* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download notes - Mr. Parish
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
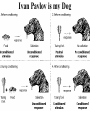
Perception- the interpretation of sensory information. Gestalt- a meaningful whole Illusion- misinterpretation of sensory information Subliminal- sensory information below level of awareness Pavlov’s Dog Pavlov Ivan Pavlov is my Dog John Watson and Little Albert Systematic Desensitization Mary Cover Jones Ivan Pavlov John Watson Stimulus Generalization Extinction • A conditioned response/behavior ceases Spontaneous Recovery • An extinct response suddenly returns after exposure to previously conditioned stimulus after a rest period. • Extinction occurs more quickly after spontaneous recovery. B.F. Skinner BF Skinner Operant Conditioning Reinforcers • Primary (unconditioned) – Food, Water, Sex • Secondary (conditioned) – – – – Paired with primary reinforcer Money Clicker Car (think of the commercials) Behaviorists C PAVLOV C WATSON O SKINNER Operant Conditioning + Reinforcement Punishment - Classical versus Operant • Learning through the association of two stimuli (i.e. bell and food, mouse and loud noise) • Learning based on consequences of actions (i.e. good boy have some candy) Martin Seligman- Learned Helplessness Classical versus Operant • Classical (Respondent) – Learning through the association of two stimuli (i.e. bell and food, mouse and loud noise) – Behavior is reflexive • Operant – Learning based on consequences of actions (i.e. good boy have some candy) – Behavior is controlled or “operates on the environment” Classical versus Operant Your father gives you a credit card at the end of your first year in college because you did so well. As a result, your grades continue to get better in your second year. Classical versus Operant When you were little the loud noises at the circus sacred you. Ever since you have been afraid of clowns Classical versus Operant A lion in a circus learns to stand up on a chair and jump through a hoop to receive a food treat. Classical versus Operant Your car has a red, flashing light that blinks annoyingly if you start the car without buckling the seat belt. You become less likely to start the car without buckling the seat belt. Classical versus Operant A professor has a policy of exempting students from the final exam if they maintain perfect attendance during the quarter. His students’ attendance increases dramatically. Systematic Desensitization Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio Interval Variable Albert Bandura • "Learning would be exceedingly laborious, not to mention hazardous, if people had to rely solely on the effects of their own actions to inform them what to do. Fortunately, most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from observing others one forms an idea of how new behaviors are performed, and on later occasions this coded information serves as a guide for action." Bandura- Modeling-Bobo Doll Social Learning Vicary Subliminal Ads Writer A A A A R R R R R R R Writer B R R A R R R A R R A Albert Bandura MODELING Our Journey •Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. perception Conditioning/learning memory