* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Bingo: Naming Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
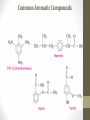
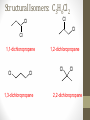
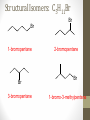
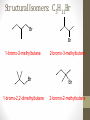
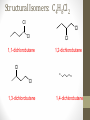
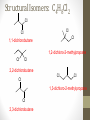
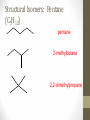
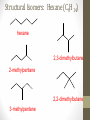
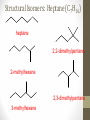
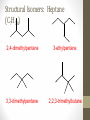
Chemical Bingo: Naming Review • There are 27 structures or names drawn on the next slide. Select 24 of them to be placed on your bingo card. • Because of space issues, I would number each bingo square and then list the names or structures on a separate sheet of paper • If I give you a name, you must match it to a structure. If I give you a structure, you must match it to a name • Any bingo winner will be awarded 20 Beaker Bank points Chemical Bingo: Alkanes R isopropyl sec-butyl tert-butyl isobutyl decane nonane 2,3,4,5-tetramethylhexane 3,4-diethylhexane 3,5-diethyl-4-isopropylheptane R R 4-tert-butyl-3,5-dimethylheptane 4-ethyl-2,2,3,5,6,6-hexamethylheptane Any isomer of C5H12 Any isomer of C6H14 R Any isomer of C7H16 Alkyl Halides • The halogen is treated as a substituent on an alkane chain • The halo-substituent is considered of equal rank with an alkyl substituent in the numbering of the parent chain • In the case where each would have the same position number, the substituent that comes first in the alphabet takes the lower number! 3 Naming Alkyl Halides • Follow the same system as with alkanes • Give the name and carbon number for the halide just like a side branch! C-C-F C-C-C 1-fluoroethane Cl C-C-C-C-C C-Br 2-chloropropane 1-bromo-2-ethylbutane Naming Practice: Haloalkanes Two equal numbering options? Number based on alpha order Cl 6 1 2 5 3 4 4F 2 5 3 Cl 1 6 F 5-chloro-2-fluorohexane 2-chloro-5-fluorohexane Br 2-chloro-4-fluoro-2,3-dimethylpentane I Br Cl 2-bromo-3-ethyl-4-iodopentane 2-bromo-4-chloro-3-isopropylpentane ALKENES AND ALKYNES Alkenes and Alkynes • Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons • Simply put, a saturated hydrocarbon has no double bonds between the carbon atoms • Therefore, there is a maximum number of hydrogens present • Like the alkanes, the alkenes and alkynes form another homologous hydrocarbon series • Alkenes form one double covalent bond between two C atoms • Alkynes form one triple covalent bond between two C atoms • Alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons • This means more hydrogen atoms can be added • General formula for alkenes: • General formula for alkynes: CnH2n CnH2n-2 Saturated vs Unsaturated Naming Alkenes and Alkynes • IUPAC nomenclature rules for alkenes and alkynes are similar to alkanes • Name the parent compound • Find the longest chain containing the double or triple bond and name the parent compound by adding the suffix –ene or –yne to the name of the main chain • Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain, beginning at the end nearest the double or triple bond • If the multiple bond is an equal distance from both ends, begin numbering at the end nearer the first branch point 9 Naming Alkenes and Alkynes •Assign numbers and names to the branching substituents, and list the substituents alphabetically •Use commas to separate numbers, and hyphens to separate words from numbers •Indicate the position of the multiple-bond carbon •The number indicates which carbon the multiple bond is AFTER •Do not use a # if there is only one possible location •If more than one multiple bond is present, identify the position of each multiple bond and use the appropriate ending diene, triene, tetraene, and so forth •Assemble the name as previously discussed 10 Example 1-butene (not 3) H HH C=C–C–C–H H H H H C4H8 CH2CHCH2CH3 2-butene H H HH H–C–C=C–C–H H H Structural Formula C4H8 Chemical formula CH3CHCHCH3 Condensed Structural formula 11 Another Example 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene C=C–C–C C C Structural Formula (w/o the H) C6H12 Chemical formula CH2C(CH3)CH(CH3)CH3 