* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3анаTest Review (KEY) 3.1 1
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
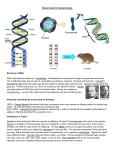
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 3 Test Review (KEY) 3.1 1. Heredity – The passing of traits from parent to offspring 2. Cross pollination – One plant fertilizes a different plant (pollen can travel by wind, rain, insects, birds) The offspring will have a different gene combination 3. True breeding – offspring will be the exact same as the parents Same genes 4. Self pollination – a plant is able to pollinate itself, has both male and female reproductive structures (eggs = ovule and sperm = pollen) Same genes in the offspring 5. Ratio – the relationship between 2 different numbers. You will have to answer a math ratio question. 6. Gregor Mendel – Father of genetics 7. Recessive – the trait that will most likely NOT show 8. Dominant – the trait that most likely WILL show 9. Trait – different forms of a characteristic, know an example 10. Characteristic a feature that has different forms in a population, know an example 11. Genotype – both inherited alleles, the genes, know an example 12. Phenotype – the physical feature, know an example 13. Punnett square is used to organize all possible combinations of offspring from particular parents. (know how to work one, too) Used to determine the probability of future offspring 14. Probability – the likelihood that an event will occur 15. Genes One set of instructions for an inherited trait. Know an example 16. Alleles the different forms (dominant or recessive) of the gene, know an example 17. What’s the difference between genes and alleles? The gene is the main category and the alleles are the different “versions” 18. How are genes and alleles related to genotype and phenotype? See notes 19. Heterozygous – What is it? and What does it look like? having a dominant AND a recessive allele (Bb) 20. Homozygous – What is it? and What does it look like? having 2 dominant (BB) or 2 recessive alleles (bb) 21. Incomplete dominance – when one trait is not completely dominant over another. A combination of both phenotypes. For example: wavy hair. 22. Explain how the environment can change a phenotype. We talked about what you can do to yourself to change your physical appearance 3.2 23. Selective breeding organisms with desirable characteristics are mated, know an example 24. Pedigree a diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family. Be able to read one and answer questions. Pedigree is a useful tool because it can help predict whether a person is a carrier of a hereditary disease. 25. How are sex cells different from other human cells? Sex cells have half the number of chromosomes. Other body cells have the full number of chromosomes. 26. How are sex cells made compared to other human cells? Sex cells go through the process of meiosis and body cells go through mitosis. 27. What did Walter Sutton discover? Genes are located on the chromosomes 28. What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis? Study the flip page in made in class 29. Sexlinked disorders – genetic disorders that are carried on the sex chromosome. Know examples from your notes