* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CURRICULUM MAP
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
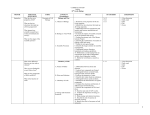
CURRICULUM MAP Subject Biology MONTH August/ January ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the seven properties of life? TOPIC Principles of Cell Biology CONTENT (Terminology) Biology and You: A. Themes of Biology What are the tiny structures that make up all living organisms? What impact does scientific research have on the environment and society? B. Biology in Your World What are the stages of the scientific process? C. Scientific Processes August/ January What is an ecosystem? How does energy flow in ecosystems? SKILLS 1. Relate the seven properties of life to a living organism. 2. Identify the tiny structures that make up all living organisms. 3. Differentiate between reproduction and heredity and between metabolism and homeostasis. 4. Evaluate the impact of scientific research on the environment and society. 5. Explain the primary task of the Human Genome Project. 6. Describe the contributions of scientists in fighting AIDS and cancer. 7. Define the term gene therapy. 8. Describe the stages common to scientific investigations. 9. Distinguish between forming a hypothesis and making a prediction. 10. Differentiate a control group from an experimental group and an independent variable from a dependent variable. 11. Define the word theory as used by a scientist. Ecosystems: A. What is an Ecosystem? How do materials cycle in ecosystems? B. Energy Flow in Ecosystems C. Cycling of Materials in Ecosystems. 1. Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. 2. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. 3. Sequence the process of succession. 4. Distinguish between producers and consumers. 5. Compare food webs with food chains. 6. Describe why food chains are rarely longer than three or four links. 7. Summarize the role of plants in the water cycle. 8. Analyze the flow of energy through the carbon cycle. 9. Identify the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. ASSESSMENT 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Group Project 1 August/ January How do populations grown and disperse? How do populations evolve? Principles of Ecology Populations: A. How Populations Grow B. How Populations Evolve September/ February What is the difference between an atom and an element? Chemistry of Life: A. Nature of Matter How can you distinguish an acid from a base? What are the components of DNA and RNA? B. Water and Solutions C. Chemistry of Cells What is the function of ATP? D. Energy and Chemical Reactions September/ February What do scientists use to visualize cells? 1. Differentiate between atoms and elements. 2. Analyze how compounds are formed. 3. Distinguish between covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds. 4. Analyze the properties of water. 5. Describe how water dissolves substances. 6. Distinguish between acids and bases. 7. Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. 8. Compare the structures and function of different types of biomolecules. 9. Describe the components of DNA and RNA. 10. State the main role of ATP in cells. 11. Evaluate the importance of energy to living things. 12. Relate energy and chemical reactions. 13. Describe the role of enzymes in chemical reactions. 14. Identify the effect of enzymes on food molecules. Cell Structure: A. Looking at Cells What are the three parts of the cell 1. Distinguish among the three patterns of dispersion in a population. 2. Contrast exponential growth and logistic growth. 3. Differentiate r-strategists from kstrategists. 4. Summarize the Hardy-Weinberg principle. 5. Describe the five forces that cause genetic change in a population. 6. Identify why selection against unfavorable recessive alleles is slow. 7. Contrast directional and stabilizing selection. 1. Describe how scientists measure the length of objects. 2. Relate magnification and resolution 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 2 theory? Why do cells need to be relatively small? What are cell membranes composed of? B. Cell Features What role does a nucleus play in cellular activities? C. Cell Organelles September/ February How does passive transport differ from active transport? Cells and Their Environment: A. Passive Transport B. Active Transport October/ March How does the metabolism of autotrophs compare with that of heterotrophs? What role does ATP in the use of microscopes. 3. Analyze how light microscopes function. 4. Compare light microscopes with electron microscopes. 5. Describe the scanning tunneling microscope. 6. List the three parts of the cell theory. 7. Determine why cells must be relatively small. 8. Compare the structure of prokaryotic cells with that of eukaryotic cells. 9. Describe the structure of cell membranes. 10. Describe the role of the nucleus in cell activities. 