* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
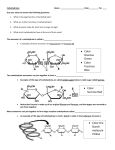
WHAT IS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY? the chemistry of carbon compounds Remember, the element symbol for carbon is C So, an organic compound is one that has carbon in it Which of the following compounds are organic? NH4 H2 0 C6H12O6 HCl CH4 Structure of Organic Molecules carbon can bond to itself to form CHAINS & RINGS the chemical bonds between carbon atoms are covalent bonds (nonmetal + nonmetal) H Ex. C6H12O6 H C OH H C OH H C OH ring chain H C OH H C OH H C OH H HO covalent bond CH2 OH H C C O H OH H C C H OH C H OH WHAT IS BIOCHEMISTRY? the chemistry of LIFE Remember, the elements found in all living things include Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur (CHNOPS) Thus, biochemistry involves carbon compounds. BIOCHEMISTRY: TERMS TO KNOW macromolecule: a very LARGE molecule (“macro” = large) monomer = the basic subunit of a macromolecule polymer = many monomers joined together by covalent bonds macromolecules are polymers MONOMERS & POLYMERS monomer monomer monomer monomer monomer } POLYMER 4 CLASSES OF MACROMOLECULES 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids macromolecule carbohydrates lipids monomer(s) polymer(s) examples monosaccharides polysaccharides starch, cellulose, chitin, glycogen, sugars 1) glycerol 2) fatty acids fats, oils, waxes fats, oils, waxes, steroids, phospholipids proteins amino acids polypeptide hemoglobin, insulin, keratin, elastin, collagen nucleic acids nucleotides DNA & RNA DNA & RNA macromolecules food examples carbohydrates bread, pasta, cereal, fruit, potatoes, carrots, candy, juice, soda, beans, rice, grains lipids butter, lard, cooking oil, full-fat dairy products (whole milk), nuts, fish oil proteins meat, beans, fish, tofu, eggs, dairy products, nuts nucleic acids nucleic acids are in your food, but have no nutritional value; thus, they are not on food labels, nor are they measured CARBOHYDRATES •contain the elements Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen •provide the body with short-term energy •carbohydrates include sugars, starches, cellulose, chitin, and glycogen •foods rich in carbohydrates include bread, pasta, potatoes, bananas, carrots, candy CARBOHYDRATES Which of the following are carbohydrates? H H C OH H C OH CH2 OH H C OH H C OH H C OH H C OH H H HO C C O H OH H C C H OH C H OH CARBOHYDRATES: Monomers & Polymers • monomers of carbohydrates are called monosaccharides (“single-sugar”) • two monosaccharides joined together = disaccharide (“double-sugar”) • polymer = polysaccharide (many monosaccharides joined together) • many carbohydrate names end in “-ose” such as “lactose” Monosaccharides & Disaccharides # of monosaccharides 1 2 Examples Chemical Formula glucose, monosaccharide fructose, galactose C6H12O6 generalized name disaccharide lactose, maltose, C12H22O11 sucrose CARBOHYDRATES: Monosaccharides • • • all have the same chemical formula: C6H12O6 they differ in the arrangement of atoms they are ISOMERS: molecules with the same formula but different structure Examples • • • glucose-important energy source fructose-sugar from fruit galactose-sugar from milk CARBOHYDRATES: Disaccharides • • • all have the same chemical formula: C12H22O11 they are ISOMERS of each other they can only be absorbed into the intestine & blood stream when they are broken down into their monomers (monosaccharides) by enzymes Examples • • • maltose = glucose + glucose: malt sugar lactose = glucose + galactose: milk sugar • people who are lactose intolerant lack the enzyme lactase that breaks up the sugar into monosaccharides sucrose = glucose + fructose: table sugar CARBOHYDRATES: Disaccharides glucose Maltose + glucose ! glucose glucose CARBOHYDRATES: Disaccharides glucose Sucrose + fructose ! glucose fructose CARBOHYDRATES: Disaccharides glucose Lactose + galactose ! glucose galactose CARBOHYDRATES: Polysaccharides • many monosaccharides bonded together (300-1000) Types: • Starch • Glycogen • Cellulose • Chitin POLYSACCHARIDES: STARCH • plants make glucose by photosynthesis and extra glucose is stored as starch • found in plant roots & seeds: potatoes, corn, rice, wheat • animals have enzymes to break down starch into monosaccharides for absorption POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE • structural polysaccharide: makes up plant cell walls • we cannot digest it; indigestible fiber is excreted POLYSACCHARIDES: GLYCOGEN • animals store extra carbs in the liver and muscle cells as glycogen POLYSACCHARIDES: CHITIN • pronounced “Kite-In” • makes up the exoskeletons of arthropods: insects, crustaceans, arachnids (spiders) • we cannot digest it