* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Exposure Therapy Works
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Impact of health on intelligence wikipedia , lookup
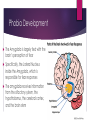
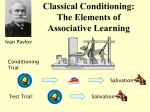
How Exposure Therapy Works PHOENIX HAMMOND Phobia Development Phobia Development Phobia: An extreme, irrational fear of a specific object or situation Classified Learned as an anxiety disorder emotional response Brain turns a previously neutral stimulus into a negative one Often learned through classical conditioning or observational learning Phobia Development The Amygdala is largely tied with the brain’s perception of fear Specifically, the Lateral Nucleus inside the Amygdala, which is responsible for fear responses The amygdala receives information from the olfactory system, the hypothalamus, the cerebral cortex, and the brain stem Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning One theory of phobia development is through classical conditioning Someone experiences a negative response to an object or situation, which turns a previously neutral stimulus into a negative one Classical Conditioning Little Albert Albert was conditioned to fear furry animals by hearing a loud noise when exposed to them https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YmtRjUt Aa84 Observational Learning Observational Learning Phobias can also be developed via observational learning For example: a child’s parent can have a phobia of spiders, the child can see how the parent responds when exposed to a spider, and the child can then develop a phobia of spiders as well What Exposure Therapy Is What Exposure Therapy Is Exposure therapy is a way of treating phobias and other conditions, like PTSD, by having the patient experience their fear over time, reducing the psychophysiological response Can lead to extinction of the learned associations between the feared object and the negative outcome Extinction: the diminished effects of classical conditioning Methods of Exposure Therapy Methods of Exposure Therapy Types of Exposure: Imaginal: Patient is asked to imagine their fear in their mind. For example, a person with agoraphobia might be asked to imagine standing in a middle of a crowded mall In Vivo: Patient is exposed to real life objects of situations. For example, a person with a fear of snakes might watch a snake in a cage Virtual Reality: Both combined. Patients are placed in a situation that may seem real but is actually fabricated or not really there. For example, a simulation of flying or falling Methods of Exposure Therapy Exposure Therapy Techniques: Systematic Desensitization: Patient is gradually exposed to more anxiety-provoking stimuli and taught relaxation techniques Prolonged exposure to the feared stimulus until the anxiety is diminished. Can be In Vivo or VR Why It Works Why It Works Exposure therapy works because exposure to the feared stimulus in a controlled environment, without the negative effects the patient believes the stimulus has will, essentially, reverse its effects and turn the negative stimulus back into a neutral one. Sources American Psychological Association. N.D. What is exposure therapy?. American Psychological Association, Division 12. http://www.div12.org/sites/default/files/WhatIsExposureTherapy.pdf Mager, R., Bullinger, A., Mueller-Spahn, F., Kuntze, F., Stoermer, R. (2001). Real-time monitoring of brain activity in patients with specific phobia during exposure therapy, employing a Stereoscopic virtual environment. Cyber Psychology and Behavior. 4:4. White, M. (2002). Phobias and the brain. Serendip. brynmawr.edu. http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/bb/neuro/neuro02/web3/mwhite.html (2015). Exposure therapy. Goodtherapy.org http://www.goodtherapy.org/learn-about-therapy/types/exposure-therapy