* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning: Principles and Applications
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
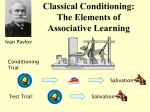
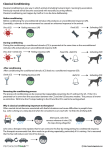
Learning: Principles and Applications Learning is basic to understanding our behavior. It is part of nearly every aspect of our lives. Learning • Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience. • Not all behaviors that we learn are acquired in the same way. • Furthermore, the same behavior can be learned in different ways. Learning Three basic types of learning: Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Modeling Classical Conditioning • Pavlov’s Dog • Ivan Pavlov (1927) began his experiments by ringing a tuning fork and then immediately placing some meat powder on the dog’s tongue. • The tuning fork was a neutral stimulus – it had nothing to do with the response to meat prior to conditioning. Classical Conditioning • After only a few times, the dog started salivating as soon as it heard the sound, even if food was not placed in its mouth. • Pavlov had demonstrated that a neutral stimulus will cause a formerly unrelated response if it is presented regularly just before the stimulus (food) that normally induces that response (salivation). Classical Conditioning • In the experiment: • Food was the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) – an event that leads to a certain, predictable response without previous training. • Salivating was the unconditioned response (UCR) – a reaction that occurs naturally and automatically when the unconditioned stimulus is presented. Classical Conditioning • Under normal conditions, the sound of a tuning fork would not cause salivation. • The dog had to be taught, or conditioned, to associate this sound with food. Classical Conditioning • An ordinary neutral event that, after training, leads to a response such as salivation is termed a conditioned stimulus (CS). • The salivation it causes is a conditioned response (CR). Classical Conditioning • A conditioned response is learned. • Controlling responses in this way so that an old response becomes attached to a new stimulus is called classical conditioning. Classical Conditioning