* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Screen Version - Michigan State University
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Second law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
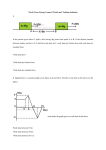
Today – Exam#2 Review • • • • Exam #2 is Tuesday 3/30 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions. Bring your calculator You can use 5 (!) pages (front and back) of notes. I don’t care if you hand write or type them. • List of topics to study is up on the web under today’s reading assignment • As with exam 1, there will be an exam 2 extra credit opening in CAPA at 4pm on Tuesday 3/30 due by Thursday morning. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -1- Energy, Work, etc. • Two kinds of energy: Kinetic – energy of motion, Potential – energy of position • Energy is measured in Joules, J • Power = Energy/time . The unit is Watts = J/s • Energy is always conserved. Energy conservation can be used to find how high something will go. • Work = force x distance, converts energy from one form to another. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -2- Chemical Energy • 1 Calorie = 4184 J • How many Calories are used by a person to lift 200 kg 1m? Assume people are 10% efficient in converting chemical energy to work. Work = mgh = 200 x 9.81 x 1 = 1962 J Chemical energy=Work/eff=1962J/.1=19620. #Calories = 19620 J/(4184 J/Cal) = 4.69 Cal ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -3- Which of the following is correct concerning temperature? A. B. C. D. E. The average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas increases at the temperature is increased. Thermal motion Is highly organized As a gas is cooled, the molecules more more rapidly. Temperature is a measure of the average potential energy of atoms. Temperature is not related to energy. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -4- Entropy • Entropy is a measure of the number of ways a system can be arranged. S = kBln(# of arrangements) • S = Heat/T – thermal energy goes toward increasing the entropy • Second Law of Thermodynamics – The entropy of a closed system always increases. • As the pendulum swings useful energy is lost to increasing the random motion of the air and pivot (heat) • 2nd law => There is no way to recollect the thermal energy and make the pendulum swing higher as in the frictionless case. (slighly less correct definition sometimes used that “entropy is the measure of microscopic disorder” in a system) ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -5- Energy Energy and Entropy - Pendulum Example If there is no friction, the pendulum swings forever, always following the same trajectory. The thermal energy (heat) is “lost” The figure shows how the energy is split into Kinetic ISP209s10 Exam2 point Review in the trajectory. And Potential energy at each -6- Energy Energy and Entropy - Pendulum Example The thermal energy (heat) is “lost” ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -7- Coin Toss Example • Suppose we have 10 coins: HHHHHHHHHH S = k ln(1) = 0 Heads Number of ways Entropy (J/K) *10-23 9 10 3.18 8 45 5.25 7 120 6.61 6 210 7.38 5 252 7.63 4 210 7.38 3 120 6.61 2 45 5.25 1 ISP209s10 Exam210 Review 3.18 -8- Why does time always move in one direction? • The Universe was created with very low entropy. Much too low for its size. It is like the Universe started with all heads. • Hence, everything in the Universe moves toward reaching the correct amount of entropy. It is very improbable to go the other way. In this case very means so improbably that it never happens. • Time has a direction because going back in time would imply the entropy could be decreased. That is very improbable. • The Universe tends toward increasing entropy. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -9- Clicker Question What principle of Nature distinguishes between the forward and backward directions of time? A) B) C) D) E) Newton’s 3rd law (“law of force pairs”) Time dilation Entropy always increases (2nd law of Thermodynamics) E = mc2 The concept of the “absolute zero” temperature Indeed, with the exception of some rare subatomic processes, the Laws of Physics (aside from the 2nd-law of Thermodynamics) Don’t distinguish between and backward flow of time.-10ISP209s10forward Exam2 Review Clicker question Which statement applies to the 2nd law of Thermodynamics? A) The total entropy or microscopic disorganization of all Participants in a physical process always increases. B) It is the reason why we never see a broken egg on the floor spontaneously reassemble itself on the table from which it fell. C) Thermal energy flows from higher to lower temperatures D) You can never convert 100% of thermal energy into work. E) All of the above. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -11- Our current understanding of Forces • There are 4 known forces in nature (Gravity, weak, EM- electromagnetic , strong) • Gravity does not fit well in our understanding with the others – It is very weak compared to the others. Why? • Our current understanding of nature is by Quantum field theory: EM - quantum electrodynamics, EM+weak - electroweak theory, Strong - quantum chromodynamics). • Our understanding of force involves the exchange of ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -12force carrying bosons between particles The particles of nature Charge +2/3 -1/3 0 -1 anti-particles have opposite charge ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -13- T. Kondo How nature is put together from the pieces… Atomic Nucleus Atoms Made of nuclei and electrons. Size: 10-9m Made of neutrons and proton. Size 10-14 m ISP209s10 Exam2 Review A proton (uud) Made of quarks: Size 10-15 m A neutron has ddu -14- A summary of the forces of nature Force Strong Electromagnetic Weak Gravity Strength Carrier Acts on 1 Gluon, g quarks 1/137 photon anything with charge 10-6 6x10-39 Range (m) 10-15 size of a proton infinite Vector quarks, electrons 10-18 Bosons (leptons) , Only 0.001 +, 0 W W,Z neutrinos width of proton Graviton (?) ISP209s10 Exam2 Review anything with mass infinite -15- Our Picture of Force A charge creates a field… Feynman diagram Picture of the field h #E#t " 4! Virtual particles can exist for a short time. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -16- Coulombs Law • Charge comes in units of 1.6E-19C. • The force between two charges is: 2 kq1q2 Nm F = 2 ; k = 8.99 ! 109 2 r12 C 1 2 r12 • Example (inverse square law): 4 times the distance kq1q2 1 kq1q2 1 kq1q2 1 F4 d = = 2 2 = = Fd 2 2 (4r12 ) 4 r12 16 r12 16 ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -17- The Earth behaves as a large magnet The Earth is like a large magnet with a south magnetic pole at the North geographic pole. N S T/F N • T North pole of a compass points north in S northern hemisphere • F North pole of a compass points south in southern hemisphere • T North pole of a compass points towards the north in the southern hemisphere ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -18- Map for the Electric Field Note: we could make similar maps for all the fields in nature (gravity, weak, EM, strong). ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -19- The relation between electric and magnetic fields • Charge creates an electric field (and potential, V) • Moving charge creates a magnetic field • The photon is responsible for transmitting both the electric and the magnetic forces • Maxwell’s equations describe the following; – – – – – Charge makes electric fields Changing magnetic field makes electric fields Changing electric fields make magnetic fields Magnets always come with a north and a south pole EM waves travel at the speed of light (in a vacuum) ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -20- Sample Problem What is the magnitude of the electric field at 2.0 m? E =- (0V ! 80V ) = 20.0 V = 20.0 N "V =! (4m ! 0m ) "x m C ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -21- Sample Problem Zero e-field Zero e-field Exam2 Review Electric field is the rateISP209s10 of change of potential with position. Highest Magnitude Of e-field -22- Simple Problem F=Eq If a charge of 1.5 C is placed on an electric field of 15.5 V/m, what is the magnitude of the force on the charge? Answer: F = 15.5 N/C x 1.5 C = 23.3 N ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -23- Flow of Charge - Current • Batteries are like pumps that lift charge to a higher potential. The charge flows down the hill to the other side of the battery. A battery is like a pump. Moving Charge does work on the way down V ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -24- Quantum Mechanics Review • Light can be described as an electromagnetic wave or a little bundle of energy (a photon). Light has particle and wave character. • Waves can overlap – this is called interference. Destructive if they cancel, Constructive if they reinforce. • Particles, for example electrons, have wave and particle properties. • The thing that is waving in the case of a particle is probability. The square of the height of the wave (wave function) is a measure of the probability density. • All objects (atoms, molecules, etc.) exist in defined states of energy. The energy is quantized (quantum mechanics) ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -25- The Uncertainty Principle What is the meaning of the Uncertainty Principle? h #x#p " 4! A. The entropy of a closed system always increases. B. It is not possible to know the exact position and momentum of a particle at the same time. C. It is not possible to ever know the exact position of a particle. D. Small objects have a wave function. E. Energy is conserved in a closed system. