* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac_Cycle
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
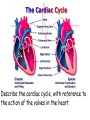
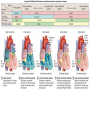
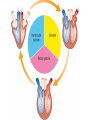
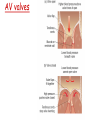
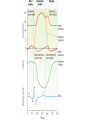
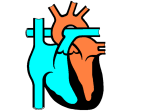
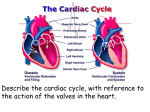
Describe the cardiac cycle, with reference to the action of the valves in the heart. • The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in one heartbeat. • It has three phases. Diastole • The atria and ventricles relax and blood flows into the heart from the veins. • Blood flows into the atria, through the AV valves and into the ventricles. – Atrial diastole - atria relax (0.7s) – Ventricular diastole - ventricles relax (0.5s) Atrial systole • Both atria contract pushing blood into the ventricles (0.1s). • Once the ventricles are full they start to contract and the AV valves shut. Ventricular Systole • All 4 valves are closed for short time. • Walls of ventricles contract (starting from apex), increasing pressure and forcing blood out of the heart, opening the semilunar valves. (0.3s). Cardiac Cycle Animation AV valves Semilunar valves Heart sounds • Sound is made by the valves closing. • First sound = lub – made by AV valve closing as ventricles start to contract. • Second sound = dub – semilunar valves closing as ventricles start to relax. Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output • Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one cardiac cycle. • Typically about 80cm3. • Stroke volume increases during exercise. • Cardiac Output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped in one minute. CO = stroke volume x heart rate. • expressed in litres of blood per minute. Factors Affecting Heart Rate • • • • Adrenaline. Movement of limbs (stretch receptors) Levels of respiratory gases in the blood Blood pressure – if it gets too high a safety mechanism prevents heart rate increasing further.