* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of the central nervous system
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
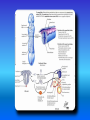
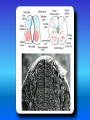
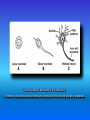
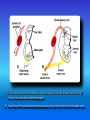
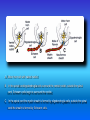
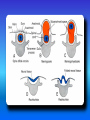
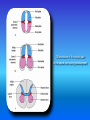
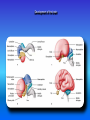
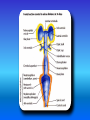
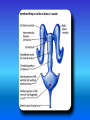
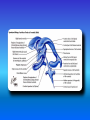
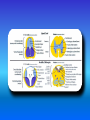
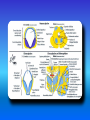
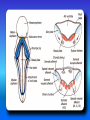
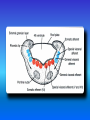
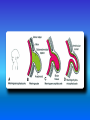
Multimedial Unit of Dept. of Anatomy JU Neural tube and neural crest Various stages of development of a neuroblast. A neuron is a structural and functional unit consisting of the cell body and all its processes. A. Motor axons growing out from neurons in the basal plate and centrally and peripherally growing fibers of nerve cells in the dorsal root ganglion. B. Nerve fibers of the ventral motor and dorsal sensory roots join to form the trunk of the spinal nerve. Origin of the nerve cell and the various types of glial cells. Neuroblasts, fibrillar and protoplasmic astrocytes, and ependymal cells originate from neuroepithelial cells. Microglia develop from mesenchyme cells. The origin of the oligodendroglia is not clear. A. Motor horn cell with naked rootlet. B. In the spinal cordoligodendroglia cells surround the ventral rootlet; outside the spinal cord, Schwann cells begin to surround the rootlet. C. In the spinal cord the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendroglia cells; outside the spinal cord the sheath is formed by Schwann cells. Terminal end of the spinal cord in relation to that of the vertebral column at various stages of development. A. Approximately the third month B. End of the fifth month C. Newborn. Differentiation of the neural tube in the spinal cord during development Development of the brain Brain vesicles and their derivatives Origins of Cranial Nerves and Their Composition Contributions of Neural Crest Cells and Placodes to Ganglia of the Cranial Nerve Thank you very much Tatra National Park J. Urbaniak