* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Conductivity System of the Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
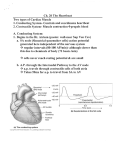
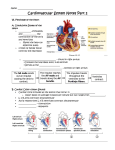
Dr.Sisara Bandara Gunaherath MBBS The heart is the pump responsible for maintaining adequate circulation of oxygenated blood around the vascular network of the body. It is a four-chamber pump, with the right side receiving deoxygenated blood from the body at low pressure and pumping it to the lungs (the pulmonary circulation) and the left side receiving oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumping it at high pressure around the body (the systemic circulation). The S-A Node is the most important element in the electrical circuit of the heart. It starts the cardiac cycle by periodically generating action potentials without any external stimulation. (Therefore, it is said to be autorhythmic.) It is also known as the pacemaker of the heart. In the right atrium Near the opening of the superior vena cava Action potentials that originate in the SA node spread to adjacent myocardial cells of the right and left atria through the gap junctions between these cells Since myocardium of the atria is separated from the myocardium of the ventricles by fibrous skeleton of the heart , however the impulse cannot be conducted directly from atria to the ventricles Therefore specialized conducting tissue ( modified myocardial cells) need for electrical conduction of the heart These specialized myocardial cells form the AV node, Bundle of His ( Atrioventricular bundle) and Purkinje fibers Once the impulse has spread through atria , it passes to the AV node, which located on the inferior portion of the interatrial septum; from there impulse continues through the bundle of His , beginning at the top of the interventricular septum The bundle of His divides in to right and left bundle branches , which are continuous with the Purkinje fibers with in the ventricular walls Stimulation of Purkinje fibers causes both ventricles to contract simultaneously and eject blood into the pulmonary and systemic circulation. The most important function of the A-V node is to regulate the timing of the ventricular contraction by delaying the action potentials. The delayed action potentials are spread over the ventricles to cause a contraction. 1.The S-A Node generates an action potential. 2. The action potential propagates in the atria and causes a contraction. It is also transmitted to the AV Node. 3.The action potential is delayed at the A-V Node. 4.The action potential is transmitted to the ventricles and causes a contraction. The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a standardized way to measure and display the electrical activity of the heart. The P Wave: Depolarization of the atria The QRS Complex: Depolarization of the ventricles The T Wave: Repolarization of the ventricles From one P Wave to the next P wave duration equals to a cardiac cycle