connected together by a glycosidic linkage. POLYSACCHARIDES: are macromolecules that are hundreds, or even thousands, of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages. You should not be a stranger to carbohydrates because you’ve known all along that these molecules were important to life when you learned about photosynthesis. You probably recall the reaction below: A carbohydrate molecule is always the same and consists of a molecular formula that has some combination of CH2O. Some sugars have just a few CH2O molecules, while others can have many. Just as amino acids have a familiar nitrogen, carbon, oxygen backbone; the carbohydrates all have the CH2O structure in common. The formula: Light + 6CO2 +6H2O C6H12O6 + O2 contains the sugar glucose, which again, should not be unfamiliar to you because glucose is what plants and animals use to power their cells. 5 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are made up of a single simple sugar molecule as pictured below. Glucose is the most common monosaccharide and contains all the hallmarks of a typical carbohydrate such as a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon except one, which is instead attached to an oxygen by a double bond which forms a carbonyl group. A monosaccharide can come in two forms: • Aldose (aldehyde sugar) • Ketose (ketone sugar) Which form they take depends on where the carbonyl group is attached. • • Glucose is an example of a aldehyde sugar Fructose is an example of a ketone sugar The number of carbons in the molecule is another way to categorize sugars. This is called the “carbon skeleton” and can range from three to seven carbons. Sugars that have six carbons are called hexose sugars, sugars with five carbons are called pentose sugars, and sugars with three carbons are called triose sugars. Other forms are less common. 6 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates One final way to classify sugars is the arrangement of atoms – sometimes these differences are very slight as in the case with glucose and galactose and sometimes these differences result in mirror images of each other. When you take organic chemistry or biochemistry you will learn more about these differences. The most important job for monosaccharides such as glucose is their role as nutrients for cells. During cellular respiration cells are able to convert glucose into the viable ATP energy molecule. Additionally, the carbon skeletons are also used to make other macromolecules such as amino acids and fatty acids (lipids). If the monosaccharides are not immediately used for metabolic processes, then they will be incorporated into storage molecules or as components of disaccharides and polysaccharides. Disaccharides are two monosaccharide molecules connected together by a glycosidic linkage. In protein synthesis the bond between two amino acids was called a peptide bond – so basically the glycosidic linkage performs the same function; to connect one sugar molecule to the next. Disaccharides can also be called glycosides after the bond used to create them. 7 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates In order to understand how this connection occurs you must first understand how the different atoms in the sugar ring are arranged and identified. All the carbons in the ring are numbered beginning with the carbon closest to the carbonyl group and that carbon is called 1. Numbering of the carbons continues down the “chain” (or in a clock-wise direction on the ring) until the end is reached. When creating a disaccharide the carbon 1 of the first sugar bonds to the carbon 4 of the second sugar. This is called a 14 glycosidic linkage. The end result is a new molecule that is linked by a common oxygen atom. 8 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Sucrose, which is the most common disaccharide, does not have a 1-4 linkage, instead it has a 1-2 linkage. This is because fructose has a five sided ring instead of a six sided ring and the carbon 1 begins in a different place. If the monosaccharides are known for their contribution to nutrition and energy metabolism, the polysaccharides are known for their exceptional structural properties. Polysaccharides are polymers and polymers are repeating chains of smaller molecules. Like disaccharides they are joined by a glycosidic linkage, but unlike disaccharides, they can have hundreds or even thousands of monomers connected together. Polysaccharides can serve as storage molecules or structural molecules. One of the most common polysaccharides is starch. You’ve probably heard of it in the context of nutrition; most notably pasta! Starches are the polysaccharide storage molecules of plants and are made up of amylose and amylopectin. 9 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Glycogen is another common polysaccharide. It is used as a short term storage center and quick energy delivery mechanism in the muscles and liver cells. Glycogen can deliver quick short blurts of immediate energy to your muscles when necessary – like when you come upon a bear in the woods and need to make a run for it! The bad thing about glycogen is that it doesn't power the muscles for very long and it will take about a day to replenish the storage of energy you just used. Both starch and glycogen are polysaccharides used for storage, but cellulose is used for structure. Cellulose is a major cell wall component of plants. Cellulose is not digestible by humans, but herbivores such as cows, deer, and horses have developed specialized digestive systems that can break down this rigid and tough polysaccharide and turn it into energy. These animals are called ruminants, and although horses are not technically ruminants, they do have a specialized compartment called the cecum where enzymes that can break down cellulose are contained. Starch and cellulose both use polysaccharides of glucose but the glycosidic linkages are not the same; this seemingly minor difference is what makes one suitable for energy storage and the other suitable for structure. Because the linkages are different, the enzymes used in the digestion of starch cannot be used in the digestion of cellulose. That’s why humans would starve if they only ate corn cobs while cows could put on some weight. 