* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Transformation — Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
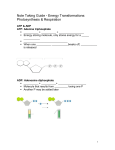
Energy Transformation — Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration by CHED on June 15, 2017 lesson duration of 6 minutes under General Biology 1 generated on June 15, 2017 at 09:06 am Tags: Energy , Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Generated: Jun 15,2017 05:06 PM Energy Transformation — Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration ( 4 hours and 6 mins ) Written By: CHED on July 11, 2016 Subjects: General Biology 1 Tags: Energy , Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration Resources Biology 8th Edition Solomon, Eldra P. et al., al., (2008). Biology 8th Edition. China: Thomson Brooks/Cole. Inquiry into Life 11th Edition Mader, Sylvia S. (2016). Inquiry into Life 11th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill. Biology 10th Edition Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill. Science and Technology 9 Alumaga, Maria Jessica B. et al., (2014). Science and Technology 9. Quezon City: Vibal Publishing House. Biology Corner https://www.biologycorner.com// Content Standard The learners demonstrate an understanding of: 1. ATP- ADP Cycle 2. Photosynthesis 3. Respiration Performance Standard Prepare simple fermentation setup using common fruits to produce wine or vinegar via microorganisms Learning Competencies 1 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community The learners explain the advantages and disadvantages of fermentation and aerobic respiration Introduction/Review 5 mins Review with the class that oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction that involves electrons passing from one molecule to another. Oxidation (also splitting) is the loss of electrons while reduction is the gain of electrons. You can show this picture to your students and try to ask questions so that you can generate critical thinking skills from them. To help them visualize the concept, a diagram of redox reaction is also shown below. Ask your students which organisms (in the picture below) photosynthesize and which respire (take note that plants both photosynthesize and respire at the same time). Then show the equation of redox reaction after your students have given their responses. You may also ask examples of oxidation reaction (e.g. (e.g.,, browning of peeled potato, banana, and eggplant). For redox reactions, examples are rusting of iron, burning of combustible material (e.g. (e.g.,, wood, coal, etc.) etc.) NOTE: ., photosynthesis and cellular respiration) is one of the difficult topics in biology. To NOTE: Energy transformation (e.g (e.g., capture the general picture of the topic, students have to be encouraged to read and re-read the key concept, write and re-write, outline and re-outline, draw and re-draw, and recite orally if they want the ideas to sink in their minds. Patience and steadfastness are important values that should be included as they study this concept. NOTE TO THE ILLUSTRATOR: ILLUSTRATOR: For the purpose of localization and contextualization, please draw a similar picture/diagram above illustrating the Philippine Tamaraw. Courtesy: Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill (Retrieved July 20, 2015). Countless chemical reactions are occurring in cells to do essential life functions with the help of ATP as the energy currency of the cells. Ask your students what are the tasks of ATP. The following are the answers: 2 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community 1. Chemical work: ATP is used for building macromolecules 2. Transport work: ATP is used for transporting ions membranes 3. Mechanical work: ATP is used for mechanical processes such as muscle contraction, cilia movement For additional information, tell the class that ATP is also involved in rigor mortis — a temporary stiffness of the body that happens soon after the death of a person. Motivation/Instruction 1 mins Post these two questions on the board. Ask the students to identify the process involved in each question so that food is manufactured and energy is released. 1. How do plants harness light energy to manufacture food? 2. How do living organisms harness energy from food? Then show to them the overall equation for each process as follows: 1. Chemical reactions for photosynthesis: 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + sunlight ? C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Which groups go in? Which groups come out? 2. Chemical reactions for cellular respiration: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + about 38 molecules of ADP ? 