* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Conducting System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
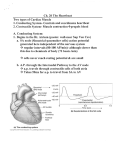
Cardiac Conducting System Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own No neural nor hormonal control “autorhythmicity’ Specialized cells: initiate and distribute depolarization 1. Sinoatrial node (SA node) a. Near entrance of superior vena cava/posterior wall of R. atrium b. “pacemaker cells” establish heart rate c. Connected to AV node via conducting pathways d. Stimulus affects only ATRIA i. Fibrous skeletal separates atria from ventricle 2. AV node: a. Floor of right atrium b. Near opening of coronary sinus c. From AV to bundle of His(bundle branches) which run along interventricular septum d. Delay at AV node allows atria to complete contraction before ventricular contraction begins 3. AV bundle(bundle of His) a. Impulse reaches AV bundle- travels along septum, splits between L & R bundle branches b. Purkinje fibers – where the bundle of His diverge into smaller branches i. Cause ventricular contraction ii. Wave action from apex(bottom) to base(top) iii. Blood is pushed out aortic and pulmonary trunk ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Monitors electrical activity of heart 1. P wave: small, atria contract after start of P wave – depolarization of atria 2. QRS complex: ventricles depolarize – STRONG electrical signal – ventricles contract AFTER peak at R 3. T wave – ventricles relax 4. Do not “see” atrial relaxation due to strong QRS Problems detected: Extension of P-R interval = damage to conducting pathways or damage to AV node Extension of Q-T interval = myocardial damage HEART ATTACK – myocardial infarction Infarct = nonfunctional area of myocardium Enzymes that detect MI= LDH; SGOT; CPK(creatine phosphokinase) Systole – contraction Diastole – relaxation On patient with stethoscope Patients upper area right of sternum – hear pulmonary semilunar valve Lower right of sternum – hear right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid) Upper right of sternum – hear aortic semilunar valve Lower right of sternum – left atrial ventricular valve – bicuspid