10 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates One more interesting factoid about cellulose is that insects use a form of it to create chitin; this is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods. As mentioned previously, glucose is the molecule that the body uses to create the ATP molecule. ATP is known as the currency of the cell and powers all vital functions. The first step in creating ATP is the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, this process is called glycolysis. 11 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Student Activities Exercise One Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Carbohydrates a. A lipid that contains one or more carbohydrate groups. Glycoproteins b. Any of a group of organic compounds that includes the fats, oils, waxes, sterols, and triglycerides. Glycolipids c. An adenosine-derived nucleotide that is used to transport energy to cells for biochemical processes. ATP d. A group of organic compounds that includes sugars, starches and celluloses. Amino Acid e. Any of a group of conjugated proteins having a carbohydrate as the nonprotein component. Nucleic acid f. Any of a group of complex compounds found in all living cells and viruses, composed of purines, pyrimidines, carbohydrates, and phosphoric acid. Lipid g. Relating to, similar to, containing, or dissolved in water; watery. Aqueous h. Any of a large number of compounds found in living cells that contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen, and join together to form proteins. 12 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Two Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. Monosaccharide a. A covalent bond in which two electron pairs are shared between two atoms. Disaccharide b. Any of several carbohydrates, such as tetroses, pentoses, and hexoses, that cannot be broken down to simpler sugars by hydrolysis. Polysaccharide c. A type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate. Glycosidic linkage d. The process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source. 5. Photosynthesis e. Any of a class of sugars, including lactose and sucrose, that are composed of two monosaccharides. 6. Hydroxyl group f. The -OH group on a molecule. Carbonyl group g. The -CO group on a molecule that has unpaired electrons. Double bond h. Any of a class of carbohydrates, such as starch and cellulose, consisting of a number of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds. 1. 2. 3. 4. 7. 8. 13 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Three Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Aldose a. The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP. Ketose b. A monosaccharide sugar, C6H12O6, occurring widely in most plant and animal tissue. It is the principal circulating sugar in the blood and the major energy source of the body. Glucose c. Any of a class of simple sugars (monosaccharides) containing a ketone group. Fructose is an example. Fructose d. A monosaccharide sugar found in honey, many fruits, and some vegetables and is linked to glucose to make sucrose. Hexose e. One of a group of monosaccharides that contain three carbon atoms. Pentose f. Any of a class of simple sugars (monosaccharides) containing an aldehyde group (CHO). Galactose, glucose, and ribose are all examples. Triose g. Any of a class of monosaccharides having five carbon atoms per molecule and including ribose and several other sugars. Cellular respiration h. Any of various simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, which have six carbon atoms per molecule. 14 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Four Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. Peptide bond a. A molecule that can combine with others of the same kind to form a polymer. Maltose b. The chemical bond formed between the carboxyl groups and amino groups of neighboring amino acids, constituting the primary linkage of all protein structures. Sucrose c. A polysaccharide composed of glucose units that occurs widely in plant tissues and is made up of amylose and amylopectin. Polymer d. Any of numerous natural and synthetic compounds of usually high molecular weight consisting of up to millions of repeated linked units, each a relatively light and simple molecule. 5. Monomer e. A carbohydrate that is a polymer composed of glucose units and that is the main component of the cell walls of most plants. 6. Starch f. A disaccharide composed of fructose and glucose. Cellulose g. A disaccharide consisting of two linked glucose molecules. 1. 2. 3. 4. 7. 