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -26- Antiparticles and Antimatter • All particles have a corresponding anti-particle with opposite quantum numbers. We write the anti-particle with a bar over the top, e.g. proton – p anti-proton p • Antimatter (matter made of anti-particles) is very difficult to make. It can artificially be produced only at large particle accelerators (“atom smashers”). • Matter and anti-matter are created naturally in pairs • So far the total amount of antimatter ever produced by humankind is a few grams. • Matter and anti-matter annihilate each other when they meet and ALL the mass is converted to energy ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -27- Why is Quantum Theory so strange? • What you thought were waves can act like particles and visa-versa (“wave-particle duality”) • Quantum uncertainty (Heisenberg) • Nature is intrinsically random • Quantum non-locality • Nature is “digital” and “discrete” • The very act of observing/measuring can change the outcome We don’t see any of the weirdness in our daily lives. But if you look at microscopically small phenomena (atoms), it seems to indeed be reality! ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -28- Look closer, you see light acts like a particle… EM fields are made of discrete bundles of energy (quanta or photons) EEM = 0, 1hf, 2hf, 3hf, 4hf, … h*f = energy of 1 photon Particle-like: h = 6.625E-34 Js Planck’s Constant We cannot predict the individual dots position. Quantum theory Can only predict the pattern that emerges with a large number of dots ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -29(probabilities). Particles acting like waves Electrons show an interference pattern in the double slit experiment. And the interference Patterns show a Discrete “lumpiness” If you look closely. “electron gun” As with light, it is impossible to predict the position Of each individual dot. Nature is intrinsically random! We can only predict “probabilities”, which is to say the ISP209s10 Exam2#Review overall pattern that emerges with a large of dots. Each “lump” is an Electron hitting the Screen. -30- Observation can alter the outcome in QM … and a watched electron doesn’t show interference If you try to find out Which slit each electron Goes thru, the wave features Go away An electron Detector Many more weird examples… ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -31- Quantum Nonlocality After interaction the wave functions are entangled. 2 2 If we measure 1 and 2 at the same time the difference in position forms an interference pattern. Interaction 1 1 If we measure 2 before 1, the measurement of 2 defines where 1 must hit. This information travels faster than the speed of light. This has been confirmed experimentally. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -32- What is “waving” for matter waves? • Probability – all particles described by a “wave function” ψ. The square of ψ gives the probability density of finding a particle per unit volume. • The ψ extends over all space, which gives weird consequences. = prob. of finding particle in a small volume V centered at the point r. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -33- Neutrinos • Neutrinos are subatomic particles that do not have charge. They only interact via the weak force. • These are very unusual particles and we still don’t know much about their properties. They have a mass, but it is so small we have not been able to measure it. • They account for about 2% of the universe but interact weakly. One light-year of lead would have only a 50% chance of stopping one. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -34- Equations – sort of Rules for Feynman Diagrams: 1). The number of leptons and baryons must be conserved. Not allowed 2). Charge must be conserved. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -35- Some examples Is the following allowed? Production of a quark and anti-quark by a collision of an electron and an anti-electron. Before After electron + anti-electron quark + antiquark Name Lepton Baryon Up quark -1/3 0 1/3 Down quard 2/3 0 1/3 electron -1 1 0 neutrino 0 1 0 ISP209s10 Exam2 Review Charge -36- Some examples Baryon Lepton Charge Before After Name Charge Lepton Baryon Electron + anti-electron Quark + anti quark Up quark -1/3 0 1/3 1/3 + (-1/3) Down quark 2/3 0 1/3 0+0 1 + -1 0+0 electron -1 1 0 -1 + 1 1/3 + (-1/3) neutrino 0 1 0 allowed ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -37- Is this possible? Yes, it is two quarks interacting via the electromagnetic force. Up quarks have electric charge of +2/3. ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -38- Force Carriers • Stong – Gluons – g • Weak – Intermediate vector bosons – Z,W • Electromagnetic – photon - γ Two quarks interacting via the strong force ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -39- Feynman Diagrams and rules Charge, baryon number, and lepton number are conserved Consider the decay of a +pion into an antimuon by the Weak force. Which diagram describes this process? !+ ud - " " time + ISP209s10 Exam2 Review correct -40- Other Examples !+ Wrong because electric force does not act on neutrinos ud - " " time + Decay of pion Baryon and lepton not conserved Charge of W is not Wrong because correct electric force does not act on neutrinos ISP209s10 Exam2 Review -41-