* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Semester Final Review PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
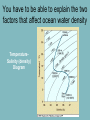
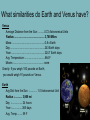
ES112 Spring Semester Final Test Study Guide Review Greenhouse Gases • Greenhouse gases are gases that exist in the atmosphere, have gotten there either naturally or by other means, and cause heat to be trapped • What are some examples? • Identify the top 3 greenhouse gases 1. Water vapor (H2O) 2. Carbon dioxide (CO2) 3.Methane (CH4) Oceans • What determines density? • What is Upwelling? You have to be able to explain the two factors that affect ocean water density TemperatureSalinity (density) Diagram Upwelling is a process in which deep, cold water rises toward the surface • Winds blowing across the ocean surface push water away. Colder water then rises up from beneath the surface to replace the water that was pushed away. Some parts of the water cycle • Condensation process by which water vapor in the air is changed into liquid water • Evaporation process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas or vapor • Transpiration water vapor released from plants • Precipitation water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail • Sublimation the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. Cellular respiration is necessary for the organism's survival, and it helps move the carbon cycle along. What gas do organisms use in cellular respiration to produce carbon dioxide and help move the carbon cycle (3.06) The Carbon cycle is tied to the Oxygen Cycle Where does the Sun’s Energy Come From? • Nuclear Fusion • Takes place in the core • Two hydrogen atoms join together to form helium • Heat and light energy are a by-product of the nuclear fusion process Planets • Terrestrial – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars • Gas – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune What two factors affect a planet’s gravity? Size and mass Rotating Planets!!! What similarities do Earth and Venus have? Venus Average Distance from the Sun :..........0.72 Astronomical Units Radius:................................................ 3,760 Miles Mass: ....................................................0.8 x Earth Day:.......................................................243 Earth days Year:..................................................... 224.7 Earth days Avg. Temperature: ................................864 F Moons :.................................................none Gravity: If you weigh 100 pounds on Earth, you would weigh 91 pounds on Venus. Earth Avg Dist from the Sun :............ 1.0 Astronomical Unit Radius :............ 3,959 mi Day :................. 24 hours Year :.................365 days Avg. Temp:........ 59 F All planets rotate counterclockwise except Venus. Eclipses • Solar – new moon, moon casts a shadow on earth • Lunar – full moon, earth casts a shadow on the moon You have to know how to interpret a diagram, and explain the sequence and causes of lunar phases Do we see all sides of the moon or always the same side? Explain your answer in 1 to 2 sentences • We see one side because the Moon is orbiting the Earth. • The Moon rotates about its axis as it orbits the Earth. NOTE: The wobble of the moon on its axis as it rotates enables us to see a little more than half (about 59%) of the moon. When looking at two stars that are the same distance away, how can you tell one star is hotter than the other? Explain the difference between comets, asteroids and meteors. • Asteroids are smaller than planets but larger than meteoroids, meaning that an asteroid can range from a few meters wide to hundreds of km wide. Most are found between Mars and Jupiter. comets • Comets are icy and travel from the outer to the inner solar system and back. • Gas tail (blue) – away from the Sun • Dust tail (yellow) – curves toward the orbital path Asteroid vs. Meteor vs. Meteorite • It all depends where it is. • When a piece hits the earth's atmosphere, it is called a meteor. If it lands on Earth, it is called a meteorite. Recap • Asteroid – solid rock that orbits the sun • Meteor – rock, iron or icy body entering the Earth’s atmosphere • Meteorite – any meteor striking the ground http://kids.discovery.com/quizzes/space/asteroid-comet-or-meteor What is light? • A transverse wave • A wave of both electricity and magnetism – Electromagnetic energy – energy that moves as a wave at the speed of light • Does not require a medium and can travel in a vacuum So you have to be able to explain what type of wave light travels as and identify the parts Be familiar with the sequential process of light moving through a telescope Define and give examples of renewable resources on earth There are 19 Multiple Choice questions worth 5 points each Have a fantastic summer!!!