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + about 38 molecules of ATP Which groups go in? Which groups are released? Instruction/Delivery 120 mins Activity 1: Overview of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Materials needed: needed: Pictures of stages of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, LCD (if available), markers, Manila paper(s), white cartolina, any updated general biology book(s), Internet (if available). Procedure: Procedure: 1. You can re-draw these pictures of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in Manila paper if LCD is not available. You can also go to computer/printing shop and make these pictures into tarpaulin for longer use. 2. Group your students into triad according to their learning skills. Give each member a task to do in order to promote mutual cooperation among them. 3. Give them questions to answer for discussions. Tell them to prepare and bring out their Manila paper and markers. 4. Have them report to the class. Picture 1: Overview of Photosynthesis 3 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Courtesy: Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill (Retrieved July 20, 2015). Picture 2: Overview of Photosynthesis Courtesy: Solomon, Eldra P. et al., al., (2008). Biology 8th Edition. China: Thomson Brooks/Cole (Retrieved July 20, 2015). Picture 3: Overview of the Stages of the Calvin Cycle in Photosynthesis 4 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Courtesy: Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill (Retrieved July 20, 2015). Picture 4:Overview 4:Overview of Glucose Breakdown Courtesy: Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill (Retrieved July 20, 2015). 5 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Picture 5: Overview of ATP Yield per Glucose Molecule Courtesy: Mader, Sylvia S. (2010). Biology 10th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill (Retrieved July 20, 2015). NOTE: NOTE: For picture number 5, familiarize your students with the events of cellular respiration. One event of redox reaction occurs in the cytoplasm. The other two events occur in the mitochondrion with its corresponding ATP molecules produced and the participation of NADH and FADH2. 6 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Processing Questions: Questions: 1. What are the two kinds of reactions in photosynthesis? (Please see pictures 1 and 2.) 2. What are the basic stages of the Calvin cycle? (Please see picture 3.) 3. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? (Please see pictures 1 and 2.) 4. In which part of the cell glycolysis happens? What about the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain? (Please see pictures 4 and 5.) 5. How many metabolic pathways are there in cellular aerobic respiration? In anaerobic respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5.) 6. What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5) 7. About how many ATP molecules does a cell obtain from the breakdown of one molecule of glucose in cellular respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5.) 8. Given the glucose, carbon dioxide and water, which one(s) is/are called high-energy molecule and which one(s) is/are called low-energy molecule? Suggested answers: answers: 1. Light-dependent reaction and light-independent reaction (also known as Calvin cycle reaction or carbon fixation reaction). 2. The basic stages of Calvin cycle reaction are: carbon dioxide fixation, carbon dioxide reduction, RuBP regeneration. 3. Reactants: carbon dioxide and water; products: carbohydrates and oxygen 4. Glycolysis happens in the cytoplasm of the cell; citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and ETC are in the mitochondrion of the eukaryotic cell. 5. In cellular aerobic respiration: three; in anaerobic respiration: one 6. Reactants: carbohydrates, oxygen, and about 38 ADP molecules; products: carbon dioxide, water and about 38 ATP molecules 7. About 36 to 38 ATP molecules (NOTE (NOTE:: This number is just a ratio. Some biology authors say there are 30, 32 or 34 ATP molecules produced depending on the shuttle used to transport the electrons and on the kind of species.) 8. High-energy molecules: glucose; low-energy molecules: carbon dioxide and water Activity 2: Major Events and Features of Photosynthesis Materials needed: needed: Individual paper and ball pen, any updated biology book(s), Internet (if available). Procedure: Procedure: 1. Fill-in the two tables below for the major events and features of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, respectively. 