* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY AND MANIFISTATIONS
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
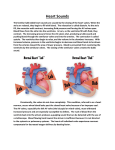
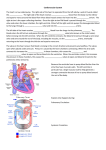
Lecture I Continued Introduction; The Cardiovascular System (CVS) Dr. Aya M. Serry 2016 Cardiac valves and their functions The human heart contains four valves: Two Atrioventricular valves (AV valves) between the atria and the ventricles: 1. Tricuspid valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. 2. Mitral valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle. Cardiac valves and their functions The human heart contains four valves: Two Atrioventricular valves (AV valves) between the atria and the ventricles: 1. Tricuspid valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle. 2. Mitral valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle. Cardiac valves and their functions Two semilunar valves: 1. 2. Aortic valve between the left ventricle and the aorta. Pulmonary valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Functions of the cardiac valves The cardiac valves allow the blood to pass only in one direction The AV valves : Allow for the blood to pass from the atria into the ventricles during ventricular diastole. During ventricular systole, the AV valves close to prevent back flow of blood from the ventricles into the atria. Functions of the cardiac valves The semilunar valves: Allow for the blood to pass from the ventricles into the arteries during ventricular systole. During ventricular diastole, these valves prevent back flow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles (as these valves become closed during ventricular diastole). Preload Vs. Afterload Preload • The preload represents the volume work of the heart. It is usually considered the end-diastolic pressure when the ventricle has been filled. • It is called the preload because it is the work or load imposed on the heart before the contraction begins. • Preload represents the amount of blood that the heart must pump with each beat, It is largely determined by the venous return to the heart and the accompanying stretch of the cardiac muscle fibers. Preload Vs. Afterload Afterload • The afterload is the pressure in which the muscle exerts its contractile force in order to move blood into the aorta. • It is called the afterload because it is the work presented to the heart after the contraction. • The systemic arterial blood pressure is the main source of afterload work on the left heart, and the pulmonary arterial pressure is the main source of afterload work on the right heart. • The afterload work of the left ventricle is also increased with narrowing (i.e., stenosis) of the aortic valve. THANK YOU…..