* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outline Mechanical Systems Kinematics Example Projectile Motion
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
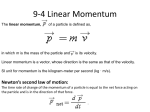
Outline CGS 3032 Interactive Modeling and Animation I • Review Feburary 9, 2007 • Today – Translation – Rotation – Scaling • Project submission guideline – Name your project with following format: <lastname>_<firstname>_<project name> – One zipped file for the project folder – Mechanical Systems – Kinematics • Projectile Motion – Linear Kinetics Mechanical Systems • What is the mechanical system – Certain portion (a part or the whole) of the object of interest • Different types of mechanical systems – Particle – A system of particles – A rigid body – A system of linked rigid bodies, or an articulated object Kinematics • Location (r) – Position of a particle at a given time instance • Velocity (v) – The rate of change in position or the rate of displacement dr v= dt • Acceleration (a) – The rate of change in velocity Example • Calculate new speed v(t + ∆t ) = v(t ) + a∆t • Calculate new location 1 r (t + ∆t ) = r (t ) + v (t )∆t + a∆t 2 2 a= dv dt Projectile Motion • Two dimensional motion – Only force: the force due to gravity. – The magnitude of the acceleration: g = 9.8 m/s2 • ay = g and ax = 0 – Do not consider the rotation of the earth • Suppose initial location (x0, y0), velocity (vx0, vy0) – – – – vx(t) = vx0 x(t) = x0 + vx0t vy(t) = vy0 + gt y(t) = y0 + vy0t + gt2/2 • Example 1 Linear Kinetics • Force (f) – Equals to the product of its mass and acceleration f = ma – Two kinds of forces • Contact Forces • Field forces Linear Kinetics – cont • Momentum (p) – The amount of motion the particle possesses – Equals to the product of its mass and velocity p = mv • Kinetic energy – Energy due to the motion of the particle T= Momentum Conservation • Momentum is conserved for any isolated collision • For a collision occurring between two objects – the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision – The momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2 Types of Collision • Inelastic collision – Example - rubber ball on a hard surface – Conserve momentum but not energy • Perfectly inelastic collision – Example - two lumps of clay – Conserve momentum and the two objects stick together • Elastic collision – Example - two billiard balls with no deformations – Conserve energy and momentum • Example 1 2 1 mv = vp 2 2 Collision • Action of objects striking or coming together • Involve forces - change in velocity • Conserve momentum, and maybe energy • Example The Three Laws of Motion • Law of inertia – No velocity change if no external force • Law of acceleration f = ma • Law of reciprocal actions – All forces occur in pairs, which are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction 2 Collision of Billiards • If assuming no spin – Conserve energy – Conserve linear momentum • Procedure Reading • http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/Phys /Class/BBoard.html • http://www.lightandmatter.com/html_books /2cl/ch01/ch01.html • http://theory.uwinnipeg.ca/physics/index.ht ml • Details 3