* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membrane Transport
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
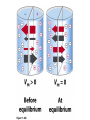
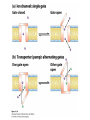
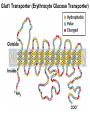
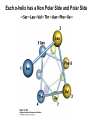
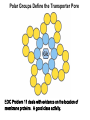
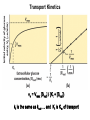
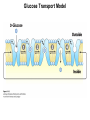
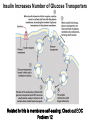
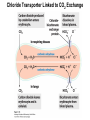
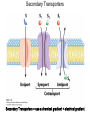
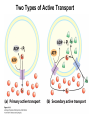
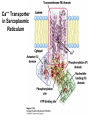
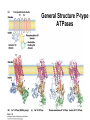
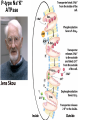
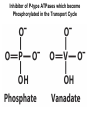
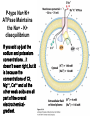
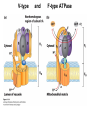
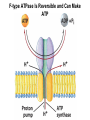
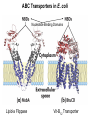
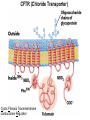
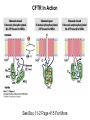
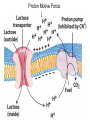
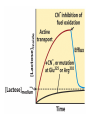
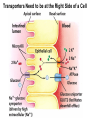
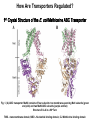
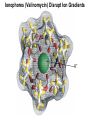
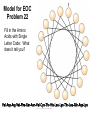
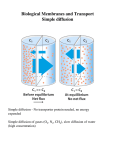
Chapter 11 Membranes: Transport Part 2 Learning Goals To KNOW: - mechanisms of molecular transport in and out of cells. - transport kinetics (really easy after Chapter 6!) - specific transporters: Ca++ transporter, Na+/K+ transporter, glucose transport in gut epithelial cells, P,V and F-type ATPases, lactose transport in bacteria - aquaporins Membrane Transport Energetics of Diffusion Transport EOC Problem 15 is all about tryptophan and indole permeability, review their structure (Chapter 3) or you already know it !! Glut1 Transporter (Erythrocyte Glucose Transporter) Each α-helix has a Non Polar Side and Polar Side Polar Groups Define the Transporter Pore EOC Problem 11 deals with evidence on the location of membrane proteins. A good class activity. Transport Kinetics vo = Vmax [Sout] / (Kt + [Sout]) kt is the same as kcat…. and Kt is Km of transport Glucose Transport Model Tissues where Expressed Kt (mM) Role Insulin Increases Number of Glucose Transporters Related to this is membrane self-sealing: Check out EOC Problem 12 Chloride Transporter Linked to CO2 Exchange Secondary Transporters Secondary Transporters = use a chemical gradient + electrical gradient. Two Types of Active Transport S1 is usually H+ or Na+ Therefore Outside Cell Membrane (Na+) or Mitochondria Membrane (H+) there is: high concentration of S1 and lower in the cytoplasm or mitochondrial matrix. On the outside: higher chemical conc. + electrical charge …….these are 2 energetic components. This is called either the Proton Motive Force Sodium Motive Force or EOC Problem 10: Energetics of symports. Ca++ Transporter in Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca++ Transporter works like a little motor General Structure P-type ATPases P-type Na+K+ ATPase Inhibitor of P-type ATPases which become Phosphorylated in the Transport Cycle P-type Na+/K+ ATPase Maintains the Na+ - K+ disequilibrium If you add up just the sodium and potassium concentrations…it doesn’t seem right, but it is because the concentrations of Cl-, Mg++, Ca++ and all the other weak acids are all part of the overall electrochemicalgradient. Ouabain Binds to the Open - Outside form of Na+K+ ATPase..and hold it there. Arrow Poison V-type and F-type ATPase F-type ATPase Is Reversible and Can Make ATP ABC Transporters in E. coli Nucleotide Binding Domains Lipid-a Flippase Vit-B12 Transporter CFTR (Chloride Transporter) Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator Cystic Fibrosis Patients Can’t Clear Bacteria in Bronchia-Trachea Cystic Fibrosis – Research at FIU in Dr. Kalai Mathee’s Lab CFTR In Action See Box 11-2 Page 415 For More Proton Motive Force Lactose Transporter in Two Forms 12 Transmembrane Helices Arg and Glu in Green, Lactose in Red Transporters Need to be at the Right Side of a Cell How Are Transporters Regulated? 1st Crystal Structure of the E. coli Methionine ABC Transporter Fig. 1. (A) ABC transporter MetNI consists of four subunits: two membrane-spanning MetI subunits (green and pink) and two MetN ABC subunits (purple and tan) Structure B is A in a 90o Turn TMD – transmembrane domain, NBD – Nucleotide binding domain, C-2 Methionine binding domain C-2 Domain of Met-Transporter Methoinine – gold structures. When bound, Met inhibits the NDB as an ATPase, Ki ~ 30 µM Ref: Kadaba, Kaiser, Johnson, Lee and Rees. 2008. The high affinity E. coli methionine ABC transporter: structure and allosteric regulation. SCIENCE 231:250-253 Ionophores (Valinomycin) Disrupt Ion Gradients K+ Discovered Aquaporins (AQP) – Water Transport Aquaporins EOC Problem 16 is a classic aquaporin water flow kinetics problem. Things to Know 1. Membrane transport kinetics: KT and kt 2. Amino acids in transmembrane domain of transporters. 3. Primary and Secondary Transporters. 4. Transporters as motors. 5. PMF. 6. Cell location of transporters: intestinal cell model. 7. Transporter regulation 8. Aquaporins 9. EOC Problems : 10-13, 15, 16, 22 . Model for EOC Problem 22 Fill in the Amino Acids with Single Letter Code: What does it tell you? Val-Asp-Arg-Val-Phe-Ser-Asn-Val-Cys-Thr-His-Leu-Lys-Thr-Leu-Gln-Asp-Lys