* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spatial learning in the Morris water maze in mice genetically
Neurobiological effects of physical exercise wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
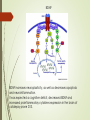
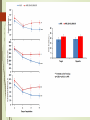
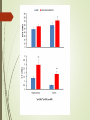
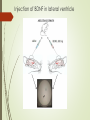
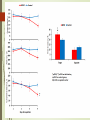
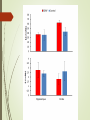
Spatial learning in the Morris water maze in mice genetically different in the predisposition to catalepsy: the effect brain-derived neurotrophic factor Kulikov A.V. Federal Research Center Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Siberian Division of Russian Academy of Sciences, 630090, Novosibirsk, Russia Catalepsy Experimental models of catalepsy haloperidol-induced catalepsy in rat drug-free pinch-induced catalepsy in CBA/Lac mice (Kulikov et al., 1993) morphine-induced catalepsy in mice Transferring of the fragment of 61 - 70 cM from CBA to the AKR genome (Kulikov et al., 2008) Generation of AKR.CBA-D13Mit76 (D13)mice D13 mice show: high level of catalepsy; activated innate immunity; reduced volume of pituitary BDNF BDNF increases neuroplasticity, as well as decreases apoptosis and neuroinflammation. It was expected a cognitive deficit, decreased BDNF and increased proinflammatory cytokines expression in the brain of catalepsy-prone D13. The aim of study was to investigate the association between hereditary catalepsy, learning, proinflammatory cytokines and BDNF expression. The 1st experiment was aimed to study the effect of the CBA-allele of main gene of catalepsy on the spatial learning, as well as the levels of mRNA of genes coding BDNF and proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 in the brain in AKR and D13 mice. The 2nd experiment studied the effects of acute icv administration of BDNF on the spatial learning and the expression of BDNF and IL-6 coding genes in the brain in D13 mice. Morris water maze Acquisition during four consecutive days the learning was evaluated by means of reduction of escape latency time, path run to platform and cumulative distance between the mouse and the platform. In the retention the memory was evaluated by comparison of time spent in the target and opposite sectors. Injection of BDNF in lateral ventricle Conclusion The transfer of the CBA allele of the main gene of catalepsy to the genome of catalepsy-resistant AKR strain reduced acquisition in the Morris water maze and elevated Il-6 mRNA levels in the cortex and hippocampus in catalepsy-prone D13 mice. An acute ivc administration of BDNF restored the reduced acquisition, improved retention in the Morris water maze, but failed to decrease the elevated level of mRNA of Il-6 gene in the cortex and hippocampus in D13 mice. The recombinant AKR.CBA-D13Mit76 mouse line is a promising model of the learning and memory disturbances and the screening of drugs for their correction. The Centre of Genetic Resources of Laboratory Animals, The Federal Research Center Institute of Cytology and Genetics SD RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia