* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Muscular System
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
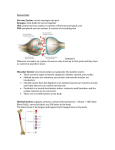
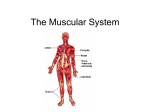
The Muscular System LIFE SKILLS SCIENCE MR. HERMANN MUSCLES There are more than 600 muscles in the human body. These muscles serve many different purposes. All movement in the body depends on muscle, they also create heat in the body. Muscle types There are 3 different types of muscle in the human body, they are smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle. All three types serve different purposes Cardiac Muscle Cardiac muscle tissue is an extremely specialized form of muscle tissue that has evolved to pump blood throughout the body. In fact, cardiac muscle is only found in the heart and makes up the bulk of the heart’s mass. The heart beats powerfully and continuously throughout an entire lifetime without any rest, so cardiac muscle has evolved to have incredibly high contractile strength and endurance. And because the heart maintains its own rhythm, cardiac muscle has developed the ability to quickly spread electrochemical signals so that all of the cells in the heart can contract together as a team. Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of groups of muscle fibers in an orderly arrangement. A small muscle may be only a few bundles of fibers, while the major muscles in the body, such as the gluteus Maximus that forms the bulk of the buttock, are made up of hundreds of bundles. Movement of the skeletal muscle is under the control of the brain Smooth or Visceral Muscle Visceral muscle tissue, or smooth muscle, is tissue associated with the internal organs of the body, especially those in the abdominal cavity. As with any muscle, the smooth, involuntary muscles of the visceral muscle tissue (which lines the blood vessels, stomach, digestive tract, and other internal organs) are composed of bundles of specialized cells capable of contraction and relaxation to create movement. If one were to slice through a muscle diagonally, he would find that it resembles a telephone cable. Muscle Groups Muscles in the body are grouped together and work as a team to perform movement of the body. Muscles are strong, but by working together, its less strain, and allows them to not have to work so hard. We will cover some of the more prominent groups. The Hamstrings Group The hamstring muscle group is the group that is used to bend your leg at the knee. The muscles flex and your knee bends. When the muscle extend or relax, the leg will go back down. This is what is referred to as negatives. The Calf Muscles Both of the muscles in the calf are responsible for flexion in the angle and the knee. These muscles taper at the bottom and are connected to the calcaneus bone by the Achilles tendon The Abdominal Muscles The abdominal muscle groups is made up of many different muscles. This is one of the largest groups in the body. The abdominals are made up of different layers of muscles that all work together in helping your body move. Summary We have covered just a few of the more than 600 muscles in the body. There are many more that are just as important as those mentioned in this lesson. All of the systems in our bodyies are equally important, but each one does a different essential job. All muscle action is started by nerves in the brain firing and sending the signals to the specific body part. This will all be covered in a later chapter.