* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
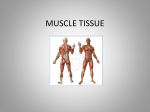
Download Name______________________________ Muscle Tissue
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Name______________________________ Muscle Tissue Epithelia cover surfaces and line passageways; connective tissues support weight and interconnect parts of the body. Together these tissues provide a strong interwoven framework within which the organs of the body can function. Several vital functions involve movement of one kind or another. For example: movement of materials along the digestive tract, movement of blood around the cardiovascular system, or movement of the body from one place to another. Movement is produced by muscle tissue, which is specialized for contraction. There are 3 types of muscle tissue: 1. Skeletal – forms large muscles necessary for gross body movement 2. Cardiac Muscle – found only in the heart and responsible for the movement of blood. 3. Smooth Muscle – found in a variety of visceral organs and other locations where it provides elasticity, contractility and support 1. Muscle tissue is specialized to _______________. Skeletal Muscle 2. These muscles form the ________________ of the body, and are controlled __________________ or consciously. 3. When they contract they pull on ______________ or _______________ and cause gross body movements or facial expressions. 4. Describe the cells of skeletal muscle ___________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ The cytoskeleton of skeletal muscle contains actin and myosin filaments organized into repeating groups. This causes a striped appearance called _____________________. In order to make the organ called a skeletal muscle, adjacent skeletal muscle tissue fibers are tied together by collagen and elastic fibers that blend into the attached tendon. Cardiac Muscle 5. Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle has _________________ or stripes. 6. Explain the “movement” caused by the contraction of cardiac muscle. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Look at the picture of Cardiac Muscle on page 85. What are two differences between the cells of skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle? ____________________ & _______________________. Cardiac muscle cells form extensive connections with each other. They form a branching network of interconnected cardiac muscle cells. The connections occur at specialized regions called intercalated discs. At each intercalated disc, the membranes are locked together by desmosomes, and gap junctions. Ion movement through gap junctions helps coordinate the contractions of cardiac muscle. 8. What are intercalated disks and what is their function in cardiac muscle tissue? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ *hint: if you don’t know what a gap junction is, look it up in you cell outline! 9. Cardiac Muscle is controlled _______________________________. Smooth Muscle The actin and myosin filaments in smooth muscle cells are organized differently from those in skeletal and cardiac muscle, so it does not have striations. The contraction of smooth muscle tissue is controlled by the nervous system, but the contractile activity is not under voluntary control. 10. Smooth muscle is called smooth muscle because it has no _________________. 11. What are the cells of smooth muscle like? _________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Name 5 organs that are made up of smooth muscle. _____________, ______________, _________________, ________________, ___________________ 13. All of these organs are ____________________. 14. The contraction of smooth muscle allows the cavity of an organ to become smaller, or elongate thus substances are_______________________________________________. Nervous Tissue The cells of nervous tissue are neurons . This tissue is specialized for conducting electrical impulses from one region of the body to another. A typical nerve cell has a cell body, which holds the nucleus. Projecting from the cell body are many branched called dendrites and one long axon. The dendrites receive the information, usually from other neurons, and the axon conducts that information to other cells. 15.The two major functional characteristics of neural tissue are ________________ and _______________________. Microscope Observations Type of Cell Appearance