* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 4 review key - Iowa State University
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
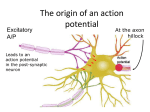
Leader: Landon Course: Biol 212 (2) Instructor: Mayfield Exam 4 Review Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Date: 4/23/11 1. Circulatory system structure arteries veins red blood cells white blood cells capillaries alveoli function Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart Carry deoxygenated blood toward the heart Specialized for gas exchange, have hemoglobin, which binds CO2 and H+ Specialized for immune functions oxygen and other nutrients diffuse through them to tissues Where gas exchange occurs 2. Where are red blood cells generated? (white blood cells too?) Stems cells in bone marrow 3. Describe epinephrine. What is it secreted by and what affect does it have on different tissues of the body? Epinephrine is a water-soluble hormone secreted by the adrenal glands, which are on top of the kidneys. It causes liver cells to release glucose, dilates skeletal muscle blood vessels, and contracts intestinal blood vessels 4. Describe the function of the following structures in transmitting a signal across a synapse: Ca++ channels 5. neurotransmitter (such as Ach) When an action potential reaches the synaptic terminal of the pre-synaptic cell, this will cause Ca++ channels to open, and Ca++ to flow into the neuron. This will cause exocytosis of neurotransmitter-filled vesicles Exocytosed from vesicles across synapse Receptor Neurotransmitter will bind to it If the intracellular concentration of Na+ is 15 mM and the extracellular concentration is 150mM what would happen if Na+ channels in the plasma membrane were opened? Na+ would flow into the cell, and the membrane potential would become less negative and depolarized.= (number 2 and 3 on graph) If the intracellular concentration of K+ is 140mM and the extracellular concentration of K+ is 5mM what would happen if K+ channels were opened? K+ would flow out of the cell, causing membrane potential to become more negative and the cell to repolarize. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu 6. How is a long distance signal sent through the nervous system? How is an action potential propogated across an axon? A stimulus will be received by the dendrite of a neuron, this will cause Na+ channels to open in a small part of the neuron. Depolarization of this one part of the neuron, will cause neighboring Na+ channels ahead of it to open and generate an action potential. As the neighboring part is depolarizing, the part behind it will repolarize and go back to resting membrane potential **opening of Na+ channels in on part will cause neighboring channels to behave in the same way 7. After acteylcholine is exocytosed from vesicle in the synaptic terminal of a somatic motor neuron into the synaptic cleft, what affect does this have on muscle contraction? Explain the process. ACh will bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of a muscle fiber (muscle cell), which will cause depolarization of the skeltal muscle cell. When the depolarization reaches a threshold level, an action potential is generated which is conducted along the plasma membrane and into T tubules. The action potential in the T tubule initiates signaling events that cause Ca++release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In the presence of a high concentration of Ca++, Ca++ binds to troponin, which causes a conformational change that exposes binding sites on the actin. This allows myosin to bind to actin and contraction to occur. 8. True or False. If false, indicate why. T or F The skin is an example of innate immunity. True, anatomic barriers, physiological barriers (such as temp, pH, O2 levels), certain proteins and chemicals that create a hostile enviro for pathogens, and phagocytic cells (such as monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and mast cells) are included in the innate immune response T or F B cells and T cells are part of acquired immune response True T or F The innate immune response is characterized by distinguishing self from non-self and having immunological memory False, these are characteristics of the acquired immune response T or F Acquired immunity is found only in vertebrates True T or F B cells and T cells are cells capable of phagocytosing a pathogen into a vesicle, which will fuse with a lysosome and be degraded by enzymes. False, B cells and T cells are not phagocytic cells. WBC’s such as neutrophils and macrophages are phagocytic. T or F Leukocytes are white blood cells and include cells involved in the adaptive and innate immune response, while erythrocytes are red blood cells with roles in gas exchange. True T or F Eosinophils are the most abundant phagocytic cells in the mammalian body. They detect signals from infected tissues and will leave the circulatory system to attack! False, this is characteristic of neutrophils T or F During an inflammatory response, damaged tissues will attract mast cells, which will release histamine. Histamine causes blood vessels to contract. False, the second sentence should say dilate. T or F B cells and T cells are differentiated from stem cells in bone marrow. The B cells stay in bone marrow and T cells migrate to the thymus. The genomes of these cells are rearranged during development and are a clear exception to the theory of genomic equivalence. True A lymphocyte a.) Expresses several different antigen receptors b.) May mature in bone marrow to a cytotoxic T cell c.) May mature in the thymus to a helper T cell d.) Is phagocytic and participates in the inflammatory response B cells mature in the bone marrow, T cells mature in the thymus Which of the following describes innate immunity? a.) Unbroken skin creates a physical barrier that cannot normally be penetrated by bacteria or viruses b.) Surface secretions from sebaceous and sweat glands give the skin an acidic pH that is unfavorable for bacterial colonization c.) Tears, saliva, and mucous secretions contain lysozyme, an enzyme that digests bacterial cell walls d.) Mucus traps microbes and other particles that come in contact with it e.) All of the Above The role of cytotoxic T cells is to attack a.) Body cells that have been infected b.) Circulating proteins circulating antibodies c.) Complement proteins d.) Extracellular viruses and bacteria Cell mediated response with class 1 MHC attracts cytotoxic t cells create pores in cell Which of the following cell types does HIV preferentially infect? a.) Cytotoxic T cells b.) Natural killer cells c.) Plasma cells d.) Helper T cells e.) Memory cells A leukocyte most effective against parasites Eosinophils . Which of the following cells are NOT a leukocyte (WBC) a.) Basophils b.) Monocytes c.) Neutrophils d.) Natural killers e.) Helper T cells Innate response gets stronger after multiple exposures to the same antigen. T or F False, acquired responses get stronger Which of the following is NOT true about lymphocytes a.) Contain B cells b.) Contain T cells c.) Apart of adaptive immunity d.) Destroy antigens through phagocytosis Explain how urine can have lower concentrations of metal ions, amino acids and sugars and a higher concentration of urea than blood. Protein and nucleic acid metabolism generates toxic ammonia. The liver of mammals converts ammonia to less toxic urea, which is carried to the kidneys to be filtered and excreted. Most excretory systems produce urine by refining a filtrate derived from body fluids. Filtration and then selective reabsorption of valuable ions, amino acids and sugars. Then secretion of urea by adding toxins from bodily fluids to the filtrate More info on page 965 of the book Explain how cytotoxic T-cells identify those body cells that are producing foreign proteins. Cytotoxic T cells make CD8, a surface protein that enhances their binding to class 1 MHC moleculeantigen fragment complexes on infected and cancerous cells Activated cytotoxic t cells then secrete proteins that initiates target cell destruction More info on page 943 of the book Explain how an action potential is transmitted from one neuronal cell to another by means of chemical synapses. In a chemical synapse, depolarization of the synaptic terminal causes syanptic vesicles to fuse with the terminal membrane and release neurotransmitters into the syaptic cleft. At many synapes, the neurotransmitters binds to ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, producing an excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic potential. After release, the NT diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, then taken up by surrounding cells or degredaded by enzymes More info on page 1058 of the book