* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Specialization - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
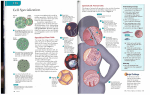
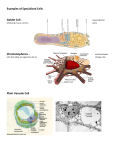
1.15 Cell Specialization thin cell wall middle lamellae a Thin-walled plant cells are found in the flexible tissues of the leaf, flower, fruit, and root. Most edible plant roots, such as potatoes and radishes, ar e composed of these cells. thicker cell wall b Thick-walled plant cells are specialized for support. Their stretchable cell walls are flexible. The tough strings of the celery stalk are made of these cells. thickest cell wall c Very thick cell walls provide rigid support. The cell wall can get so thick, as the plant matures, that it becomes difficult for nutrients to enter the cell. The cell usually dies, leaving an empty chamber surrounded by a thick wall. Fabrics such as linen are made from these cells. Figure 1 Plants, like animals, are made of tissues and organs. Each kind of tissue contains a special type of cell. 48 Unit 1 Imagine how difficult life would be without specialists. Could you build your own television? Grow your own food? Do your own surgery? Unicellular organisms are not specialists. Each cell must carry out all the functions of life. Multicellular organisms, such as you, benefit from cell specialization. We have cells that come in a variety of sizes and shapes, each designed to car ry out a special function. Specialized Plant Cells Nerve cells tend to be long and thin. Many nerve cells are protected by a coating of insulation that prevents short circuits. 1 3 Blood tissue The long, thin strings inside a celery stalk, the pit in an apricot, the thin leaves of the lettuce are all evidence that there is a variety of different types of plant cells (Figure 1). The cell wall is one very noticeable feature of plant cells. As plants develop, a primary cell wall is formed around each cell. Once the plant stops growing, an additional secondary cell wall may form inside the primary cell wall. This structure provides added strength. The spaces between plant cells, referred to as the middle lamellae, contain a sticky, sugary substance called pectin. Pectin acts like cement, sticking plant cells together. The sticky syrup that often forms on the top of a baked apple pie is pectin. 5 Fat tissue 1 Nerve tissue 5 In fat cells, most of the cytoplasm is occupied by a vacuole that stores fat molecules. a Red blood cells carry oxygen in a special protein called hemoglobin. The cells are filled with this protein. b White blood cells protect the body from invaders by engulfing them and digesting them, or by killing them with antibodies. 3 a b Specialized Animal Cells Understanding Concepts The shape of animal cells provides a clue to their function. Many of the features of unicellular organisms can be found in animal cells as you can see in Figure 2. Figure 2 Some specialized cells found in human bodies. 2 The respiratory system 2 a a Particles that attempt to enter your lungs are trapped in mucous and then swept away from the lungs by cells with cilia. b Cells of the lung are very thin. This allows gases to exchange rapidly between the air and the blood. 1. What are the advantages of cell specialization for an organism? 2. Predict what might happen to multicellular plants if a microorganism that digests pectin was accidentally released from a laboratory. 3. What is the advantage of a highly folded cell membrane? 4. What advantage does a thick, flexible plant cell wall provide over a thick, rigid cell wall? 5. Examine the cell shape in Figure 3: Figure 3 4 The stomach Your stomach contains a powerful acid. Cells of the lining of the stomach ar e protected from the acid by a layer of mucous. These cells also have many Golgi apparatuses to store the proteins that break down food. b 4 Three cell shapes (a) Which cell would be best suited as an egg cell? Give your reasons. (b) Which cell would be best suited for movement? Give your reasons. (c) Which cell would be best suited as a covering for an organ? Give your reasons. 6. Identify body cells that have a structure similar to that of a unicellular organism. Reflecting 7. Why are specialized cells dependent on other specialized cells? 6 6 The small intestine Cells that line the small intestine absorb food. Fingerlike projections increase the surface area for absorption. Is the structure of the cell that you are building suited for its special function? What changes should you make in your design now that you know more about specialized cells? Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems 49