* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What do my employees do? - College of Business, UNR
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
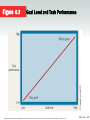
6 Learning and Performance Management Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part. Definition of Learning Learning – the development of experience, insights, knowledge, and understanding that eventually leads to a change in behavior. Information, Understanding, Knowledge • Information deals with the what questions: What do my employees do? • Knowledge deals with the how questions: How do my employees do what they do? How do I get them to do things differently? • Understanding deals with the why questions: Why do my employees do the things they do? I K U Behavioral Models of Learning in Organizations Classical conditioning • Modifying behavior by pairing a conditioned stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit an unconditioned response • Has limited applicability to human behavior in organizations Operant conditioning • Modifying behavior through the use of positive or negative consequences following specific behaviors • Uses reinforcement, punishment, and extinction strategies to influence behavior Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 4 Positive and Negative Consequences Positive Consequences Results of a behavior that a person finds attractive or pleasurable Negative Consequences Results of a behavior that a person finds unattractive or aversive Reinforcement, Punishment, and Extinction Reinforcement • Cultivates desirable behavior by either bestowing positive consequences or withholding negative consequences • Types - Continuous, intermittent, fixed ratio, variable ratio, fixed interval, and variable interval Punishment • Discourages undesirable behavior by either bestowing negative consequences or withholding positive consequences Extinction • Weakens behavior by attaching no consequences to it Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 6 Figure 6.1 Reinforcement and Punishment Strategies SOURCE: Table from Organizational Behavior Modification by Fred Luthans and Robert Kreitner. Copyright © 1985, p. 58 by Scott Foresman and Company and the authors. Reprinted by permission of the authors. Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 7 Examples of Negative Reinforcement Focused on desirable behaviors that occur more frequently: If a clerical worker feels that being ahead is a favorable condition, the worker will be motivated to work hard in order to avoid the unpleasant state of being behind. An instructor deducts 10 points from a student’s grade for each observed absence but there is no effect on a student’s grade for attendance. Example of an alarm in a child’s room. 6-8 Examples of Punishment Focused on undesirable behaviors that should occur very infrequently: If you exhibit unprofessional behavior in this class, you will lose a letter grades If you are caught cheating on an exam, you could fail the course If you steal something at work, you will be terminated. 6-9 Bandura’s Social Learning Theory • Learning occurs when one observes others and models their behavior • Task-specific self-efficacy: One’s internal expectancy to work effectively • Sources - Prior experiences and behavior models - Persuasion from other people - Assessment of current physical and emotional capabilities Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 10 Goal Setting at Work Establishing desired results • To guide and direct behavior Characteristics of effective goals • Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound Functions • Increases work motivation and task performance • Reduces stress caused by confusing expectations • Improves the accuracy and validity of performance evaluation Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 11 Employee Participation Goal acceptance Goal commitment Goal accomplishment Figure 6.2 Goal Level and Task Performance Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 13 Problems with Goal Setting? Evaluating Performance Performance management • Process of defining, measuring, appraising, providing feedback on, and improving performance Organizational citizenship behavior • Behavior above and beyond the call of duty • Enhanced by employee involvement programs • Emphasizes collective performance Measuring performance • Performance appraisal systems Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 15 Effective Appraisal Systems • Develop people and enhance careers • Requires establishment of mutual trust between supervisors and employees • Characteristics • • • • Validity Reliability Responsiveness Flexibility and equitability Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 16 Actual and Measured Performance Communicating Performance Feedback • Refer to specific verbatim statements and observable behaviors • Focus on changeable behaviors • Both supervisor and employee should plan and organize before the session • Begin with something positive It is more effective to ask employees to do something differently than it is to ask them to be different Your employees are not responsible for fixing their systems. That is YOUR responsibility as a manager, and it is the abdication of management to blame employees for problems when there are almost always systemic variables that need continuous improvement. PA Exercise Individual or Team Rewards Individual reward systems • Directly affect individual behavior • Encourage competition within a work team • Skill-based and pay-for-knowledge systems Team reward systems • Encourage cooperation, joint efforts, and the sharing of information and expertise • Gain-sharing plans Copyright ©2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly acce ssible website, in whole or in part. ORBG5 | CH6 21 Organizations get the performance they reward, not the performance they say they want. © 2011 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.