* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Quantum Mechanical Model
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
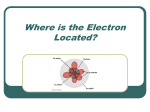
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Quantum Mechanical Model Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-source, collaborative, and web-based compilation model, CK-12 pioneers and promotes the creation and distribution of high-quality, adaptive online textbooks that can be mixed, modified and printed (i.e., the FlexBook® textbooks). Copyright © 2015 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/about/ terms-of-use. Printed: September 19, 2015 www.ck12.org C HAPTER Chapter 1. The Quantum Mechanical Model 1 The Quantum Mechanical Model Lesson Quiz Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Multiple Choice: 1. The study of motion in large objects is called a. b. c. d. traditional mechanics quantum mechanics classical mechanics quantized mechanics 2. According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, the velocity and position of which of the following can never be measured very accurately? a. b. c. d. a traveling missile an electron in motion a hockey puck shot at the goal atomic emission lines 3. An electron cloud a. b. c. d. shows exactly where the electron is located gives a 75% probability of where the electron is located gives a 90% probability of where the electron is located gives a 65% probability of where the electron is located 4. Each electron can be described by _____ quantum numbers. a. b. c. d. two four six eight 5. The highest allowable sublevel for n = 3 is a. b. c. d. s f d p 6. The spin quantum number has _____ values. a. b. c. d. two three one four 7. The units of mass in the de Broglie wave equation are a. µg 1 www.ck12.org b. mg c. g d. kg 8. An increase in the quantum number n means ________ in the distance of the electron from the nucleus. a. b. c. d. an increase no change a decrease a variable response 9. If the principal quantum number n = 4, the angular quantum number can have values for zero to a. b. c. d. 2 4 1 3 10. The magnetic quantum number tells us the a. b. c. d. shape of the orbital orientation of the orbital around the nucleus distance of the orbital from the nucleus spin of the orbital True/False: 11. _____ The Bohr model of the atom only explains the behavior of the hydrogen electron. 12. _____ Electrons in atoms do not have defined energy levels. 13. _____ It is not possible to measure simultaneously the exact velocity and location of a jet plane traveling at 645 miles/hour. 14. _____ The Schrödinger wave equation predicts the probability of finding an electron in a given area of space. 15. _____ An orbital represents a two-dimensional area of space. 16. _____ The spin quantum number can have up to four values. 17. _____ The s orbital has a spherical shape. 18. _____ The principal quantum number designates the principal energy level occupied by the electron. 19. _____ The term for the discrete energy levels of an electron is quantal. 20. _____ Two electrons in the same orbital cannot have the same spin quantum number. Fill in the Blank: 21. The following image is a depiction of a ____ orbital. 22. 23. 24. 25. 2 A d orbital electron can assume any one of _____ different orientations. If the angular momentum quantum number has an l of 0, that designates an ___ orbital. The study of the motions of subatomic particles is called ______ ________ . Solutions to the Schrödinger equation are called _______ functions. www.ck12.org 26. 27. 28. 29. Chapter 1. The Quantum Mechanical Model Each electron can be described by ____ quantum numbers. A maximum of ____ electrons can be found in p orbitals. The equation that described the wave nature of any particle was developed by ______ _________ . Calculate the wavelength of a space shuttle with a mass of 2.05 × 107 kg travelling at a rate of 7.85 × 103 m/s. Short Answer: 30. What major change in our thinking about the path of a moving electron had to be made with the advent of quantum theory? 3