* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
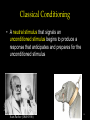
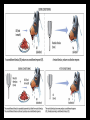
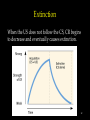
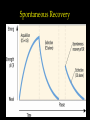
Learning Chapter 8 1 Learning • Learning is a relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience. • How do we learn things? – Associative Learning – Observational Learning 2 Associative Learning 3 Associative Learning • Classical Conditioning – Associating two stimuli • Operant Conditioning – Associating a response with a consequence 4 Behaviorism • John Watson • Behaviorism 1. Psychology = objective science 2. Study behavior w/out mental processes 5 Classical Conditioning Sovfoto • A neutral stimulus that signals an unconditioned stimulus begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) 6 Classical Conditioning Terms • Neutral Stimulus • Unconditioned Stimulus • Unconditioned Response • Conditioned Response 7 Pavlov’s Experiments • Pavlov paired tone when feeding dogs • Over time, dogs salivated with tone • Can you identify the following terms in the experiment? • Neutral Stimulus • Unconditioned Stimulus • Unconditioned Response • Conditioned Response 8 9 Acquisition • Acquisition is the initial stage in classical conditioning 1. NS needs to come before the US. 2. Only ½ second between stimuli 10 Acquisition 11 Extinction When the US does not follow the CS, CR begins to decrease and eventually causes extinction. 12 Spontaneous Recovery 13 Generalization and Discrimination • Generalization – CR with stimulus similar to CS • What might be an example of that for Pavlov’s experiment? • Discrimination – distinguishing between CS and other stimuli. 14 Biological Predispositions John Garcia 15 Courtesy of John Garcia Garcia showed that the duration between the CS and the US may be long (hours), but yet result in conditioning. A biologically adaptive CS (taste) led to conditioning and not to others (light or sound). Biological Predispositions Even humans can develop classically to conditioned nausea. 16 Applications of Classical Conditioning Watson researched conditioning with infants “Little Albert” Experiments Brown Brothers John B. Watson 17 Applications of Classical Conditioning 1. Conditioning can be used to get rid of bad behavior (limited ability) 2. Classical conditioning can aid in drug therapies 18 Operant vs Classical Conditioning • Classical = respondent behavior (automatic) • Operant = behavior operates on the environment for predictable consequence 19