* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Physiology - Riverside Preparatory High School
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
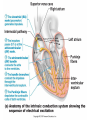
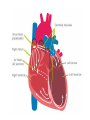
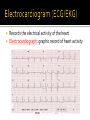
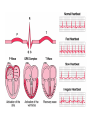
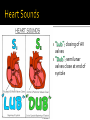
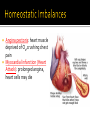
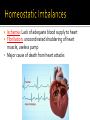
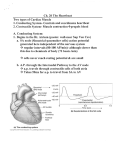
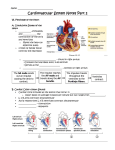
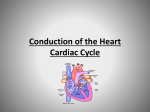
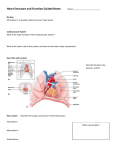
Draw the human heart and the main blood vessels in/out of the heart. Label the following on your diagram: 4 chambers 4 valves All blood vessels going into/out of heart Using a blue pencil, indicate oxygen-poor blood flow Using a red pencil, indicate oxygen-rich blood flow Cardiac muscle cells can contract spontaneously and independently Regulation of heart activity: 1. Autonomic nervous system ▪ Epinephrine, thyroxine: heart rate ▪ Low Ca2+ levels: heart rate 2. Intrinsic conduction system ▪ Built into heart tissue & sets basic rhythm ▪ Pacemaker = Sinoatrial (SA) Node Sequence of action: 1. Sinoatrial (SA) node – right atrium ▪ Generates impulses Starts each heartbeat 2. Atrioventricular (AV) node – between atria & ventricles ▪ Atria contract 3. Bundle of His (or AV bundle) 4. Bundle branches – interventricular septum 5. Purkinje fibers – spread within ventricle walls ▪ Ventricles contract Records the electrical activity of the heart Electrocardiograph: graphic record of heart activity P wave: atria contract QRS complex: ventricles contract T wave: ventricles relax Cardiac cycle = events of one heartbeat Systole: contraction of ventricles Diastole: relaxation of ventricles Cardiac Output Animation “Lub”: closing of AV valves “Dub”: semilunar valves close at end of systole Angina pectoris: heart muscle deprived of O2,crushing chest pain Myocardial infarction (Heart Attack): prolonged angina, heart cells may die Ischemia: Lack of adequate blood supply to heart Fibrillation: uncoordinated shuddering of heart muscle, useless pump Major cause of death from heart attacks Damage to SA node slower heart rate Install artificial pacemaker Damage to AV node Heart block: ventricles beat at own rate (slower or not at all) Tachycardia: rapid heart rate (>100 beats/min) Bradycardia: very slow heart rate (<60 beats/min) Heart murmur: abnormal or unusual heart sounds Often valve problems Cardiac Output (CO) = Heart Rate (HR) x Stroke Volume (SV) Stroke volume: volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each best Average adult: CO = HR (75 beats/min) x SV (70 ml/beat) CO = 5250 ml/min Progressive weakening of heart Low heart efficiency circulation inadequate to meet tissue needs Caused by: Coronary atherosclerosis – clogged coronary vessels Persistent high blood pressure Multiple heart attacks – scar tissue