* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnets - kdavis10
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
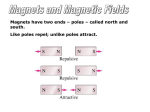
Magnets Two Poles What is a magnet? • A magnet is an object that attracts certain materials usually objects made of iron or steel. • A magnet has two ends called magnetic poles or just poles for short. • A magnet’s pull is strongest at the poles. • Poles are usually marked North and South. • What is each end of a magnet called? •Magnetic Forces • Forces you feel when playing with magnets can be pushes or pulls. • A magnetic field is the space all around a magnet where the force of the magnet can act. • You can’t see the field. • Forces between magnetic poles are like forces between electric charges. • Opposite magnetic poles attract, and like poles repel. North and South poles attract. • North and North poles repel or push away. • South and South poles repel or push away. • Where is the pull of a magnet strongest? Compass • The North and South seeking poles of magnets have been helpful to people for hundreds of years. •People have used magnets to find direction. • The first magnets used were made of heavy natural material called a lodestone, which is a mineral magnetite. • A compass today uses a lightweight magnetic needle that is free to turn. • A compass needle points along an imaginary line connecting the North and South poles. This is because earth is like a giant magnet. • Field lines of earth’s magnetic field come together close to the planet’s North and South poles. • How does a compass work? • The north-seeking pole of the free-moving magnet in the compass points to Earth’s North Pole. Summary • Magnets are objects that attract materials such as iron. • Every magnet has two magnetic poles. • Magnetic forces are caused by the interaction of magnetic fields. • Earth’s magnetic field is like the field of a bar magnet. • A compass needle interacts with earth’s magnetic field. Review • How can you find the poles of a magnet? • Find out where the magnet’s pull is strongest. • What is a magnetic field? • The place where magnetic forces act. • Which type of magnet has a field that is about the same shape as the magnetic field of the earth? • A bar magnet • How many poles does a magnet have? Two The End • Thank You any questions? • By: Rachel Tanner