* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12 Endocrine Disorders - Crestwood Local Schools
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypoglycemia wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
Diabetes management wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic hypoglycemia wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic ketoacidosis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial pancreas wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
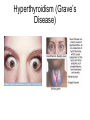
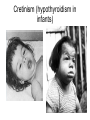
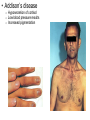
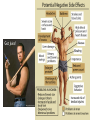
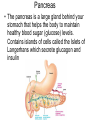
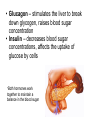
Endocrine Disorders GIGANTISM • Hyperfunction of pituitary – too much growth hormone • In preadolescent – overgrowth of long bones leads to excessive tallness These are pictures of the man known as “The Alton Giant”, Robert Wadlow. ACROMEGALY • Hyperfunction of pituitary – too much growth hormone in adulthood • Overdevelopment of bones in face, hands and feet • Attacks cartilage – so the chin protrudes, lips nose and extremities enlarge • Rx – drugs to inhibit growth hormone, radiation Richard Kiel DWARFISM • Hypofunction of pituitary in childhood • Small size, but body proportions and intellect are normal • Sexual immaturity • Rx – early diagnosis, injection of growth hormone Problems with the pituitary gland can result in Dwarfism HYPERTHYROIDISM • Overactive thyroid gland • Too much thyroxine secreted leading to enlargement of gland • People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight • Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) • Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation Goiter Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s Disease) HYPOTHYROIDISM • Not enough thyroxine secreted • May be due to lack of iodine (simple goiter) • Major cause of other types is inflammation of thyroid which destroys the ability of the gland to make thyroxine • Symps – dry and itchy skin, dry and brittle hair, constipation, muscle cramps at night Hypothyroidism Before and After Treatment Cretinism (hypothyroidism in infants) TETANY • In hypoparathyroidism, decreased calcium levels affect function of nerves • Convulsive twitching develops, person dies of spasms in the respiratory muscles • Rx – Vitamin D, calcium and parathormone CUSHING’S SYNDROME • Hypersecretion of adrenal cortex • May be caused by adrenal cortical tumor or prolonged use of prednisone • Symps – high blood pressure, muscle weakness, obesity, poor healing, tendency to bruise, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), menstrual disorders • Rounded moon face and buffalo hump • Rx – surgical removal of tumor Adrenal Gland Disorders • Cushing’s syndrome o o hypersecretion of cortisol Round “moon” face and “buffalo hump” ADDISON’S DISEASE • Hypofunction of adrenal cortex • Symps – bronzing of skin, hypoglycemia, hypotension, etc. • Rx – replace deficient hormones • Addison’s disease o o o Hyposecretion of cortisol Low blood pressure results Increased pigmentation Steroid Abuse in Sports • Anabolic steroids (androgens) can help build bigger, stronger muscles • Risks far outweigh temporary improvements – males have liver changes, atrophy of testicles, breast enlargement, and cardiovascular disease • Female risks include amenorrhea, abnormal placement of body hair, baldness, voice changes Diabetes Mellitus Pancreas • The pancreas is a large gland behind your stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. Contains islands of cells called the Islets of Langerhans which secrete glucagon and insulin • Glucagon – stimulates the liver to break down glycogen, raises blood sugar concentration • Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells *Both hormones work together to maintain a balance in the blood sugar Diabetes • Diabetes Mellitus – results from an insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hypoglycemia) and excess is excreted in the urine. • Type I - insulin dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile onset diabetes, often caused by inherited immune disorder that destroys pancreatic cells • Type II – mature onset diabetes (usually after the age of 40), often individuals are overweight, can be controlled with diet and exercise Blood sugar test, device pricks the finger and measures the amount of sugar in the blood Injection of insulin will lower the blood sugar levels Hypoglycemia can occur if levels become too low, can be cured with direct injection of glucose or with eating something high in sugar. This is why diabetics often have candy.