15 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Five Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. Cell wall a. A polysaccharide stored in animal liver and muscle cells that is easily converted to glucose to meet metabolic energy requirements. Glycogen b. Any of various cud-chewing hoofed mammals having a stomach divided into four compartments in order to digest and extract energy from cellulose. Ruminants c. A hard outer structure, such as the shell of an insect or crustacean, that provides protection or support for an organism. Chitin d. Jointed-foot invertebrates such as arachnids, crustaceans, insects, millipedes, and centipedes. Exoskeleton e. - An ATP-generating metabolic process that occurs in nearly all living cells in which glucose is converted in a series of steps to pyruvate. 6. Arthropods f. A polysaccharide that is the principal component of the exoskeletons of arthropods. 7. Pyruvate g. The end result of glycolysis. 8. Glycolysis h. The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 16 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Six Circle the HYDROXYL GROUPS only in these two carbohydrate molecules. 17 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Seven Circle the CARBOXYL GROUPS only in these two carbohydrate molecules. 18 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Final Quiz 1. What is the chemical bond formed between the carboxyl groups and amino groups of neighboring amino acids, constituting the primary linkage of all protein structures? a. b. c. d. 2. What is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate? a. b. c. d. 3. Amino Peptide Lydolipic Glycosidic What are simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, which have six carbon atoms per molecule? a. b. c. d. 4. Amino Peptide Glycosidic Acidic Glycosides Hexose Pentose Cellulose What is the process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source? a. b. c. d. Cellular respiration Photosynthesis Glycolysis Glycogen 19 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 5. What is a protein called when is has a carbohydrate hooked to it? a. b. c. d. 6. Which carbohydrate is a polymer composed of glucose units and is the main component of the cell walls of most plants? a. b. c. d. 7. Hexose sugar Monosaccharide Both of these None of these Which types of organisms can digest cellulose? a. b. c. d. 9. Cellulose Glycogen Amylose Starch What kind of carbohydrate is glucose? a. b. c. d. 8. Glycoprotein Glyco acid Amino acid Glyconitro Humans Ruminants All organisms Cellulose is indigestible What is the name of the structural carbohydrate that makes up the exoskeleton in arthropods? a. b. c. d. Cellulose Amylose Chitin Starch 20 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 10. Which polysaccharide is composed of glucose units that occurs widely in plant tissues and is made up of amylose and amylopectin? a. b. c. d. 11. What is the process by which glucose is changed into pyruvate in cellular respiration? a. b. c. d. 12. Glycogen Glycolysis Cellular respiration None of these What is the name of a molecule that can combine with others of the same kind to form a polymer? a. b. c. d. 13. Starch Cellulose Chitin Pyruvate Monosaccharide Monomer Monolipid None of these What is the name of a group of monosaccharides which contain three carbon atoms? a. b. c. d. Pentose Hexose Triose None of these 21 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 14. Which monosaccharide sugar is found in honey, many fruits, and some vegetables and is linked to glucose to make sucrose? a. b. c. d. 15. Galactose Fructose Glucose Ribose Which disaccharide is made up of two linked glucose molecules? a. b. c. d. Maltose Galactose Fructose Sucrose 22 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Parent Solutions Exercise One Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. d e a c h f b Carbohydrates a. A lipid that contains one or more carbohydrate groups. Glycoproteins b. Any of a group of organic compounds that includes the fats, oils, waxes, sterols, and triglycerides. Glycolipids c. An adenosine-derived nucleotide that is used to transport energy to cells for biochemical processes. ATP d. A group of organic compounds that includes sugars, starches and celluloses. Amino Acid e. Any of a group of conjugated proteins having a carbohydrate as the nonprotein component. Nucleic acid f. Any of a group of complex compounds found in all living cells and viruses, composed of purines, pyrimidines, carbohydrates, and phosphoric acid. Lipid g. Relating to, similar to, containing, or dissolved in water; watery. Aqueous h. Any of a large number of compounds found in living cells that contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen, and join together to form proteins. g 8. 23 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Two Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. b Monosaccharide a. A covalent bond in which two electron pairs are shared between two atoms. Disaccharide b. Any of several carbohydrates, such as tetroses, pentoses, and hexoses, that cannot be broken down to simpler sugars by hydrolysis. Polysaccharide c. A type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate. Glycosidic linkage d. The process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source. Photosynthesis e. Any of a class of sugars, including lactose and sucrose, that are composed of two monosaccharides. Hydroxyl group f. The -OH group on a molecule. Carbonyl group g. The -CO group on a molecule that has unpaired electrons. Double bond h. Any of a class of carbohydrates, such as starch and cellulose, consisting of a number of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds. e 2. 3. h c 4. 5. d 6. f 7. 