2. The option tables are given for you to answer the needed materials and end products of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Reaction Series Light-dependent reactions Needed Materials a. End Products a. 7 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community (takes place in the thylakoid b. membrane.) c. Photochemical reactions Electron transport Chemiosmosis Carbon fixation reactions (takes place in stroma.) stroma.) 2. b. c. 2. Option Table Electrons NADPH, O2 Electrons, NADP+, H2O, electron acceptors Proton gradient, ADP + P, ATP synthase Light energy; pigments (chlorophyll) Carbohydrates, ADP + P, NADP+ ATP Ribulose bisphosphate, bisphosphate, CO2, ATP, NADPH, necessary enzymes Major Events and Features of Cellular Respiration Stage Starting Materials 1. Glycolysis (in cytosol) 2. Preparatory reaction 3. Citric acid cycle 4.Electron transport and chemiosmosis End Products Option Table Pyruvate, ATP, NADH NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP Pi Acetyl CoA, H2O, NAD+, FAD, ADP Pi Acetyl CoA, CO2, NADH Glucose, ATP, NAD+, ADP Pi Pyruvate, Coenzyme A, NAD+ CO2, NADH, FADH2, ATP ATP, H2O, NAD+, FAD Suggested answers: answers: Major Events and Features of Photosynthesis Reaction Series 1.Light-dependent reactions (takes place in the thylakoid membrane.) Needed Materials End Products a. Light-energy; pigments (chlorophyll) a. Electrons b. NADPH, O2 b. Electron transport b. Electrons, NADP+, H2O, electron acceptors c. Proton gradient, ADP + P, ATP synthase d. Chemiosmosis 2.Carbon fixation reactions (takes place in stroma.) stroma.) 2. Ribulose bisphosphate, bisphosphate, CO2, ATP, NADPH, necessary enzymes 2. Carbohydrates, ADP + P, NADP+ a. Photochemical reactions c. ATP Major Events and Features of Cellular Respiration 8 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Stage 1. Glycolysis (in cytosol) 2. Preparatory reaction 3. Citric acid cycle 4. Electron transport and chemiosmosis Starting Materials Glucose, ATP, NAD+, ADP Pi Pyruvate, Coenzyme A, NAD+ Acetyl CoA, H2O, NAD+, FAD, ADP Pi NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP Pi End Products Pyruvate, ATP, NADH Acetyl CoA, CO2, NADH CO2, NADH, FADH2, ATP ATP, H2O, NAD+, FAD Activity 3: Gaseous Products of Photosynthesis NOTE: NOTE: If there is enough time and the materials are available, let the class do this activity. Materials needed: needed: 1000 mL beaker, 3 grams of sodium bicarbonate, Hydrilla or Elodea, Elodea, funnel, test tube. Procedure: Procedure: 1. Half-fill a 1000 mL beaker with tap water. 2. Add 3 grams of sodium bicarbonate. 3. Place Hydrilla or Elodea in the bottom of the beaker. 4. Put a funnel over the plant. 5. Fill the test tube with water up to the brim. Secure the mouth of the test tube with your thumb. Invert the tube and place it on top of the funnel. 6. Place the beaker under direct sunlight. Count the bubbles that appear in the test tube after 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 210 seconds. 7. After several minutes, slowly remove the test tube from the funnel. Place your thumb over its mouth. Turn the tube right up and insert a glowing match to test the presence of the oxygen in the tube. Adapted from: Science and Technology II for the Modern World. (2003). Makati City: Diwa Scholastic Press, Inc. Enrichment 30 mins Directions: Directions: Show the basic similarity and differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The options are provided for in the other table below. PART I: I: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Raw materials End products Electron transfer compound Location of electron transport chain Organelle involved ATP production Source of electron for ETC Type of metabolic reaction Terminal electron acceptor for electron transport chain 9 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Option Table O2 Glucose, oxygen NADP+ is turned to NADPH Phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation Chloroplast Photophosphorylation In noncyclic electron transport :H2O Glucose, oxygen In noncyclic electron transport: NADP+ Anabolism Carbon dioxide, water NAD+ is turned to NADH+ Mitochondrial inner membrane (cristae) Mitochondrion Thylakoid membrane Immediate source: NADH and FADH2 Catabolism Carbon dioxide, water Suggested answers: answers: 1.Raw materials 2.End products 3.Electron transfer compound 4.Location of electron transport chain Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide, water Glucose, oxygen NADP+ is turned to NADPH Thylakoid membrane Cellular Respiration Glucose, oxygen Carbon dioxide, water NAD+ is turned to NADH+ Mitochondrial inner membrane (cristae) 