* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 30 Notes October 9, 2014 (DID NOT FINISH CONITNUE ON
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Norepinephrine wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
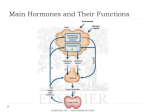
Biology 30 Notes October 9, 2014 (DID NOT FINISH CONITNUE ON OCTOBER 14th) Biology 30 Notes Endocrine System Continued. Notes and Then Work on Assignment. FYI – Goiter – Review THE THYROID GLAND TSH – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone is an anterior pituitary hormone which triggers the thyroid to secrete thyroxine. Iodine is needed to make thyroxine, if there is not enough thyroxine will not be produced. What happens is that there is no “negative feedback loop” and the anterior pituitary gland continues to secrete TSH. This creates a goitre, enlargement of the thyroid gland. Extra - http://www.medicinenet.com/thyroid_pictures_slideshow/article.htm Calcitonin A hormone produced by the thyroid glands. The role of this hormone is to regulate the concentration (amount) of calcium in the blood. When the concentration of calcium gets too high in the blood calcitonin stimulates the uptake of calcium in the bones, thus reducing the amount of calcium in the blood. THE PARATHYROID GLANDS Four small glands attached to the thyroid. It produces a hormone called PTH – parathyroid hormone. This hormone is released when the concentration of calcium in the blood is low. The hormone stimulates bone cells to break down bone material and release calcium into the blood, causes the kidneys to reabsorb calcium from the urine, and activates vitamin D which stimulate the absorption of calcium from food. THE ADRENAL GLANDS We have two of them, located above the kidneys. They are made up of two layers; The adrenal medulla and cortex produce different hormones and are controlled differently. 1. Inner Layer Adrenal Medulla (SHORT TERM STRESS RESPONSE) It produces two hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine, otherwise known as adrenalin and noradrenaline. These hormones regulate the short-term stress response “fight or flight”. The effects of these hormones are the body are similar to those caused by the stimulation of the SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM. Quick Review – have the students break down the different components of the Nervous System The way a works is a bit different than other glands and hormones. Neurons from the sympathetic system carry a signal from the hypothalamus directly to the adrenal medulla. It is neurons not other hormones that stimulate this gland. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. Effects – increase breathing rate, heart rate, blood pressure, blood flow to the heart and muscles, and conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver (NEED ENERGY). The pupils of the eyes dilate, blood flow to the extremities decreases. The effects of Epinephrine are quick, used to treat medical condition. Shot may be given if someone is having a severe allergic reaction (EPIPEN). It is quick because its released is controlled by the nervous system. Difference is that the effects of epinephrine hormone last 10 times longer than those effects of the sympathetic nervous system. 2. Outer Layer Adrenal Cortex (LONG TERM STRESS RESPONSE) This gland is controlled by the anterior pituitary and ACTH Produces: Glucocorticoids which increase blood sugar. Mineralocorticoids which increase blood pressure. Small amounts of female and male sex hormones.