* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Translocation
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
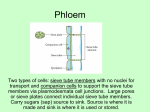
Translocation • • • • Occurs in Phloem Bidirectional Composition Mechanism of translocation • Munch Pressure flow hypothesis • Phloem loading and unloading • Source-sink relationships Phloem Structure • • • • • • • Sieve tube members: Angiosperms; Sieve cells: Gymnosperms Companion cells Sieve tube members/companion cells derived from same mother cell Both living at maturity Sieve tube members lose organelles at maturity contain cytoplasm Sieve plate with pores P-protein Primary phloem 2ndary Phloem Phloem Electron Micrograph Companion cell Sieve tube elements Composition of phloem • Girdling experiments • analysis of aphid exudate • composition • sugars • amino acids (nitrogen):ureides, glutamic acid, glutamine • organic acids • hormones Composition Sugars • Types of sugars • sucrose main transport sugar: nonreducing sugar • some species: raffinose, stachyose transported • sugar alcohols: sorbitol, mannitol Nitrogen compounds • Transport from the root • Amino acids • uriedes Mechanism of translocation • Munch Pressure flow hypothesis • Sugar loaded into phloem • increase in solute potential • leads to increase in water uptake from xylem • builds up hydrostatic pressure • unloaded at sink Source-sink relationships • Bidirectional: up and down plant • is it in same cell, not clear • rate 30-150 cm/hr, slower than water Source to Sink • Proximity of source to sink is critical • sinks may change during life cycle • young leaves net import • as mature become exporter • roots, shoots, tubers, fruits are strong sink Phloem Loading/unloading • • • • Active process evidence from respiratory inhibitors Loading: apoplast or symplast apoplast retrieve leaky sucrose? Sugar transporters •Sugar- H+ co-transport symplast via plasmodesmata:polymer trapping Summary of loading Unloading at sink • symplast young leaves • apoplast seeds/grain • acid invertase Loading/unloading