* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ivan Pavlov`s Classical Conditioning
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
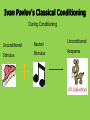
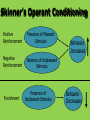
স্বাগতম উপস্থাপনায় ডঃ সু লতানা জাকিয়া হি প্রভাষি,গাইডডন্স এন্ড িাউডসন্সকলিং টিচাসস ট্রেকনিং িডলজ, রাজশাহী কচত্রগুডলা লক্ষ্য িরুন বয়ঃসকিিাল বলডত িী ট্রবাডেন? শশশবিাল ট্রশষ হবার পর ট্র ৌবনিাডল পদাপস ডনর জনয ট্র সমডয় শদকহি, মানকসি ও সামাকজি প্রস্তুকত চডল তাডি বয়ঃসকিিাল বডল। সাধারনত দশ বছর হডত উকনশ বছর প স ন্ত এর কবস্তৃকত। “Constructivism is a philosophy of learning founded on the premise that, by reflecting on our experiences, we construct our own understanding of the world we live in” (Brooks & Brooks) It is “based on a type of learning in which the learner forms, or constructs, much of what she learns or comprehends” (Cashman et al 390) Constructivism is the idea that learning doesn’t just happen by the traditional methods of teachers standing in front of the class and lecturing. It is best described by Confucius’ quote: “I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand.” (Cashman et al 390) Jerome Bruner Jean Piaget Lev Vygotsky John Dewey Very influential psychologist His concern with cognitive psychology “led to a particular interest in the cognitive development of children… and just what the appropriate forms of education might be” (Smith) Developed the cognitive learning theory Felt children were “active learners” who constructed new knowledge “as they moved through different cognitive stages, building on what they already knew” (Cushman et al 392) Sensorimotor “learning takes place primarily through the child’s senses and motor actions” (Cushman et al 393) Preoperational “children begin to use symbols and images” (Cushman et al 393) Concrete Operational “children begin to think logically” (Cushman et al 393) Formal Operational Children begin to think in an abstract way Developed the social cognition theory which “asserts that culture is the prime determinant of individual development” because humans are the only creatures to have created cultures and therefore it effects our learning development. (“Vygotsky and Social Cognition”) Vygotsky theorized that a child’s cultural upbringing greatly effects their learning development. Believed that learning should be engaging to the students… they will learn better if they are interested. Was a huge influence on our education system Believed in “educating the whole child, physically, mentally, and socially, and not just on the dispensation of facts and information” (Cushman et al 395) “In a constructivist setting… the role of the teacher is to organize information around conceptual clusters of problems, questions and discrepant situations in order to engage the student’s interest. Teachers assist the students in developing new insights and connecting them with their previous learning” (Hanley) In the classroom, students must work on building upon the knowledge they already have. “Inferences, elaborations, and relationships between old perceptions and new ideas must be personally drawn by the student in order for the new idea to become an integrated, useful part of his/her memory” (Hanley) What is behaviorism? • Behavioral psychology is the study of external behavior •Behavior is the response of an organism to stimuli “Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own special world to bring them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to be any type of specialist I might select – a doctor, a lawyer, artist…” -Watson 1924 Ivan Pavlov History of Behaviorism • Pavlov (1927), a Russian physiologist discovered classical conditioning in dogs. Ivan Pavlov's Classical Conditioning Before Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus Neutral Stimulus Unconditioned Response No Response Ivan Pavlov's Classical Conditioning During Conditioning Unconditioned Neutral Unconditioned Stimulus Stimulus Response Ivan Pavlov's Classical Conditioning After Conditioning Conditioned Conditioned Stimulus Response Playing soothing music, dimming the lights to calm and relax students Unintentional classical conditioning: Test anxiety Math anxiety Public speaking anxiety General school anxiety B.F. Skinner (1904 –1990) • American psychologist - influential from the 1930’s 60’s – developed operant conditioning • Skinner was interested in education – He believed that behavior is sustained by reinforcements or rewards, not by free will. • Famous for the skinner box & the teaching machine • Often worked with pigeons & rats and applied what he learned with these animals to human learning With Operant Conditioning the Response comes before the Stimulus (the opposite of CC) R S Teachers can deliberately use operant conditioning with their students (training) How someone reacts to our behaviors determines whether or not we continue the behavior if we are rewarded for something we will likely do it again - do you do this as a teacher? Skinner’s Operant Conditioning Positive Reinforcement Presence of Pleasant Stimulus Negative Reinforcement Absence of Unpleasant Stimulus Punishment Presence of Unpleasant Stimulus Behavior Increases Behavior Decreases Behaviorism is seen when teachers use the following methods: a. Testing specific skills b. More individual work than group learning c. Using positive and negative reinforcement Students learn through experiences and practices. Learning is also modified with positive and negative reinforcements. Students begin to give predicted responses to a stimulus