* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conservation*s Challenges: Global Problems
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
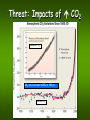
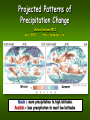
Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Warren G. Abrahamson Biology Department Bucknell University Threat: Impacts of CO2 Atmospheric CO2 CO2 has increased ≈25% in 100 yrs. Ice Core CO2 Global Mean Temperatures: Rising Faster with Time United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2007 Period Rate 50 0.13 0.03 100 0.07 0.02 Years C/decade Projected Patterns of Precipitation Change United Nations IPCC April 2007 http://www.ipcc.ch/ Winter Summer Bluish = more precipitation to high latitudes Reddish = less precipitation to most low latitudes Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines 3. More frequent & severe disturbances 4. Species shifts 5. Increases of invasive species 6. Impacts to agriculture/forestry Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: Causing a mismatch between Peak of food availability & 1. Phenology changes food needs for nestlings (Earlier spring activity) Birds nesting & laying eggs earlier Trees leafing out earlier Earlier flowering of plants (Bertinet (Ahola 2008; al. 2008; Thompson Tombre andetClark al. 2008; 2008; Menzel et al. 2006) Husek and Adamik 2008; Both et al. 2006) Both et al. 2006 Global Climate Change: Morris Arthur Phillip Dustan Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines Alexander Bogolyubov Effects on Biodiversity Adelie penguin populations declined by 1/3 over past 25 years (Antarctic sea ice habitat declining) Coral reefs declining (rising seawater temperatures) Cool-climate communities (e.g., spruce-fir aspen-birch) (Emmerson and Southwell 2008; (Baker et al. 2008; Wilson et al. 2008) predicted to decline >90% in USA Hinke et al. 2007) Decline of Carysfort Reef (Florida) (Botkin et al. 2007; Gullison et al. 2007) Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Enyalioides palpebralis Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines Tropical ecotherms narrower tolerance & live closer to physiological optima than high-latitude species Consequently, more vulnerable to climate thermal change (Tewksberry et al. 2008. Putting the heat on tropical animals. Science 320: 1297-1297) Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines 3. More frequent & severe disturbances Lake Michigan Ludington Lighthouse Nov 2008 Sea level rise & enhanced storms Alter 25-80% of USA coastal wetlands Catastrophic impacts on low-lying countries (e.g., Bangladesh) Increased incidence of fire in xeric communities Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines 3. More frequent & severe disturbances 4. Species shifts Shifts in Species Distributions due to Climate Change Netherlands Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency 2003 Comma Butterfly Eurosta solidaginis “gigantea” race gall Shifts in Species Some Need It Cold Distributions due to Shift in Species Range Climate Change Southern-most population moved 130 miles north Gall-inducing fly Eurosta solidaginis 2003 Southern-most population of “gigantea” host race of Eurosta solidaginis X ● 1999 W.G. Abrahamson, unpublished data 12 Shifts in Species Pygmy Skunk Distributions due to Distribution Shifts Climate Change with Climate Change A Reserve to Protect Pygmy Skunk in 2000 Inadequate by 2050 Hannah et al. 2007 Shifts in Community A Reserve to Protect Glacier National Park Species in 1910 Distributions due to Est. 1910 Inadequate before 2100 Climate Change Climate change will cause shifts in species distributions & will impact ecological reserves Shifts in Distributions Temperate-zone climate regions will shift toward the poles: >10% of species unable to survive warmer climates Extinction if they can’t migrate to new localities Habitat fragmentation will slow or prevent migration “Island” constrained species have nowhere to go – They face extirpation or extinction Miller-Rushing and Primack 2004, Malcolm et al. 2006, Sekercioglu et al. 2008 Shifts in Distributions Temperate-zone climate regions will shift toward the poles: Dries Buytaert Most impacted: Limited-distribution, poor-dispersal species Advantage to: Widely distributed, easily dispersed species Miller-Rushing and Primack 2004, Malcolm et al. 2006, Sekercioglu et al. 2008 Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines 3. More frequent & severe disturbances 4. Species shifts 5. Increases of invasive species Invasive Species Warmer conditions & elevated CO2 levels may favor invasive species & outbreaks of pest species ♀ ovipositing Asian-origin Japanese European/Asian-origin Hemlock Woolly Gypsy Honeysuckle Adelgid Moth Global Climate Change: Effects on Biodiversity Organisms and/or biological communities are experiencing: 1. Phenology changes 2. Population declines 3. More frequent & severe disturbances 4. Species shifts 5. Increases of invasive species 6. Impacts to agriculture/forestry Climate Change Could Devastate Crops Examples: By 2030: Southern Africa could lose >30% of its main crop, maize Southern Asia could lose >10% of regional staples, including rice, millet & maize Crop Importance Production Impact (%) Red = More important Orange = Important Yellow = Less important Production Impact (%) Lobell et al. 2008. Prioritizing climate change adaptation needs for food security in 2030. Science 319: 607-610. Pennsylvania: Ag/Forestry Possible Impacts Union of Concerned Scientists, Oct 2008 Faced with Huge Challenges: To save biodiversity, need global action Edward Abbey wrote… “…love of the wilderness is more than a hunger for what is always beyond reach; it is also an expression of loyalty to the earth which bore us and sustains us, the only home we shall ever know, the only paradise we ever need – if only we had the from Desert Solitaire 1968` eyes to see.”