* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4th Nine Weeks Benchmark
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
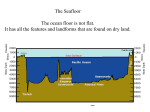
NAME __________________________________ 4th Nine Weeks Benchmark Study Guide CHAPTER 21 1. What is a light-year? 2. What are 5 characteristics used to classify stars? 3. What color are the coolest stars? 4. A star is born when ______________________ starts. 5. The lifetime of a star depends on its _________________________. 6. A supernova is the explosion of a dying ___________ - mass star. 7. The Milky Way galaxy is an example of a(n) ___________________ galaxy. 8. The absolute brightness of a star depends on its ___________________________________. 9. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram shows that main-sequence stars _________________ in brightness as they _________________ in temperature. 10. The force that tends to pull together the matter in stars is ________________________. CHAPTER 14 11. Benthos are organisms that live where? 12. List three examples of nekton. 13. The part of the ocean that extends from the low-tide line to the edge of the continental shelf is the _____________________ zone. 14. Kelp forests grow in the ____________________ zone. 15. Organisms in tide pools must survive changes in ____________________ caused by rainfall and evaporation. 16. In what zone are hydrothermal vents located? 17. In the open ocean, algae live only in the ________________________ zone. 18. Organisms in the deep ocean that produce their own light are called ____________________________. 19. A nearly flat region of the ocean floor, covered with thick layers of sediment, is called a(n) ____________________________________. 20. The area that stretches from the highest high-tide line on land out to the point on the continental shelf exposed by the lowest low tide is called the _________________________________. 21. A ring-shaped reef surrounding a shallow lagoon is known as a(n) _______________________. 22. An area where ocean water rises through cracks in the ocean floor, having been heated by the magma beneath the ocean floor, is called a(n) ________________________________. 23. Coral reefs are found in warm waters in the ______________________ zone. 24. Beyond the edge of the continental shelf lies the ____________________ zone, which includes the deepest and darkest areas of the ocean. 25. Which ocean floor feature is made up of a range of mountains that wind through the ocean? 26. A deep canyon in the ocean floor is called a(n) _____________________. 27. Animals in the ____________________ zone must be able to survive periods of being exposed to air as well as periods of being underwater. 28. Why is studying the ocean floor so difficult? 29. Free-swimming animals that can move throughout the water column are called _______________________. 30. A coastal inlet or bay in which freshwater from rivers mixes with salty ocean water is called a(n) _________________________________. 31. The most common plant in a salt marsh is _________________________. 32. _______________ uses sound waves to measure the depth of the ocean floor. 33. Are diatoms and copepods examples of plankton, nekton, or benthos? 34. Are crabs, lobsters, and sponges examples of plankton, nekton, or benthos? 35. The organisms that form the base of most open-ocean food webs are _______________________. 36. Coastal wetlands that feature short, gnarled trees with arching prop roots are called ______________________. 37. Algae can only live in parts of the ocean that receive enough ____________________ to allow them to carry out photosynthesis. Label the parts of the ocean floor. 38. A - __________________________ 42. E - __________________________ 39. B - __________________________ 43. F - __________________________ 40. C - __________________________ 44. G - __________________________ 41. D - __________________________ BIOMES 45. The Great Plains are the _____________________ biome of the United States. 46. A _____________________ climate occurs where precipitation is less than potential evaporation. 47. Tropical grasslands that have distinct dry and wet seasons are called _________________________. 48. _________________________ climates are found along the coasts of continents in the temperate zone. 49. A cool type of climate called ____________________ is found at the tops of mountains and is surrounded by other climate regions. 50. Tundra and ice cap biomes are examples of ____________________ climates. 51. Climates are classified according to what two major factors? 52. ____________________ are forests that have year-round heat and heavy rainfall. 53. Permafrost and mosses, lichens, and wildflowers are common in which biome? 54. A rain forest biome exists in the United States only in _________________. 55. Trees do not grow in the ____________________, which has short, cool summers, bitterly cold winters, and permafrost. 56. Regions that receive less than 10 inches of rain annually are called ________________________________.