* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3_Cardiac_Cycle
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
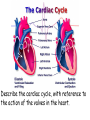
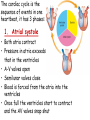
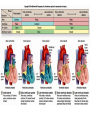
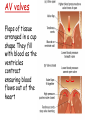
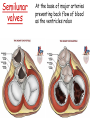
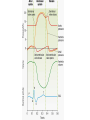
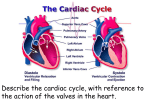
Describe the cardiac cycle, with reference to the action of the valves in the heart. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events in one heartbeat, it has 3 phases: 1. Atrial systole • Both atria contract • Pressure in atria exceeds that in the ventricles • A-V valves open • Semilunar valves close • Blood is forced from the atria into the ventricles • Once full the ventricles start to contract and the AV valves snap shut 2. Ventricular Systole • • • • Atria relax Ventricles contract (starting from apex) A-V valves and semilunar valves closed Pressure increases forcing blood out of the heart by opening the semilunar valves 3. Diastole • • • • • Atria and ventricles relax Elastic recoil returns ventricles to original size A-V and semilunar valves are closed Blood flows passively into the atria from the veins. The A-V valves open and blood starts to enter the ventricles Cardiac Cycle Animation AV valves Flaps of tissue arranged in a cup shape They fill with blood as the ventricles contract ensuring blood flows out of the heart Semilunar valves At the base of major arteries preventing back flow of blood as the ventricles relax Heart sounds • Sound is made by the valves closing. • First sound = lub – made by AV valve closing as ventricles start to contract. • Second sound = dub – semilunar valves closing as ventricles start to relax. Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output • Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one cardiac cycle. • Typically about 80cm3. • Stroke volume increases during exercise. • Cardiac Output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped in one minute. CO = stroke volume x heart rate. • expressed in litres of blood per minute. Factors Affecting Heart Rate • • • • Adrenaline. Movement of limbs (stretch receptors) Levels of respiratory gases in the blood Blood pressure – if it gets too high a safety mechanism prevents heart rate increasing further. Electrocardiograms (ECG) • Place electrodes on the skin over opposite sides of the heart and record the electrical potentials generated P is the wave of excitation sweeping over the atrial walls T is the recovery of the ventricle walls QRS complex is the wave of excitation speading through the ventricular walls