5.Organelle involved 6.ATP production Chloroplast Photophosphorylation 7.Source of electron for ETC In noncyclic electron transport :H2O (undergoes photolysis to yield electrons, protons, and oxygen) Anabolism In noncyclic electron transport: NADP+ (becomes reduced to form NADPH) Mitochondrion Phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation Immediate source: NADH and FADH2, Ultimate source: glucose 8.Type of metabolic reaction 9.Terminal electron acceptor for electron transport chain Catabolism O2 (becomes reduced to form H2O) Connecting the Concepts with the Biological Systems Chloroplasts and mitochondria play a significant role in metabolism and their enzyme-requiring pathways permit a flow of energy through all living things. The energy transformations that take place in these organelles result in a loss of energy in the form of heat. Therefore, all organisms are in need of a constant supply of energy, which they get from their food. Food is ultimately produced by plants, which have the ability to capture solar energy. Photosynthesizing organisms form the basis of most food chains on Earth. 10 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Adapted from: Mader, Sylvia S. (2011). Biology 11th Edition. USA: McGraw-Hill Evaluation 90 mins Directions: Directions: Summarize the similarity of the two organelles as they carry out opposite processes. PART II: II: Revisit of Energy Organelles SET A: Revisit of Energy Organelles Structure Use of Membrane Electron Transport Chain Enzyme Chloroplast Mitochondrion SET B: B: Photosynthesis versus Cellular Respiration Directions: Directions: Using the following descriptions for photosynthesis and cellular respiration below, bring out your long bond paper or Oslo paper, pencil, ruler, ball pen and coloring materials. Show an illustration/diagram comparing the structure and function of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Label the parts of the organelles. The suggested rubric for the drawing is given below. In Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis: Water is oxidized and oxygen is released. Has electron transport chain located within the grana of chloroplasts, where ATP is produced by chemiosmosis. Has enzyme-catalyzed reactions within the semi-fluid interior. Carbon dioxide is reduced to a carbohydrate. In Cellular respiration: Oxygen is reduced to water. Has electron transport chain located within the cristae of the mitochondria, where ATP is produced by chemiosmosis. Has enzyme-catalyzed reactions within the semi-fluid interior. A carbohydrate is oxidized to carbon dioxide. Rubric for the Drawing Standard Contrast and intensity of drawing Blending of colors Neatness Excellent (7 points) Shows exceptional artistic and skillful color contrast; and meaningful color concentration. Color mix is exceptionally creative, appropriate and meaningful. Completely free from mess. Good (5 points) Shows generally acceptable artistic and skillful color contrasts; and meaningful color concentration. Color mix is generally creative, appropriate and meaningful. Almost free from mess. Fair (3 points) Shows generally vague color contrasts; and indiscernible sense of color concentration. Color mix needs improvement. Messy. PART III: III: Construction of a Concept Map 11 / 12 CHED.GOV.PH K-12 Teacher's Resource Community Directions: Directions: Group the class into triad. Make each group construct a concept map to help them develop their understanding of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Suggested rubric is given below. Rubric for the Concept Map Standard Excellent (10 points) Content knowledge Information is complete and accurate. Originality in organization of Exceptionally well-organized ideas and understandable. Neatness Completely free from mess. Good Fair (7 points) (4 points) Information is mostly Information is mostly complete and accurate. incomplete and inaccurate. Generally well-organized and Fairly understandable. understandable. Almost free from mess. Messy. PART IV: IV: Sequence in Aerobic Respiration Directions: Directions: Arrange the following to get the right energy flow sequence in aerobic respiration. NADH Electron Transport Chain Glucose ATP Suggested answers: answers: 1. Glucose 2. NADH 3. Electron Transport Chain 4. ATP Directions: Directions: Identify the following statements as photosynthesis or cellular respiration. _______________1. Energy-releasing pathways _______________2. Energy-acquiring pathways Suggested answers: answers: 1. Cellular respiration 2. Photosynthesis Download Teaching Guide Book 0 mins 12 / 12 Powered Poweredby byTCPDF TCPDF(www.tcpdf.org) (www.tcpdf.org)