* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Co-ordination of the Cardiac Cycle
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
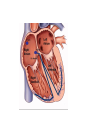
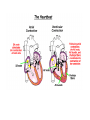
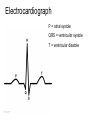
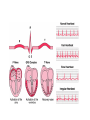
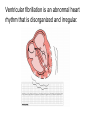
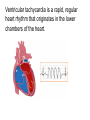
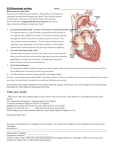
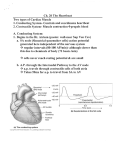
05 May 2017 Co-ordination of the Cardiac Cycle Aims •Describe how heart action is coordinated with reference to the sinoatrial node (SAN), the atrioventricular node (AVN) and the Purkyne tissue •Be able to interpret and explain electrocardiogram (ECG) traces, with reference to normal and abnormal heart activity • The heart is made of cardiac muscle. • When the cells receive an electrical impulse they contract - causing a heartbeat. • Cardiac muscle is myogenic - it can contract on its own, without needing nerve impulses. Sinoatrial node (SA node) • This specialized node is found on the upper inside wall of the right atrium. • The SA node is known as the pacemaker of the heart and initiates a heartbeat every 0.85 seconds. • This signal travels across the atria causing them to contract and load the ventricles with blood. • Ventricles are electrically insulated from atria so they don’t contract yet. Atrio-ventricular node (AV node) • The AV node is located on the bottom surface of the right atria and is responsible for initiating the contraction of the ventricles. • Electrical impulse passes to ventricles via AV node and the Bundle of His. They pass the impulse to the base of the ventricles (~ 0.1 s delay). • The bundle of His is a group of fibres that conduct impulses to Purkyne fibres which carry impulses to left & right ventricles. • Ventricles then contract from the bottom upwards. No impulse • Cardiac muscle relaxes = diastole Electrocardiograph P = atrial systole QRS = ventricular systole T = ventricular diastole • Records electrical activity of heart to monitor heart function. • Pacemaker generates electrical currents in body fluids around the heart - detected by electrodes to produce ECG • Heart muscle: depolarises (loses electrical charge) when it contracts repolarises (regains charge) when it relaxes Ventricular fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm that is disorganized and irregular. Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid, regular heart rhythm that originates in the lower chambers of the heart. Heart block refers to a delay in the normal flow of electrical impulses that cause the heart to beat. This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.