* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
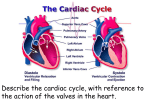
Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Cardiac Cycle • Cardiac Cycle: the events of one complete heart beat, both atria and ventricles contract and then relax • Systole: When the heart is contracting • Diastole: When the heart is relaxing • Since most of the pumping work is done by the ventricles, these terms always refer to the ventricles Cardiac Cycle • We will consider the cardiac cycle in terms of events during 3 period: mid-late diastole, ventricular systole, early diastole Mid-late diastole • At the beginning, the pressure in the heart is low • Blood is flowing passively into and through the atria into the ventricles from the pulmonary and systemic circulation • The semilunar valves are closed and the AV valves are open • Then the atria contract and force the blood remaining in their chambers into the ventricles Ventricular Systole • Ventricular contraction begins and the pressure within the ventricles increases rapidly, closing the AV valves • The semilunar valves are forced open and blood rushes through them out of the ventricles • The atria are relaxed and their chambers are again filling with blood Early Diastole • At the end of systole, the ventricle relax, the semilunar valves snap shut (preventing backflow) and for a moment, the ventricles are completely closed chambers • During early diastole, the AV valves are forced open and the ventricles again, begin to refill rapidly with blood, completing the cycle Heart sounds • The heart sounds are often described by the two syllables “lub” and “ dup” • The first sound “lub” is caused by the closing of the AV valves • The second heart sound “dup” occurs when the semilunar valves close at the end of systole Cardiac Output (CO) • It is the amount of blood pumped out by each side of the heart (actually each ventricle) in 1 minute • It is the product of heart rate (HR) and Stroke volume (SV): CO = HR X SV • Stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped out by a ventricle with each heartbeat: - In general, stroke volume increase as the force of ventricular contraction increase Regulation of Stroke Volume • A healthy heart pumps out about 60% of the blood that enters it • The critical factor controlling stroke volume is how much the cardiac muscle cells are stretched just before they contract: the more they are stretched, the stronger the contraction will be • The important factor stretching the heart muscle is venous return, the amount of blood entering the heart and swell out its ventricles • Anything that increase the volume or speed of venous return also increase stroke volume and force of contraction Regulation of Heart Rate • Although heart contraction does not depend on the nervous system, its rate can be changed temporarily by the autonomic nerves - Sympathetic nervous system: speeds up heart rate - Parasympathetic nervous system: slows down heart rate Regulation of Heart Rate • The heart rate is also modified by various chemicals, hormones and ions - Epinephrine/ thyroxine: increases heart rate - Deficit Potassium ions: cause the heart to beat without strength and abnormal heart rhythms • The average heart rate in female is 72-80 beats per min • The average heart rate in male is 64-72 beats per min