11. Analyze the role of internal membranes in protein production. 12. Summarize the importance of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. 13. Identify three structures in plant cells that are absent from animal cells. 1. Relate concentration gradients, diffusion, and equilibrium. 2. Predict the direction of water movement into and out of cells. 3. Describe the importance of ion channels in passive transport. 4. Identify the role of carrier proteins in facilitated diffusion. 5. Compare active transport with passive transport. 6. Describe the importance of the sodium-potassium pump. 7. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. 8. Identify three ways that receptor proteins can change the activity of a cell. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: A. Energy and Living Things 1. Analyze the flow of energy through living systems. 2. Compare the metabolism of autotrophs with that of heterotrophs. 6. Group Project 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 3 play in metabolism? Where does photosynthesis take place in plants? B. Photosynthesis What three environmental factors can affect the rate of photosynthesis? C. Cellular Respiration October/ March What is the basic building block of DNA? What three components make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the role of ATP in metabolism. 4. Describe how energy is released from ATP. 5. Summarize how energy is captured from sunlight in the first stage of photosynthesis. 6. Analyze the function of electron transport chains in the second stage of photosynthesis. 7. Relate the Calvin cycle to carbon dioxide fixation in the third stage of photosynthesis. 8. Identify three environmental factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis. 9. Summarize how glucose is broken down in the first stage of cellular respiration. 10. Describe how ATP is made in the second stage of cellular respiration. 11. Identify the role of fermentation in the second stage of cellular respiration. 12. Evaluate the importance of oxygen in aerobic respiration. DNA: The Genetic Material: A. Identifying the Genetic Material How does DNA replicate? B. The Structure of DNA C. The Replication of DNA 1. Relate Griffith’s conclusions to the observations he made during the transformation experiments. 2. Summarize the steps involved in Avery’s transformation experiments, and state the results. 3. Evaluate the results of the Hershey and Chase experiment. 4. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. 5. Develop a model of the structure of a DNA molecule. 6. Evaluate the contributions of Chargaff, Franklin, and Wilkins in helping Watson and Crick determine the double-helical structure of DNA. 7. Relate the role of the base-pairing rules to the structure of DNA. 8. Summarize the process of DNA replication. 9. Describe how errors are corrected during DNA replication. 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 4 10. Compare the number of replication forks in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. October/ March What is the difference between a gene, a DNA molecule, a chromosome, and a chromatid? Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction: A. Chromosomes How do haploid and diploid cells differ? What are the five phases of the cell cycle? What are the four stages of mitosis? B. The Cell Cycle C. Mitosis and Cytokinesis November/ April What are the stages of meiosis? What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? Principles of Genetics 1. Identify four examples of cell division in eukaryotes and one example in prokaryotes. 2. Differentiate between a gene, a DNA molecule, a chromosome, and a chromatid. 3. Differentiate between homologous chromosomes, autosomes, and sex chromosomes. 4. Compare haploid and diploid cells. 5. Predict how changes in chromosome number of structure can affect development. 6. Identify the major events that characterize each of the five phases of the cell cycle. 7. Describe how the cell cycle is controlled in eukaryotic cells. 8. Relate the role of the cell cycle to the onset of cancer. 9. Describe the structure and function of the spindle during mitosis. 10. Summarize the events of the four stages of mitosis. 11. Differentiate cytokinesis in animal and plant cells. Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction: A. Meiosis B. Sexual Reproduction 1. Summarize the events that occur during meiosis. 2. Relate crossing-over, independent assortment, and random fertilization to genetic variation. 3. Compare spermatogenesis and oogenesis. 4. Differentiate between asexual and sexual reproduction. 5. Identify three types of asexual reproduction. 6. Evaluate the relative genetic and 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 5 evolutionary advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproduction. 