* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
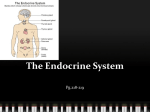
The Endocrine System WHAT IS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM? What is it? • The endocrine system (ES) regulates long term changes in the body such as growth and development. • It also controls many of your body’s daily activities and influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies. • It regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function, and reproductive processes. Endocrine Glands • Gland - a group of cells that produces and secretes, or gives off, chemicals. • Your ES is made up of a group of organs, called endocrine glands. • An endocrine gland produces and releases chemical substances that signal changes in other parts of the body. Hormones • A chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland • Chemical messengers • Each hormone has a specific function and specific “targets” in the body • Many different hormones move through the bloodstream, but each type of hormone is designed to affect only certain cells. FUNCTIONS OF ENDOCRINE GLANDS Functions • Each of your endocrine glands plays a specific, important role in your body • • • • • • • • Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Thymus glands Adrenal glands Pancreas Reproductive glands (M&F) Hypothalamus • Located in the lower center part of the brain • Links the nervous and endocrine systems • Controls many of the pituitary gland functions Pituitary Gland • “Master gland” • Located at the base of the brain, below the hypothalamus • It makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands Thyroid • Located in the front part of the lower neck • Produces the thyroid hormones thyroxin, which controls the rate at which we burn food • Controls calcium levels in the blood stream Parathyroid Glands • Attached to the thyroid • Four glands • They release parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood with the help of calcitonin, which is produced in the thyroid Adrenal Glands • Two glands, located on the top of each kidney, triangular in shape • Produces epinephrine, also called adrenaline, which increases blood pressure and heart rate when the body experiences stress Pancreas • Part of the digestive system • Produces insulin and glucagon – work together to maintain blood sugar levels Reproductive Glands • Gonads – main source of sex hormones • Puberty – the period of sexual development during which a person becomes sexually mature and is physically able to reproduce Male gonads – testes Testosterone – male sex hormone Female gonads – ovaries Estrogen – female sex hormone • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lBWIkKfb W8U