Condensed Structural formula Assigning Priority • Alkenes and alkynes are considered to have equal priority • In a molecule with BOTH a double and a triple bond, whichever is closer to the end of the chain determines the direction of the numbering • In the case where each would have the same position number, the double bond takes the lower number • In the name, “-ene” comes before “-yne” because of alphabetization 13 Multiple Double/Triple Bonds Learning Check Write the IUPAC name for each of the following unsaturated compounds: A. CH3CH2CCCH3 CH3 CH3 B. CH3C=CHCH3 C. Properties of Alkenes and Alkynes • Like the alkanes, alkenes and alkynes are: • • • • • • Non-polar Insoluble in water Soluble in non-polar organic solvents Less dense in water Flammable Non-toxic • Unlike the alkanes: • Alkenes and alkynes are chemically reactive at the multiple bond • Alkenes display cis-trans isomerism when each double-bond carbon atom has different substituents WAIT…WHAT IS CIS-TRANS ISOMERISM? Recall Way Back When… • Draw the Lewis Dot structures and predict the shapes of the following molecules: •Methane •Ethylene (C2H4) •Acetylene (C2H2) •What carbon families are these molecules a apart of? Answers • As predicted by the VSEPR theory discussed earlier: • Methane (an alkane) is tetrahedral (sp3 hybridization) • Ethylene (an alkene) is planar (sp2 hybridization) Acetylene (an alkyne) is linear (sp hybridization) Molecule Rotation • In alkanes, there is free rotation around the single bond • In alkenes, there is NO rotation around the double bond • The double bond is “fixed” • As a consequence, a new kind of structural isomerism is possible • Called stereoisomerism • More specifically, this type of stereoisomerism is called cis-trans isomerism Stereoisomerism • To see this new kind of isomerism, look at the following butene compounds: • The two 2-butenes are called cis-trans isomers • They have the same formula and connections between atoms, but different structures Cis- and Trans- Isomerism • • • • A cis-isomer contains substituents on the same side of the double bond A trans-isomer contains substituents on opposite side of the double bond Cis-trans isomerism occurs in an alkene whenever each double-bond carbon is bonded to two different substituent groups If one of the double-bond carbons is attached to two identical groups, cis-trans isomerism is not possible as shown below TIME FOR PRACTICE! AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Benzene Structure • Benzene as 6 electrons shared equally among the 6 C atoms • Resonant bonding It is also represented as a hexagon with a circle drawn inside Benzene, C6H6, is one of the most important industrial chemicals Benzene is regarded as a highly carcinogenic substance • Use and disposal of benzene are regulated • Compounds containing benzene rings are not necessarily toxic Aromatic Compounds • At the time of its discovery, many compounds containing benzene had fragrant odors • So, the family of benzene compounds became known as aromatic compounds Common Aromatic Compounds Naming Aromatic Compounds • Aromatic compounds are named • with benzene as the parent chain • with one side group named in front of benzene CH3 Methylbenzene Cl Chlorobenzene Naming Aromatic Compounds Several base names… benzene aniline toluene benzaldehyde phenol benzoic acid Abbreviations Used with Di-Substitution 1,2 difluoro benzene Ortho difluoro benzene o – difluoro benzene 1,3 dichloro benzene Meta dichloro benzene m – dichloro benzene 1,4 dibromo benzene Para dichloro benzene p – dichloro benzene Toluene • For methylbenzene, the common name, toluene, may be used Xylene • For isomers of dimethylbenzene, the common name, xylene may be used Naming Aromatic Compounds with Three Substituents • Use numbers for giving the positions: Cl CH3 Cl Cl 1 CH3 Br 1 Br Cl Br Cl 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene 2,6-Dibromo-4-chlorotoluene 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene Learning Check Select the correct name(s) for each of the following compounds. A. chlorocyclohexane B. chlorobenzene Cl C. 1-chlorobenzene A. 1,2-dimethylbenzene B. 1,3-dimethylbenzene C. m-xylene CH 3 CH 3 Solution Cl B. chlorobenzene CH 3 B. 1,3-dimethylbenzene or C. m-xylene CH 3 Learning Check Draw the condensed structural formulas for each of the following. 1. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 2. o-chlorotoluene Solution One possible way to draw each… Cl 1. 1,3-dichlorobenzene Cl CH 3 2. o-chlorotoluene Cl Benzene as a Substituent… • If you have the aromatic ring as an attachment, it is named phenyl Try one… • What would this name be? Answer… • 4-phenyl octane Learning Check Draw and identify the organic family (functional group) for each of the following. A. B. C. D. Solution The functional groups are as follows… A. alkene B. cycloalkane (alkane) C. alkyne D. aromatic FUNCTIONAL GROUPS Classified according Compounds to functional group Types of Organic Alkane Alcohol Carboxylic acid O OH OH Alkene Ether Amine NH2 O Alkyne C Ketone Amide O O C NH2 Haloalkane Aldehyde Amino acid O O Cl Br H2N H OH Problems: • Draw the following alkenes: • • • • 2-Butene methylpropene 4–Methyl–2-pentene 3,3-Dimethyl-1-butene 45 Can you name this compound? 46 3-ethyl-1-pentyne Problems Name this alkyne: C C-C-C=C-C-C-C-C C C C C C C 5,7-diethyl-3-methyl-4-decyne 47 Isomers The fat dog shook himself, and then rolled over on the wet rug. OR The dog shook the fat rug, then rolled over and wet on himself. These two statements use the same words... but have very different meanings! Likewise, isomers may have the same formula, but have very different structures… Structural Isomers of C4H10 2-methylpropane or • On piece of your own paper, draw AND name ALL Structural Isomer Practice of the isomers for the following alkanes: # isomers Formulas Pentane C5H12 3 Hexane C6H14 5 Heptane C7H16 9 Some of your drawings may look different, but they are only different structures (isomers) if they also have different names If you complete that, try to draw and name all of the isomers for octane (C8H18). There are 18 of them! On piece of your own paper, draw AND name ALL Structural Isomer Practice of the isomers with the following formulas: Formulas C 4H 9I C3H6Cl2 C5H11Br C4H8Cl2 # isomers 4 4 8 9 To be honest, there may be more…this is what I found, so try and prove me wrong! Extra Credit to anyone who can find more structures… Some of your drawings may look different, but they are only different structures (isomers) if they also have different names Structural Isomers: C4H9I I 1-iodobutane I 2-iodobutane I I 2-iodo-2-methylbutane I 1-iodo-2-methylbutane Structural Isomers: C3H6Cl2 Cl Cl Cl Cl 1,1-dichloropropane Cl Cl 1,3-dichloropropane 1,2-dichloropropane Cl Cl 2,2-dichloropropane Structural Isomers: C5H11Br Br Br 1-bromopentane Br 3-bromopentane 2-bromopentane Br 1-bromo-3-methylpentane Structural Isomers: C5H11Br Br Br 1-bromo-2-methylbutane Br 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylbutane 2-bromo-3-methylbutane Br 2-bromo-2-methylbutane Structural Isomers: C4H8Cl2 Cl Cl Cl 1,1-dichlorobutane Cl 1,2-dichlorobutane Cl Cl Cl Cl 1,3-dichlorobutane 1,4-dichlorobutane Structural Isomers: C4H8Cl2 Cl Cl Cl Cl 1,1-dichlorobutane 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpropane Cl Cl 2,2-dichlorobutane Cl Cl Cl 1,3-dichloro-2-methylpropane Cl 2,3-dichlorobutane Structural Isomers: Pentane (C5H12) pentane 2-methylbutane 2,2-dimethylpropane Structural Isomers: Hexane (C6H14) hexane 2,3-dimethylbutane 2-methylpentane 2,2-dimethylbutane 3-methylpentane Structural Isomers: Heptane (C7H16) heptane 2,2-dimethylpentane 2-methylhexane 2,3-dimethylpentane 3-methylhexane Structural Isomers: Heptane (C7H16) 2,4-dimethylpentane 3-ethylpentane 3,3-dimethylpentane 2,2,3-trimethylbutane Comparing Structural Isomers C5H12 Structure (Same formula, different structure) Name Boiling point (°C) pentane 36.0 2-methylbutane 27.9 2,2-dimethylpropane 9.5 More branching → weaker London dispersion forces BP/MP of Linear alkanes > BP/MP of branched alkanes Structural Isomers What are the possible structural isomers of C3H7Br? Br Br 1-bromopropane 2-bromopropane What are the possible structural isomers of C4H9Cl? Cl Cl 1-chlorobutane 2-chloro-2-methylpropane Cl 2-chlorobutane Cl 1-chloro-2-methylpropane