7. Differentiate between the three major sexual life cycles found in eukaryotes. November/ April Who is the father of heredity? Why is a garden pea a good subject for genetic study? What is the difference between a Punnett square and a test cross? Mendel and Heredity: A. The Origins of Genetics B. Mendel’s Theory What five factors influence patterns of heredity? C. Studying Heredity Why do mutations cause genetic disorders? What are some examples of genetic disorders? November/ April D. Complex Patterns of Heredity 1. Identify the investigator whose studies formed the basis of modern genetics. 2. List characteristics that make the garden pea a good subject for genetic study. 3. Summarize the three major steps of Gregor Mendel’s garden pea experiment. 4. Relate the ratios that Mendel observed in his crosses to his data. 5. Describe the four major hypotheses Mendel developed. 6. Define the terms homozygous, heterozygous, genotype, and phenotype. 7. Compare Mendel’s two laws of heredity. 8. Predict the results of monohybrid genetic crosses by using Punnett squares. 9. Apply a test cross to determine the genotype of an organism with a dominant phenotype. 10. Predict the results of monohybrid genetic crosses by using probabilities. 11. Analyze a simple pedigree. 12. Identify five factors that influence patterns of heredity. 13. Describe how mutations can cause genetic disorders. 14. List two genetic disorders, and describe their causes and symptoms. 15. Evaluate the benefits of genetic counseling. How Proteins Are Made: A. From Genes to Proteins 1. Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA. 2. Summarize the process of transcription. 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 6. Power Point Presentation 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 6 B. Gene Regulation and Structure November/ April What observations led Darwin to conclude that species evolve? What is natural selection? The Theory of Evolution: A. The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection B. Evidence of Evolution C. Examples of Evolution December/ May Who is Carl Linnaeus? What are the seven 3. Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that results after translation. 4. Outline the major steps of translation. 5. Discuss the evolutionary significance of the genetic code. 6. Describe how the lac operon is turned on or off. 7. Summarize the role of transcription factors in regulating eukaryotic gene expression. 8. Describe how eukaryotic genes are organized. 9. Evaluate three ways that point mutations can alter genetic material. Classification of Organisms: 1. Identify several observations that led Darwin to conclude that species evolve. 2. Relate the process of natural selection to its outcome. 3. Summarize the main points of Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection as it is stated today. 4. Contrast the gradualism and punctuated equilibrium models of evolution. 5. Describe how the fossil record supports evolution. 6. Summarize how biological molecules such as proteins and DNA are used as evidence of evolution. 7. Infer how comparing the anatomy and development of living species provided evidence of evolution. 8. Identify four elements in the process of natural selection. 9. Describe how natural selection has affected the bacteria that cause tuberculosis. 10. Relate natural selection to the beak size of finches. 11. Summarize the process of species formation. 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 7 levels of biological classification? A. Categories of Biological Classification What characteristics do biologist use to classify organisms? B. How Biologists Classify Organisms December/ May What features do animals have in common? What are the different body systems? Exploring Invertebrates 1. Describe Linnaeus’s role in developing the modern system of naming organisms. 2. Summarize the scientific system for naming a species. 3. List the seven levels of biological classification. 4. List the characteristics that biologists use to classify organisms. 5. Summarize the biological species concept. 6. Relate analogous structures to convergent evolution. 7. Describe how biologists use cladograms to determine evolutionary histories. Introduction to Animals: A. Characteristics of Animals B. Animal Body Systems 1. Identify the features that animals have in common. 2. Distinguish radial symmetry from bilateral symmetry. 3. Summarize the importance of a body cavity. 4. Identify how scientists determine evolutionary relationships among animals. 5. Summarize the functions of the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nervous, skeletal, and excretory systems. 6. Compare a gastrovascular cavity with a one-way digestive system. 7. Differentiate open from closed circulatory systems. 8. Distinguish asexual from sexual reproduction. 4. Lab 5. Exam 1. Class discussion 2. Daily work 3. Quiz 4. Lab 5. Exam 6. Power Point Presentations 8