* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
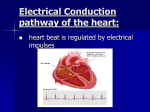
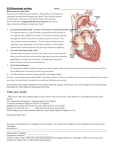
Electrical Activity of the Heart Chloe, Chanel, Raj Conducting System AV node Sa node Purkinje fibers Bundle of his SA node Sinoatrial node Specialized group of cardiac muscle cells that don’t contract located in the right atrium of the heart Adapted to automatically generate impulses generator of heart rhythm Basically the pace maker Function It triggers the electrical impulses that are carried around to other heart cells The electrical impulses cause the atria to contract at a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute Signals atria to contract, passes the blood to bottom Causes contraction AV node Atrioventricular node electrically connects atrial and ventricular chambers specialized tissue between the atria and the ventricles of the heart Also automatically generates impulses- cause contraction Functions begins when it gets an electrical impulse from the SA node The rhythm of the heart contractions is set by the AV node. It delays the impulse by about 0.12 seconds. This is delay is very important as it helps the atria eject the blood in them into the ventricles before the contraction of the ventricles. The delay also helps in protecting the ventricles from atrial arrhythmia (type of arrhythmia). Sends the signal it receives to the fibers below, opens the semilunar, blood is forced out http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0xUifyll2Oc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lIQXzgesdDg Purkinje fibers located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium. consist of specialized cardiomyocytes that are able to conduct cardiac action. allow the heart's conduction system to create synchronized contractions of its ventricles, and are therefore essential for maintaining a consistent heart rhythm. Bundle of his collection of heart muscle cells, known as cardiomyocytes, specialized for electrical conduction that transmits electrical impulses. The fascicular branches then lead to the Purkinje fibers which provide electrical conduction to the ventricles, causing the cardiac muscle of the ventricles to contract at a paced interval. Basically directs orders to branches that allow a Heart to contract. These branches that the His bundle directs, are the Purkinje fibers. EKG- What is it? Electrocardiogram Checks for problems with the electrical activity of your heart Natural electrical system causes the heart muscle to contract and pump blood Translates electric activity in heart into line tracings on paper Spikes and dips in line tracings called waves Why Is it done? Find cause of unexplained chest pain Find cause of symptoms of heart disease Check thickness of heart chambers (hypertrophied) Check effectiveness of medicines Check overall health of heart How it’s done EKG paste placed between the electrodes and your skin to help conduction of electrical impulses Several electrodes are attached to the skin and hooked to machine Machine traces heart activity on paper Works Cited http://www.beltina.org/health-dictionary/atrioventricular-avnode.html http://biology.about.com/library/organs/heart/blatrionode.htm http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-purkinje-fibers.htm http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Purkinje+fiber http://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/electrocardiogram http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/ekg/ http://www.beltina.org/pics/atrioventricular__av__node.gif