8. g a 24 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Three Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. f Aldose a. The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of ATP. Ketose b. A monosaccharide sugar, C6H12O6, occurring widely in most plant and animal tissue. It is the principal circulating sugar in the blood and the major energy source of the body. Glucose c. Any of a class of simple sugars (monosaccharides) containing a ketone group. Fructose is an example. Fructose d. A monosaccharide sugar found in honey, many fruits, and some vegetables and is linked to glucose to make sucrose. Hexose e. One of a group of monosaccharides that contain three carbon atoms. Pentose f. Any of a class of simple sugars (monosaccharides) containing an aldehyde group (CHO). Galactose, glucose, and ribose are all examples. Triose g. Any of a class of monosaccharides having five carbon atoms per molecule and including ribose and several other sugars. Cellular respiration h. Any of various simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, which have six carbon atoms per molecule. c 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. b d h g e a 25 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Four Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. 1. b Peptide bond a. A molecule that can combine with others of the same kind to form a polymer. Maltose b. The chemical bond formed between the carboxyl groups and amino groups of neighboring amino acids, constituting the primary linkage of all protein structures. Sucrose c. A polysaccharide composed of glucose units that occurs widely in plant tissues and is made up of amylose and amylopectin. Polymer d. Any of numerous natural and synthetic compounds of usually high molecular weight consisting of up to millions of repeated linked units, each a relatively light and simple molecule. Monomer e. A carbohydrate that is a polymer composed of glucose units and that is the main component of the cell walls of most plants. Starch f. A disaccharide composed of fructose and glucose. Cellulose g. A disaccharide consisting of two linked glucose molecules. g 2. 3. f d 4. 5. a 6. c 7. e 26 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Five Write the letter of the correct match next to each problem. Cell wall a. A polysaccharide stored in animal liver and muscle cells that is easily converted to glucose to meet metabolic energy requirements. Glycogen b. Any of various cud-chewing hoofed mammals having a stomach divided into four compartments in order to digest and extract energy from cellulose. Ruminants c. A hard outer structure, such as the shell of an insect or crustacean, that provides protection or support for an organism. Chitin d. Jointed-foot invertebrates such as arachnids, crustaceans, insects, millipedes, and centipedes. Exoskeleton e. - An ATP-generating metabolic process that occurs in nearly all living cells in which glucose is converted in a series of steps to pyruvate. Arthropods f. A polysaccharide that is the principal component of the exoskeletons of arthropods. 7. g Pyruvate g. The end result of glycolysis. 8. e Glycolysis h. The rigid outermost cell layer found in plants. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. h a b f c d 27 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Exercise Six Exercise Seven 28 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates Final Quiz 1. What is the chemical bond formed between the carboxyl groups and amino groups of neighboring amino acids, constituting the primary linkage of all protein structures? a. b. c. d. 2. What is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate? a. b. c. d. 3. Amino Peptide Lydolipic Glycosidic What are simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, which have six carbon atoms per molecule? a. b. c. d. 4. Amino Peptide Glycosidic Acidic Glycosides Hexose Pentose Cellulose What is the process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source? a. b. c. d. Cellular respiration Photosynthesis Glycolysis Glycogen 29 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 5. What is a protein called when is has a carbohydrate hooked to it? a. b. c. d. 6. Which carbohydrate is a polymer composed of glucose units and is the main component of the cell walls of most plants? a. b. c. d. 7. Hexose sugar Monosaccharide Both of these None of these Which types of organisms can digest cellulose? a. b. c. d. 9. Cellulose Glycogen Amylose Starch What kind of carbohydrate is glucose? a. b. c. d. 8. Glycoprotein Glyco acid Amino acid Glyconitro Humans Ruminants All organisms Cellulose is indigestible What is the name of the structural carbohydrate that makes up the exoskeleton in arthropods? a. b. c. d. Cellulose Amylose Chitin Starch 30 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 10. Which polysaccharide is composed of glucose units that occurs widely in plant tissues and is made up of amylose and amylopectin? a. b. c. d. 11. What is the process by which glucose is changed into pyruvate in cellular respiration? a. b. c. d. 12. Glycogen Glycolysis Cellular respiration None of these What is the name of a molecule that can combine with others of the same kind to form a polymer? a. b. c. d. 13. Starch Cellulose Chitin Pyruvate Monosaccharide Monomer Monolipid None of these What is the name of a group of monosaccharides which contain three carbon atoms? a. b. c. d. Pentose Hexose Triose None of these 31 By J. Anne Huss ©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies – Carbohydrates 14. Which monosaccharide sugar is found in honey, many fruits, and some vegetables and is linked to glucose to make sucrose? a. b. c. d. 15. Galactose Fructose Glucose Ribose Which disaccharide is made up of two linked glucose molecules? a. b. c. d. Maltose Galactose Fructose Sucrose 32 By J. Anne Huss